Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Application Chapter 12 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Application Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Biotechnology and its Application Assignments Class 12 Biology
Question. A transgenic food crop, which may help in solving the problem of night blindness in developing countries is :
(a) Bt soyabean
(b) Golden rice
(c) Flavr savr tomatoes
(d) Starlink maize
Answer
B
Question. GEAC stands for :
(a) Gene evaluation approval committee
(b) Genetic engineering approval committee
(c) Genetic engineering applied committee
(d) Gene enhancement approval committe
Answer
B
Question. Conventional methods to diagnose a disease are :
(a) Serum and urine analysis
(b) PCR
(c) ELISA
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Transgenic mice are being developed for use in :
(a) Testing the safety of polio vaccines before they are used on human
(b) Molecular diagnosis of diseases
(c) Production of human protein enriched milk
(d) Production of human insulin
Answer
A
Question. The first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4-year old girl with ADA deficiency in :
(a) 1984
(b) 1986
(c) 1992
(d) 1990
Answer
D
Question. The first transgenic cow, which produced human protein enriched milk was named :
(a) Andy
(b) Dolly
(c) Rosie
(d) Dumpy
Answer
C
Question. Two polypeptide chains of insulin are linked together by :
(a) disulphide bonds
(b) hydrogen bonds
(c) Phosphodiester bonds
(d) Glycosidic bonds
Answer
A
Question. ‘Flavr Savr’ is a transgenic variety of :
(a) Potato
(b) Tomato
(c) Soyabean
(d) Rice
Answer
B
Question. When cut by the restriction enzyme, the DNA fragments can be joined together using :
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) DNA ligase
(c) Alkaline phosphatase
(d) DNA gyrase
Answer
B
Question. Genetically engineered human insulin is made in
(a) Fungus
(b) Protista
(c) Plants
(d) Bacterium
Answer
D
Question. Toxin present in Bacillus thuringiensis does not kill the bacterium because it is inactive form what makes it active inside the insect ?
(a) the alkaline pH of the gut, which solubilises the crystals
(b) the acid pH of the gut
(c) the neutral pH of the gut
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Infection by pathogen can be detected by the presence of antigens or by detecting the antibodies synthesised against the pathogen, on this principle a test is based which is ?
(a) PCR
(b) ELISA
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Indian parliament recently cleared, which amendment of the Indian patents bill,
(a) First amendment
(b) Second amendment
(c) Third amendment
(d) Fourth amendment
Answer
B
Question. The technique that serves the purpose of early diagnosis of disease or pathogen :
(a) Recombinant DNA technology
(b) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
(c) Enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA)
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. Transgenic tobacco which is developed through RNA interference, prevents the infection of :
(a) A nematode – Meloidegyne incognitia
(b) A bacterium – Pseudonomonas putida
(c) A fungi – Tricoderma
(d) An insect
Answer
A
Question. The organisation set up for making decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing GM organism for public services is :
(a) Genetic engineering approval committee
(b) Genetic engineering advanced company
(c) Genetic engineering applied committee
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper autorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment is called :
(a) Biotheft
(b) Biopatent
(c) Biopiracy
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is widely used in contemporary biology as
(a) Source of industrial enzyme
(b) Indicator of water pollution
(c) Insecticide
(d) Agent for production of dairy products.
Answer
C
Question. Bt toxin is produced by Bacillus thuringiensis which is :
(a) Bacterium
(b) Protozoa
(c) Fungus
(d) Virus
Answer
A
Question. Cry1 Ab gene produces proteins which control?
(a) Bollworms
(b) Corn borer
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. For the control of the cotton bollworms, which one of the genes is useful ?
(a) Cry 1 Ac
(b) Cry 1 Ab
(c) Cry 1 Ad
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Milk of transgenic cow ‘Rosie’ contains a substance that was nutritionally more balanced product for human babies is :
(a) a-lactalbumin
(b) b-lactalbumin
(c) g-lactalbumin
(d) d-lactalbumin
Answer
A
Question. Which peptide is not present in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin?
(a) A-peptide
(b) B-peptide
(c) C-peptide
(d) Both (1) and (2)
Answer
C
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following passage and answer the questions from given below.
Insulin used to cure diabetes was earlier extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pigs. Insulin extracted from an animal source, though caused some patients to develop allergy or other types of reactions to the foreign protein. Human insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains : chain A and chain B, that are linked together by disulphide bridges.
In mammals including humans, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C-peptide. This C peptide is not present in mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
Question. Identify A in the given figure.
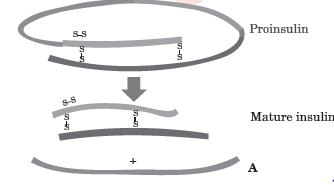
(a) Polypeptide chain A
(b) Polypeptide chain B
(c) Polypeptide chain C
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. To insert the insulin gene into bacterial DNA, both the bacterial plasmid and the human
chromosome containing the insulin gene are treated with the same restriction enzyme. Using
the same restriction enzyme ensures that
(a) DNA ligase is able to join the segments of human and bacterial DNA
(b) the exact length of nucleotides matching the insulin gene is removed from the plasmid
(c) both the bacterial and human DNA will contain sticky ends
(d) sticky ends in the cut plasmid and insulin gene are complementary.
Answer
D
Question. A bacteriologist carries out his first attempt at engineering E.coli with the gene for human
insulin. During the process, he realises that his stock of DNA ligase has depleted but decides to
continue anyway. What is a likely consequence of his decision?
(a) Bacteria with the rDNA will not be able to form colonies in a fermenter.
(b) The resulting plasmids are not able to enter the E.coli bacteria even after applying heat shock.
(c) The resulting E.coli bacteria do not contain the human insulin gene.
(d) The bacterial plasmids do not have sticky ends and are unable to accommodate the human gene.
Answer
C
Case II : Read the following passage and answer the questions from given below.
Transgenic cows have extra gene or genes inserted into their DNA. Firstly the genes for the desired product is identified and sequenced.
Then a gene construct containing this desired gene is introduced into female cow cells.
Transgenic bovine cells are selected and fused with bovine oocytes that have had all of their chromosomes removed. Once fused with the oocyte, the transgenic cells chromosomes are reprogrammed to direct development which can be implanted into a recipient cow. The resulting transgenic cow only express the transgene in her milk. This is because expression of the transgene
is controlled by a promoter specific to lactating mammary cells.
Question. Production of transgenic cow fulfill the objective of
(a) increased milk production
(b) increased meat production
(c) molecular farming
(d) all of these.
Answer
D
Question. Transgenic cow is produced through the implantation of ________ containing transgene into recipient cow.
(a) ova
(b) embryo
(c) mammary cell
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Transgenic food may cause toxicity or produce allergy.
Reason : Transgenic plants have high nutrient content.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Biopatents are awarded for biological entities and all products derived from them.
Reason : Patent on use of turmeric in wound healing was cancelled in 2008.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Mouse is the most preferred mammal for studies on gene transfers.
Reason : Mouse possesses features like short oestrous cycle and gestation period, relatively short generation time, production of several offspring per pregnancy, etc.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : ADA deficiency cannot be cured permanently by gene therapy.
Reason : The lymphocytes from the blood of patient are grown in culture outside the body.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Flavr-Savr tomato was the first transgenic commercial crop that entered the market.
Reason : Roundup variety of soybean was prepared through breeding.
Answer C
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What was the speciality of the milk produced by the transgenic cow Rosie ?
Answer : The first transgenic cow, Rosie produced human protein enriched milk which contained the human alpha lactalbumin and was nutritionally more balanced product for human babies than natural cow milk.
Question. Biotechnologists refer to Agrobacterium tumefaciens as a natural genetic engineer of plants. Give reasons to support the statement.
Answer : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is called natural genetic engineer of plants because genes carried by its plasmid produce effect in several parts of the plant.
Question. Name two transgenic microorganisms that have been used for large scale production of amino acids.
Answer : Two transgenic microorganisms used for large scale amino acid production are:
(i) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
(ii) Lactobacillus casei
Question. Give an example of bioweapon.
Answer : Bacillus anthracis
Question. What is gene therapy?
Answer : Gene therapy is the technique of genetic engineering which involves replacement of a faulty gene by a normal healthy functional gene.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is a transgenic crop ? Which plant is used to produce blood anticoagulant protein ? What is this protein called?
Answer : Transgenic crops or genetically modified crop contain and express one or more useful foreign genes or transgenes.
Brassica napus is used to produce blood anticoagulant protein. The protein is called hirudin.
The protein hirudin is an anticoagulant which is present in leech. Its gene was chemically synthesized and introduced in Brassica napus. The seeds of the latter came to have hirudin which could be extracted and purified.
Question. Write the functions of
(a) cryIAc gene
(b) RNA interference (RNAi).
Answer : (a) cryIAc gene controls cotton bollworms in Bt cotton.
(b) RNA interference (RNAi) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense. This method involves silencing of a specific mRNA.
Question. What are transgenic animals? Give an example.
Answer : Transgenic animals are those animals which contain in their genome, a foreign gene introduced by recombinant DNA technology. Such gene is called transgene. Examples of transgenic animals are transgenic mice and transgenic rabbit etc.
Question. Write the full form of ELISA. Give an example of the clinical application of ELISA test.
Answer : Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a non isotopic immunoassay. ELISA is based on the immunochemical principles of antigen-antibody reaction. ELISA is used for
determining small quantity of proteins (hormones, antigens and antibodies). ELISA is also used for diagnosis of HIV.
Question. List any two molecular diagnostic techniques and write one application of each of them.
Answer : The two molecular diagnostic technique are as follows :
(i) PCR is polymerase chain reaction. It is used to detect HIV infection and mutations in genes in suspected cancer patient.
(ii) ELISA is Enzyme- Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is used to detect infections by pathogens.
Question. What is the full form of GEAC? Describe the main objectives of GEAC set up by the Indian government.
Answer : GEAC is Genetic Engineering Approval Committee. It makes decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing GM organisms for public services. The objectives of setting up GEAC by our government is as follows:
(i) To permit the use of GM organisms and their products for commercial applications.
(ii) To adopt procedures for restriction, production, import, export and application of GM organisms.
(iii) To approve for conduct of large scale field trials and release of transgenic crops in the environment.
(iv) To curb and take punitive action against agencies if they disturb ecological balance.
Question. Refer to the given figure and answer the following questions.
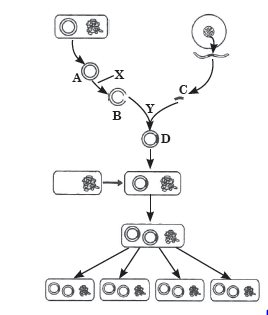
(a) Name the process shown in the given figure.
(b) Identify A to D in the given figure.
(c) Name the processes X and Y. Also mention the enzymes involved in both steps.
Answer : (a) The given figure shows the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
(b) In the given figure, A is plasmid vector, B is cut plasmid, C is fragment of DNA containing gene of interest and D is recombinant DNA.
(c) Process X is restriction digestion and Y is annealing.
Enzymes involved in X and Y are restriction endonuclease and DNA ligase respectively.
Question. What are transgenic plants? Explain any two disadvantages of transgenic plants.
Answer : The plants in which foreign genes have been introduced through genetic engineering are called transgenic plants.
Following are the disadvantages of transgenic plants :
(i) Gene transfer to non-target species : Transgenic crop plants can crossbreed with weeds, resulting in the transfer of transgene. These “super weeds” can then be difficult to eradicate. Other non-transgenic crops can also get the transgenes by cross breed.
(ii) Allergies : The transgenic food may cause toxicity or produce allergies to human beings. The enzyme produced by the antibiotic resistance gene can cause allergies, because it is a foreign protein.
Question. Name the nematode that damages the roots of tobacco plants. How is transgenic tobacco plant made resistant to nematode using biotechnology?
Answer : A nematode Meloidogyne incognita infects the roots of tobacco plants and causes a great reduction in yield. A novel strategy that was adopted to prevent this infection was based on the process of RNA interference (RNAi). RNA interference (RNAi) is the phenomenon of inhibiting activity of a gene by synthesis of RNA molecules complementary to the mRNA.
The normal (in vivo synthesised) mRNA of a gene is said to be “sense” because it carries the codons that are “read” during translation. Normally, the complement to the mRNA “sense” strand will not contain a sequence of codons that can be translated to produce a functional protein; thus, this complementary strand is called “anti-sense RNA”. The antisense RNA and mRNA molecules will anneal to form duplex RNA molecules that can not be translated. Thus, the presence of anti-sense RNA will block translation of the mRNA of the affected gene. The source of this complementary RNA could be from an infection by viruses having RNA genomes or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate. Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematodespecific anti-sense genes are introduced into the host plant.
The introduction of DNA produces anti-sense RNA in the host cells. The transgenic host plants expresses anti-sense RNA. As in consequence, nematode infestation fails in the transgenic plants because the complementary anti-sense RNA forms a double stranded RNA (ds RNA) which interferes or blocks the translation and thus, silences the mRNA of the nematode. The result was that the parasite could not survive in transgenic plant. In such way, the transgenic plant gets protected from the parasite.
Question. List advantages of genetically modified plants.
Answer : Advantages of genetically modified plants are as follows:
(i) Genetically modified plants are resistant to (a) diseases resulting from viral, bacterial and fungal infections (b) pests, such as nematodes and insects and (c) pesticides.
(ii) GM plants can tolerate adverse abiotic stresses such as cold, drought, salt, heat.
(iii) GM plants show increased efficiency of mineral usage (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil).
(iv) GM plants have high nutritional value, e.g., vitamin A enriched rice.
(v) Plants such as poplar (Populus) trees have been genetically engineered to clean up heavy pollution from contaminated soil.
(vi) These plants helped to reduce post harvest losses, e.g., Flavr savr transgenic tomato.
Question. Explain how b-carotene rich rice varieties are produced.
Answer : Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice (Oryza sativa) which contains good quantities of b-carotene (provitamin A-inactive state of vitamin A). b-carotene is a principal source of vitamin A. Since the grains (seeds) of the rice are yellow in colour due to b-carotene, the rice is commonly called golden rice. b-carotene (provitamin A) is converted into vitamin A. Thus, golden rice is rich in vitamin A. It is required by all individuals as it is present in retina of eyes. Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness and skin disorder. Since the contents of vitamin A are very low in rice, vitamin A is synthesised from b-carotene which is precursor of vitamin A. Prof. Ingo Potrykus and Peter Beyer produced genetically engineered rice by introducing three genes associated with synthesis of carotene. The grains (seeds) of transgenic rice are rich in provitamin.
Question. (a) Name the deficiency for which first clinical gene therapy was given.
(b) Mention the cause and one cure for this deficiency.
Answer : (a) Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency
(b) Adenosine deaminase enzyme is necessary for the proper functioning of our immune system. ADA deficiency is caused by the defect in the gene coding for enzyme adenosine deaminase. The possible treatments that can be given to a patient exhibiting adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency are:
(i) bone marrow transplantation
(ii) enzyme replacement therapy.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Write short note on the following:
(i) Transgenic tomato
(ii) ANDI
(iii) Transgenic sheep
(b) To which virus is transgenic chicken resistant?
Answer : (a) (i) Flavr Savr is a transgenic variety of tomato.
In this variety native tomato gene, which produces enzyme polygalacturonase is inactivated. The non-availability of this enzyme prevents over-ripening because the enzyme is essential for degradation of cell walls. Thus, fruit remains fresh for long time and it also retains flavour, superior taste and higher quantity of total soluble solids. So, it prevents post harvest and over ripening losses, and is preferred over normal native variety.
(ii) ANDI – DNA of a fluorescent jelly fish was introduced into an unfertilised egg of a Rhesus monkey in the test tube. The diploid egg underwent cleavage and the early embryo was implanted in a surrogate mother. It has been named ANDI, the acronym of “inserted DNA”.
This work would be helpful for curing diseases such as breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes and AIDS.
(iii) Tracy, the transgenic ewe was born in Scotland.
Transgenic sheep have been produced to achieve better growth and meat production. For example, human genes for blood clotting factor IX and for a1-antitryspin have been transferred in sheep and expressed in mammary tissue. This was achieved by fusing the genes with the mammary tissue-specific promoter of the bovine b-lactoglobulin gene. Human growth hormone gene has also been introduced in sheep in order to promote growth and meat production. However, they also showed several undesirable effects like joint pathology, skeletal defects, gastric ulcers, infertility, etc.
(b) Transgenic chicken is resistant to avian leukosis virus (ALV).



