Please refer to Assignments Class 11 Chemistry States of Matter Chapter 5 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 11 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 5 States of Matter Class 11 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
States of Matter Assignments Class 11 Chemistry
Question. Grahams law refers to :
(a) Boiling point of water
(b) Gaseous Diffusion
(c) Gas Compression
(d) Volume changes of gases
Answer
B
Question. Sl unit of pressure is :
(a) Pascal
(b) torr
(c) mm of Hg
(d) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. A gas will approach ideal behaviour at
(a) Low temperature, low pressure
(b) Low temperature, high pressure
(c) High temperature, low pressure
(d) High temperature, high pressure
Answer
C
Question. The rise or fall of a liquid within a tube of small bore is called :
(a) Surface Tension
(b) Capillary Action
(c) Viscosity
(d) Formation of Curvature
Answer
B
Question. The internal resistance to the flow of a liquid is called :
(a) Surface Tension
(b) Diffusion
(c) Viscosity
(d) Osmosis
Answer
C
Question. Three containers A, B, C of equal volume contain oxygen, neon and methane respectively at same temperature and pressure. The increasing order of their masses is
(a) A < B < C
(b) B < C < A
(c) C < A < B
(d) C < B < A
Answer
D
Question. The temperature above which the gas cannot be liquified by pressure alone is called :
(a) Melting Point
(b) Critical Temperature
(c) Transition Temperature
(d) Absolute Zero
Answer
B
Question. If helium and methane are allowed to diffuse out of the container under the similar conditions of temperature and pressure, then the ratio of rate of diffusion of helium to methane is:
(a) 2 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 3 : 5
(d) 4 : 1
Answer
A
Question. Containers A and B have same gas. Pressure, volume and temperature of A are all twice those of B. The ratio of number of molecules of A and B is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 4
(d) 4 : 1
Answer
B
Question. According to kinetic theory of gases,in an ideal gas,between two successive collisions a gas molecule travels
(a) In a circular path
(b) In a wavy path
(c) In a straight line path
(d) With an accelerated velocity
Answer
C
Question. van der Waals equation of state is obeyed by real gases. For n moles of a real gas, the expression will be

Answer
D
Question. Containers A and B have same gases. Pressure, volume and temperature of A are all twice as that of B, then the ratio of number of molecules of A and B are
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 4
(d) 4 : 1
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following expressions does not represent Charles’ law?

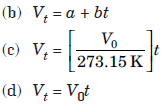
Answer
D
Question. Dipole-induced dipole interactions are present in which of the following pairs?
(a) HCl and He atoms
(b) SiF4 and He atoms
(c) H2O and alcohol
(d) Cl2 and CCl4
Answer
A
Question. To raise the volume of a gas by four times, the following methods may be adopted. Which of the methods is wrong?
(a) T is doubled and P is also doubled.
(b) Keeping P constant, T is raised four times.
(c) Temperature is doubled and pressure is halved.
(d) Keeping temperature constant, pressure is reduced to 1/4 of its initial value.
Answer
A
Question. Dimension of universal gas constant (R) is
(a) [VPT–1n–1]
(b) [VP–1Tn–1]
(c) [VPTn–1]
(d) [VPT–1n]
Answer
A
Question. At high pressure, the compressibility factor Z is equal to
(a) unity
(b) 1 − Pb/RT
(c) 1 + Pb/RT
(d) zero.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statements is wrong for gases?
(a) Gases do not have a definite shape and volume.
(b) Volume of the gas is equal to volume of container confining the gas.
(c) Confined gas exerts uniform pressure on the walls of its container in all directions.
(d) Gases are not compressible.
Answer
D
Question. At 25°C and 380 mm pressure, 400 mL of dry oxygen was collected. If the temperature is constant, what volume will the oxygen occupy at 760 mm pressure?
(a) 200 mL
(b) 400 mL
(c) 569 mL
(d) 621 mL
Answer
A
Question. The types of attractive forces between a polar molecule and a non-polar molecule are
(a) dipole-dipole forces
(b) hydrogen bonds
(c) dipole-induced dipole forces
(d) dispersion forces.
Answer
C
Question. A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in the figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?

(a) p1 > p2 > p3 > p4
(b) p1 = p2 = p3 = p4
(c) p1 < p2 < p3 < p4
(d) p1 < p2 = p3 < p4
Answer
C
Question. The mole fraction of dioxygen in a neon‑dioxygen mixture is 0.18. If the total pressure of the mixture is 25 bar, the partial pressure of neon in the mixture would be
(a) 25.18 bar
(b) 25.82 bar
(c) 4.5 bar
(d) 20.5 bar
Answer
D
Question. When the product of pressure and volume is plotted against pressure for a given amount of gas, the line obtained is
(a) parallel to x-axis
(b) parallel to y-axis
(c) linear with positive slope
(d) linear with negative slope.
Answer
A
Question. Select the correct statement. In the gas equation, PV = nRT
(a) n is the number of molecules of a gas
(b) n moles of the gas have a volume V
(c) V denotes volume of one mole of the gas
(d) P is the pressure of the gas when only one mole of gas is present.
Answer
B
Question. The volume occupied by 1.8 g of water vapour at 374°C and 1 bar pressure will be
[Use R = 0.083 bar L K–1mol–1]
(a) 96.66 L
(b) 55.87 L
(c) 3.10 L
(d) 5.37 L
Answer
D
Question. Gas deviates from ideal gas nature because molecules
(a) are colourless
(b) attract each other
(c) contain covalent bond
(d) show Brownian movement.
Answer
B
Question. 25 g of each of the following gases are taken at 27°C and 600 mm pressure. Which of these will have the least volume?
(a) HBr
(b) HCl
(c) HF
(d) HI
Answer
D
Question. Molar volume of CO2 is maximum at
(a) NTP
(b) 0°C and 2.0 atm
(c) 127°C and 1 atm
(d) 273°C and 2.0 atm.
Answer
C
Question. The correction factor ‘a’ to the ideal gas equation corresponds to
(a) density of the gas molecules
(b) volume of the gas molecules
(c) electric field present between the gas molecules
(d) forces of attraction between the gas molecules.
Answer
D
Question. The van der Waals equation reduces itself to the ideal gas equation at
(a) high pressure and low temperature
(b) low pressure and low temperature
(c) low pressure and high temperature
(d) high pressure and high temperature.
Answer
C
Question. Intermolecular forces in solid hydrogen are
(a) covalent forces
(b) van der Waals forces or London dispersion forces
(c) hydrogen bonds
(d) all of these.
Answer
B
Question. Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of particles. This statement is direct consequence of
(a) perfect gas law
(b) partial law of volumes
(c) Charles’ law
(d) ideal gas equation.
Answer
D
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs :
A statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : van der Waals equation is applicable only to non-ideal gases.
Reason : Ideal gases obey the equation PV = nRT.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Three states of matter are the result of balance between intermolecular forces and thermal energy of the molecules.
Reason : Intermolecular forces tend to keep the molecules together but thermal energy of molecules tends to keep them apart.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Compressibility factor (Z) for for non ideal gases is always greater than 1.
Reason : The gases which lave Z > 1 are difficult to compress.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : The graph between P v/s 1/V is a straight line.
Reason : At constant temperature, P ∝ 1/V.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : At constant temperature, PV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason : At high pressure all gases have Z > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have Z < 1.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Vapour pressure of NH3 is higher than C2H5OH.
Reason : H-bonding is observed in both the molecules.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : The plot of volume (V) versus pressure (P) at constant temperature is a hyperbola in the first quadrant.
Reason : V ∝ 1/P at constant temperature.
Answer
A