Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Chapter 11 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Biotechnology Principles and Processes Assignments Class 12 Biology
Question. The specific DNA sequence in a chromosome which is responsible for initiation of replication is :
(a) Cloning region
(b) Termination region
(c) Initiation region
(d) Origin of replication
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following reproduction preserves the genetic informations ?
(a) Asexual reproduction
(b) Sexual reproduction
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The stickiness of the ends, facilitates the action of enzyme :
(a) DNA ligase
(b) DNA polymerase
(c) Alkaline phosphatase
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Two enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in E.coli were isolated in 1963, one of these cut DNA, while other :
(a) Add propyl group to DNA
(b) Add ethyl group to DNA
(c) Add methyl group to DNA
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Taq polymerase is used in, polymerase chain reaction, because :
(a) It becomes inactive at high temperature
(b) it makes other enzyme active at high temperature
(c) It remains active during high temperature
(d) It is obtained from thermostable virus.
Answer
C
Question. The vessels, where large volumes of culture can be processed are :
(a) Bioreactors
(b) Biovessels
(c) Biocontainers
(d) All of above
Answer
A
Question. Bombardment of high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA on target cells is :
(a) Biolistics
(b) Micro-injection
(c) Electroporation
(d) Bombing
Answer
A
Question. In micro injection :
(a) DNA is bombarded on target cells
(b) DNA is placed through a vector
(c) DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of animal cell
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. pBR322 has two antibiotic resistance genes, they are :
(a) Streptomycin and Ampicillin resistant gene
(b) Chloromycetin and tetracycline resistant gene
(c) Tetracycline and neomycin resistant genes
(d) Ampicillin and tetracyclin resistant genes
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is not required in PCR?
(a) Oligonucleotide primer
(b) DNA template
(c) Taq polymerase
(d) Helicase enzyme
Answer
D
Question. Select incorrect statement :
(a) Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis produce proteins that kill certain insects such as Lepidopterans, Coleopterans and Dipterans
(b) RNA interference takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence
(c) Genetically modified crops are more sensitive to abiotic stresses
(d) Golden rice is protein enriched rice
(e) Agrobacterium is used to deliver desirable genes into animal cell
(1) only a
(2) a, b and c
(3) a, c and d
(4) c, d and e
Answer
D
Question. Most common matrix is agarose a natural polymer used in gel electrophoresis is extracted from :
(a) an animal
(b) a fungus
(c) Sea weeds
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. To isolate DNA from the plant cells we have to break the wall this is done by :
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Cellulase
(c) Chitinase
(d) Invertase
Answer
B
Question. Agrobacterium tumifaciens a pathogen transform normal plant cells into a tumor, similarly in animals the normal cells transformed into cancerous cells by:
(a) Retro viruses
(b) DNA viruses
(c) Ribo viruses
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. You have three copies of a particular DNA molecule what technique would you use to make more copies of the molecule?
(a) Gel electrophoresis
(b) Sequencing
(c) PCR
(d) Restriction fragment analysis
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is best way to determine paternity ?
(a) Gene counting
(b) Chromosome counting
(c) DNA finger printing
(d) Protein analysis
Answer
C
Question. Restriction enzymes belong to a larger class of enzymes called :
(a) Cellulases
(b) Hydrolases
(c) Polymerases
(d) Nucleases
Answer
D
Question. Which one is not a basic step in genetically modifying an organism
(a) Identification of DNA with desirable genes
(b) Introduction of the identified DNA into the host
(c) Introduction of unidentified DNA into the host
(d) Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host and transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
Answer
C
Question. If any protein encoding gene is expressed in a hetero logous host then protein is known as :
(a) Recombinant gene
(b) Recombinant protein
(c) Selectable marker
(d) Homogenous protein
Answer
B
Question. Which enzyme is used in PCR technique ?
(a) Thermostable DNA polymerase
(b) Thermostable RNA polymerase
(c) Thermostable ligase
(d) Thermostable vector
Answer
A
Question. The construction of the first recombinant DNA was done by ?
(a) Stanley cohen and Herbert Boyer
(b) Nathan’s and Smith
(c) Maeselson and Stahl
(d) Allec Jeffreys
Answer
A
Question. The most commonly used bioreactors are of
(a) Simple stirring type
(b) Sparged stirring type
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Downstream processing is :
(a) Process of separation of DNA fragments
(b) Process of joining the vector and the host DNA
(c) Process including separation and purification of the product
(d) Process of transferring DNA.
Answer
C
Question. Vector which is commonly used to transfer foreign gene in a crop plant is :
(a) Plasmids of Salmonella
(b) l bacterio phage vector
(c) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following enzymes is known as ‘genetic glue’?
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) Alkaline phosphatase
(c) DNA ligase
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. Small chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA at 3′ end used in PCR are :
(a) Primers
(b) Dimers
(c) Small strands
(d) Large fragments
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is must in Biotechnology?
(a) Restriction endonuclease + DNA ligase
(b) Restriction exonuclease + DNA polymerase
(c) Alkaline phosphate + DNA Ligase
(d) RNA polymerase + DNA polymerase
Answer
A
Question. Taq. polymerase is obtaned from :
(a) Bacillus thuriengiensis
(b) Thermus aquaticus
(c) Salmonella typhimurium
(d) Eischerichia coli
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is used to deliver desirable gene in to animal cell :
(a) Disarmed retrovirus
(b) Disarmed agrobacterium
(c) Disarmed E.coli
(d) Disarmed plant pathogen
Answer
A
Question. Agrobacterium tumifaciencs, a pathogen of several dicot plants is able to deliver a piece of DNA and it is known as :
(a) R-DNA
(b) S-DNA
(c) M-DNA
(d) T-DNA
Answer
D
Question. To denature the DNA template in PCR it is heated to
(a) 70°C
(b) 54°C
(c) 80°C
(d) 94°C
Answer
D
Question. Roman numbers following the names of restriction endonuclease indicate :
(a) The order in which the enzymes were isolated from that strain of bacteria
(b) strain of bacteria
(c) the order in which genus is taken to isolate the enzyme
(d) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. The science, which deals with techniques of using live organisms or enzymes from organism to produce products and processes useful to human is :
(a) Genetics
(b) Biotechnology
(c) Bioinformatics
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Autonomously replicating circular extra chromosomal DNA of bacteria is :
(a) Plastid
(b) Nucleus
(c) Plasmid
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Exonuclease removes nucleotides from
(a) Specific positions
(b) the ends of the DNA
(c) any where in DNA
(d) All the above
Answer
B
Question. Alternative selectable markers developed to differentiate non-recombinants from recombinants on the basis of :
(a) Ability of separate them according to size
(b) Ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate
(c) Ability to not produce colour
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following passage and answer any four questions given below:
Rama lives in a society where a robbery occurred last night. Robbers came into the flat and murdered the old lady residing there. Police came and restricted the entry into the flat. They took samples from the room, where the dead body was found. While examining, they found that there is some blood and tissue in the nails of old lady.
According to their observation, police filtered out their inspection to three suspects viz. servant, cook and milkman. Finally after two days of robbery, police caught the criminal. It was the old lady’s cook. Rama was amazed to see that how quickly police completed and shut the case. She asked the inspector that how they did it? The police man told her that it become possible due to the sample collected from the victim, that lead them to the criminal. The sample taken from nail scraping was amplified using PCR and then tested.
Question. In PCR, the temperature used to denature the DNA is about
(a) 76°C
(b) 25°C
(c) 95°C
(d) 40°C.
Answer
C
Question. Taq polymerase synthesises DNA region between the primers using
(a) Mg2+
(b) dNTPs
(c) DNA ligase
(d) both (a) and (b).
Answer
D
Case II : Read the following passage and answer any four questions given below:
The DNA, which is transferred from one organism into another by joining it with the vehicle DNA is called passenger or foreign DNA. Generally three types of passenger DNAs are used. These are complementary DNA (cDNA), synthetic DNA (sDNA) and random DNA. Complementary DNA (cDNA) is synthesized on RNA template (usually mRNA) with the help of reverse transcriptase.
Synthetic DNA (sDNA) is synthesized on DNA template or without a template. Random DNA are small fragments formed by breaking a chromosome of an organism in the presence of restriction endonucleases.
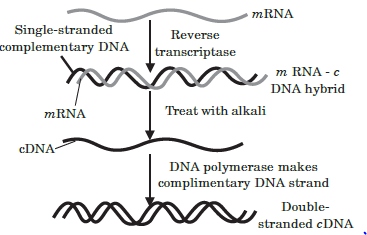
Question. Reverse transcriptase enzyme was discovered by
(a) Temin and Baltimore
(b) Cohen and Boyer
(c) Arber and Nathan
(d) Paul Berg.
Answer
A
Question. Enzyme that helps in the formation of double stranded cDNA is
(a) DNA synthetase
(b) ligase
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) helicase.
Answer
C
Question. DNA synthesised without a template is referred to as
(a) complementary DNA
(b) random DNA
(c) synthetic DNA
(d) Z-DNA.
Answer
C
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : The insertion of DNA fragment into pBR 322 plasmid using enzyme Pst I or Pvu I make ampicillin resistant gene non functional.
Reason : Bacterial cells containing recombinant pBR322 is unable to grow in the presence of ampicillin.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Amplification of a gene of interest can be done by polymerase chain reaction.
Reason : It is possible to amplify DNA segment approximately 1 billion times within a span of one day.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA to produce sticky ends or blunt ends.
Reason : Stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Bacteriophage vectors are more advantageous than plasmid vectors.
Reason : Bacteriophage vectors can be easily detected at the time of cloning experiments.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Type I restriction endonucleases are not used in recombinant DNA technology.
Reason : Type I restriction endonucleases recognise specific sites within the DNA but do not cut these sites.
Answer
A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why do DNA fragments move towards the anode during gel-electrophoresis?
Answer : DNA is a negatively charged molecule hence during gel electrophoresis it moves towards anode (positive electrode) under the influence of electrical field.
Question. Name the host cells in which microinjection technique is used to introduce an alien DNA.
Answer : Microinjection technique is used to introduce an alien DNA directly into the nucleus of the animal host cells such as oocytes, eggs and embryo.
Question. Mention the source of thermostable DNA polymerase.
Answer : Thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus is the source of thermostable DNA Taq polymerase.
Question. What are synthesising enzymes?
Answer : The enzymes that are used to synthesise DNA strands on suitable templates are called synthesising enzymes. They are of two types : DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase.
Question. What are the drawbacks of stirred tank bioreactors?
Answer : The main drawback of stirred-tank bioreactor is that it is relatively expensive to run, which is mainly due to high energy requirements.
Question. During the isolation of DNA, how can you remove RNA and protein from the DNA solution?
Answer : RNA can be removed by treatment with ribonuclease whereas proteins can be removed by treatment with protease.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Write the role of ‘ori’ and ‘restriction’ site in a cloning vector pBR322.
Answer : Origin of replication (ori) site in cloning vector pBR322 is a sequence from where replication starts. Any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within host cell. Restriction site within the markers tetR and ampR genes permit an easy selection for cells transformed or the recombinant pBR322.
Question. What are the two main discoveries that led to the built of genetic engineering ?
Answer : Genetic engineering is the technique to form recombinant DNA and then to introduce recombinant DNA into appropriate host. Two main discoveries which led to genetic engineering are :
(i) Discovery of plasmid by William Hays and Joshua Lederberg in 1952.
(ii) Discovery of restriction endonuclease by Arber in 1962.
Question. Why is it essential to maintain sterile condition in biotechnological processes?
Answer : Sterile condition enable growth of only the desired microbe/ eukaryotic cell in large quantities for the biotechnological products like antibiotics, enzymes, etc.
Question. State the role of UV-light and ethidium bromide during gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments.
Answer : DNA fragments can be seen only after staining. Ethidium bromide is used to stain DNA fragments followed by exposure to UV radiation. This gives bright orange colour to DNA fragments which helps to view separated DNA fragments.
Question. Why are genes encoding resistance to antibiotics considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector? Explain with the help of one example.
Answer : Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli cloning vector because they help in selecting transformant cell from non-transformant ones.
The genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, kanamycin or chloramphenicol, etc. are useful selectable markers for E. coli. The common E. coli cells are not resistant to any of these antibiotics. Plasmid pBR322 has two antibiotic resistance genes – ampicillin resistance (ampR) and tetracycline resistance (tetR) which are considered useful for selectable markers.
The presence of restriction sites within the markers tetR and ampR permits an easy selection for cells transformed with the recombinant pBR322. For example, insertion of the DNA fragment into the plasmid using enzyme PstI or PvuI places the DNA insert within the gene ampR. This makes ampR nonfunctional. Bacterial cells containing such a recombinant pBR322 will be unable to grow in the presence of ampicillin, but will grow on tetracycline.
Question. Refer to the given figure and answer the following questions.
(a) Identify the labelled part A and mention its function.
(b) What does B and C represent?
(c) Briefly describe the process shown in the given figure.
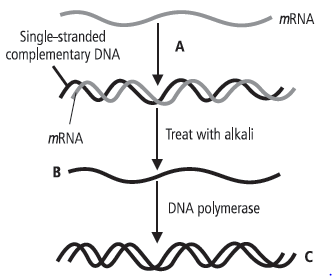
Answer : (a) Labelled part A represents the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is used to synthesise DNA or complementary DNA by using mRNA as template.
(b) The labelled part B represents the separated singlestranded complementary DNA after the RNA-DNA complex is treated with alkaline phosphatase enzyme. The labelled part C is the newly formed double-stranded cDNA.
(c) This diagram represents the synthesis of complementary DNA or cDNA from RNA. With the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase, an RNA-DNA complex is formed from RNA (usually mRNA) where RNA acts as the template. The mRNA in the RNA-DNA complex is digested in the presence of alkaline phosphatase enzyme. A cDNA is formed on the separated single-stranded DNA template with the help of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Question. How does β-galactosidase coding sequence act as a selectable marker? Why is it a referred selectable marker to antibiotic resistance genes? Explain.
Answer : Some genes called selectable markers help in selecting those host cells which contain the vectors and eliminating the non-transformants. b-galactosidase is an alternative selectable marker developed to differentiate recombinants and non-recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substance.
A recombinant DNA is inserted in the coding sequence of an enzyme b-galactosidase. This causes inactivation of theenzyme which is called insertional inactivation. If the plasmid in the bacterium does not have an insert, the presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies.
Presence of insert results into insertional inactivation of the b-galactosidase and, therefore, the colonies do not produce any colour, these colonies are marked as recombinant colonies.
β-galactosidase is a preferred selectable marker to antibiotic resistance genes because due to inactivation of antibiotics, selection of recombinants becomes burdensome process as it requires simultaneous plating on two plates having different antibiotics. But by using b-galactosidase as selectable marker, we can select recombinants and non-recombinants on a single plate.
Question. How and why is the bacterium Thermus aquaticus employed in recombinant DNA technology ? Explain.
Answer : Taq DNA polymerase isolated from thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus synthesises the DNA region from gene of interest between the primers, using dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates) and Mg2+. The primers are extended towards each other so that the DNA segment lying between the two primers is copied. It is stable even at high temperatures.
Taq polymerase is heat stable enzyme and is able to withstand high temperature induced denaturation of DNA during PCR.
Hence it is preferred in PCR reactions.
Question. (a) Why must a cell be made ‘competent’ in biotechnology experiments? How does calcium ion help in doing so?
(b) State the role of ‘biolistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Answer : (a) Competent host is essential for transformation with recombinant DNA. Since DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, it cannot pass through membranes, so the bacterial cells must be made capable to take up DNA i.e., made competent.
This is done by treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent cations, such as calcium which increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall. Recombinant DNA (rDNA) can then be forced into such cells by incubating the cells with recombinant DNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 42°C (heat shock), and then putting them back on ice. This enables the bacteria to take up the recombinant DNA.
Other methods are:
(i) Microinjection : DNA is inserted through microneedles or micropipettes.
(ii) Electroporation : Electric impulse induce transient pores.
(iii) Gene gun or biolistic : DNA coated with microscopic pellets of gold or tungsten is shot with high velocity into target cells.
(b) Biolistic gun helps in the process of gene transfer into the host cell without using a vector. In biolistic method or gene gun method, tungsten or gold particles, coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. This method is suitable for plants, but is also used to insert genes into animal that promote tissue repair into cells (particularly cancer of mouth) near wounds. It has made great impact in the field of vaccine development.
Question. Explain the importance of ( i ) ori, (ii) ampR and (iii) rop in the E.coli vector shown below.

Answer : (i) ori : ori is the origin of replication. This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within host cells. It controls the copy number of the linked DNA.
(ii) ampR : Gene for ampicillin resistance which helps in selecting the transformants.
(iii) rop : rop codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Question. (a) Mention the difference in the mode of action of exonuclease and endonuclease.
(b) How does restriction endonuclease function?
Answer : (a) Differences between action of exonucleases and endonucleases are as follows :
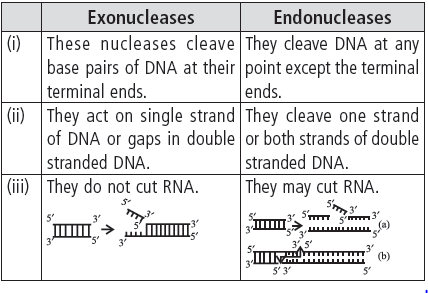
(b) Restriction nucleases act as molecular scissors or chemical scalpels. Each restriction endonuclease functions by ‘inspecting’ the length of a DNA sequence. Once it finds its specific recognition sequence, it will bind to the DNA and cut each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbones. Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
Question. (a) What is EcoRI? What does ‘R’ represent in this?
(b) Give the palindromic nucleotide sequence recognised by it.
(c) Explain its action.
Answer : (a) Enzyme EcoRI is named as follows :
The capital letter E comes from the genus Escherichia. The letters co are derived from the species name coli. The letter R is from RYI3 (strain). The Roman number I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from the bacterium E. coli RYI3.
(b) EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease enzyme it recognises base sequences
5′-GAATTC-3′
3′-CTTAAG-5′ in DNA duplex.
(c) It cut each of the two strands between G and A producing sticky ends.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is cloning vector ? Why is it used ?
Explain the technique of using such a vector in E.coli.
Answer : The cloning vectors are DNA molecules that can carry a foreign DNA segment and replicate inside the host cell.
These are plasmids, cosmids, phagemids, yeast artificial chromosome (YAC), bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), transposons and virus.
Cloning vector carry rDNA and they generally have high copy number, they can produce multiple number of required gene.
Vectors help in easy linking of foreign DNA and in selection of recombinants from non recombinants.
The entire procedure of gene cloning or recombinant DNA technology may be classified into the following six steps for the convenience in description and on the basis of the chief activity performed.
(i) Production and isolation of the DNA fragments to be cloned.
(ii) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable vector to obtain recombinant DNA.
(iii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable organism/cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation).
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment.
(v) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host.


