Please refer to Assignments Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics Chapter 6 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 11 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 6 Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Thermodynamics Assignments Class 11 Chemistry
Question. An ideal gas is taken through the cycle A → B → C → A as shown in figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in cycle is 5 J, the work done by the gas in the process C → A.

(a) -5 J
(b) -15 J
(c) -10 J
(d) -20 J
Answer
A
Question. Hesss law is an application of
(a) 1st law of Thermodynamics
(b) 2nd law of Thermodynamics
(c) Entropy change
(d) ΔH = ΔU + PΔV.
Answer
A
Question. Identify the correct statement from the following in a chemical reaction.
(a) The entropy always increases
(b) The change in entropy along with suitable change in enthalpy decides the fate of a reaction
(c) The enthalpy always decreases
(d) Both the enthalpy and the entropy remain constant
Answer
B
Question. Third law of thermodynamics provides a method to evaluate which property?
(a) Absolute Energy
(b) Absolute Enthalpy
(c) Absolute Entropy
(d) Absolute Free Energy
Answer
C
Question. At absolute zero the entropy of a perfect crystal is zero. This statement corresponds to which law of thermodynamics?
(a) Zeroth Law
(b) First Law
(c) Second Law
(d) Third Law
Answer
D
Question. The bond energy (in kcal mol-1) of a C-C single bond is approximately
(a) 1
(b) 10
(c) 83-85
(d) 1000
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following has the highest entropy?
(a) Mercury
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Water
(d) Graphite
Answer
B
Question. A student runs a reaction in a closed system. In the course of the reaction, 64.7 kJ of heat is released to the surroundings and 14.3 kJ of work is done on the system. What is the change in internal energy (ΔU) of the reaction?
(a) -79.0 kJ
(b) 50.4 kJ
(c) 79.0 kJ
(d) -50.4 kJ
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is/are a reason that water is a desirable heat sink for use in calorimeters?
I) Waters heat specific capacity is very precisely known.
II) Water is readily available.
III) Water has an unusually large specific heat capacity.
(a) I only
(b) I and II
(c) I, II and III
(d) II only
Answer
C
Question. Calculate the heat required to make 6.4 Kg CaC2 from CaO(s) and C(s) from the reaction: CaO(s) + 3 C(s) → CaC2(s) + CO (g) given that Δf H° (CaC2) = -14.2 kcal. Δf H° (CO) = -26.4 kcal.
(a) 5624 kca
(b) 1.11 × 104 kcal
(c) 86.24 × 10³
(d) 1100 kcal
Answer
B
Question. System in which there is no exchange of matter, work or energy from surroundings is
(a) closed
(b) adiabatic
(c) isolated
(d) isothermal.
Answer
C
Question. For one mole of NaCl(s) the lattice enthalpy is
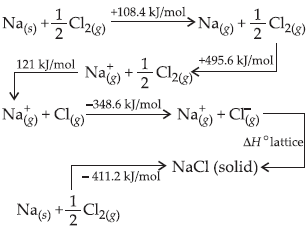
(a) –788 kJ/mol
(b) +878 kJ/mol
(c) +788 kJ/mol
(d) –878 kJ/mol
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements is false?
(a) Work is a state function.
(b) Temperature is a state function.
(c) Change in the state is completely defined when the initial and final states are specified.
(d) Work appears at the boundary of the system.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following processes is a nonspontaneous process?
(a) Dissolution of salt or sugar in water
(b) Mixing of different gases through diffusion
(c) Precipitation of copper when zinc rod is dipped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate
(d) Flow of heat from a cold body to a hot body in contact
Answer
D
Question. The correct figure representing isothermal and adiabatic expansions of an ideal gas from a particular initial state is
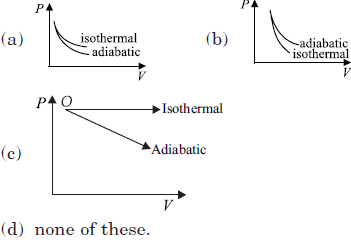
Answer
A
Question. Choose the reaction with negative ΔS value.
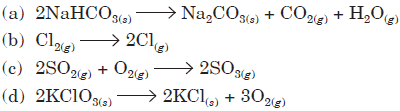
Answer
C
Question. The heat of neutralization is maximum when
(a) sodium hydroxide is neutralized by acetic acid
(b) ammonium hydroxide is neutralized by hydrochloric acid
(c) sodium hydroxide is neutralized by formic acid
(d) sodium hydroxide is neutralized by hydrochloric acid.
Answer
D
Question. In an adiabatic process, no transfer of heat takes place between system and surroundings. Choose the correct option for free expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic condition from the following.
(a) q = 0, ΔT ≠ 0, w = 0
(b) q ≠ 0, ΔT = 0, w = 0
(c) q = 0, ΔT = 0, w = 0
(d) q = 0, ΔT < 0, w ≠ 0
Answer
C
Question. According to the 3rd law of thermodynamics, the entropy at 0 K is zero for
(a) elements in their stable form
(b) perfectly crystalline solid
(c) substances at 1 atm and 25 °C
(d) gaseous substances only.
Answer
B
Question. Five moles of a gas is put through a series of changes as shown graphically in a cyclic process. The processes A → B, B → C and C → A respectively are

(a) isochoric, isobaric, isothermal
(b) isobaric, isochoric, isothermal
(c) isothermal, isobaric, isochoric
(d) isochoric, isothermal, isobaric
Answer
A
Question. Enthalpy of combustion of carbon to CO2 is –393.5 kJ mol–1. What amount of heat will be released upon formation of 35.2 g of CO2 from carbon and oxygen gas?
(a) 214.8 kJ
(b) 314.8 kJ
(c) 414.8 kJ
(d) 514.8 kJ
Answer
B
Question. In thermodynamics, which one of the following properties is not an intensive property?
(a) Pressure
(b) Temperature
(c) Volume
(d) Density
Answer
C
Question. Bond Bond enthalpy
N ≡ N 945 kJ mol–1
H — H 436 kJ mol–1
N — H 391 kJ mol–1
Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
(a) –89 kJ mol–1
(b) –93 kJ mol–1
(c) –105 kJ mol–1
(d) 105 kJ mol–1
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) The presence of reacting species in a covered beaker is an example of open system.
(b) There is an exchange of energy as well as matter between the system and the surroundings in a closed system.
(c) The presence of reactants in a closed vessel made up of copper is an example of a closed system.
(d) The presence of reactants in a thermos flask or any other closed insulated vessel is an example of a closed system.
Answer
C
Question. The heats of neutralization of CH3COOH, HCOOH, HCN and H2S are –13.2, –13.4, –2.9 and –3.8 kcal per equivalent respectively. The correct increasing order of acid strength is
(a) HCOOH < CH3COOH < H2S < HCN
(b) HCN < H2S < CH3COOH < HCOOH
(c) HCOOH < CH3COOH < HCN < H2S
(d) CH3COOH < H2S < HCN < HCOOH
Answer
B
Question. The enthalpies of the elements in their standard states are assumed to be
(a) zero at 298 K
(b) unity at 298 K
(c) zero at all temperatures
(d) zero at 273 K.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reactions correspondsto the definition of enthalpy of formation ?
(a) C(g) + O2(g) CO2(g)
(b) C(s) + O2(l) CO2(g)
(c) C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g)
(d) C(l) + O2(s) CO2(g)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following condition is not favourable for the feasibility of a reaction?
(a) ΔH = +ve, TΔS = +ve and TΔS > ΔH
(b) ΔH = –ve, TΔS = +ve
(c) ΔH = –ve, TΔS = –ve and TΔS < ΔH
(d) ΔH = +ve, TΔS = +ve and TΔS < ΔH
Answer
D
Question. The second law of thermodynamics states that
(a) entropy of the universe is decreasing continuously.
(b) energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
(c) all spontaneous processes are thermodynamically irreversible.
(d) at absolute zero free energy is zero.
Answer
C
Question. In conversion of limestone to lime,
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
the values of ∆H° and ∆S° are +179.1 kJ mol–1 and 160.2 J/K respectively at 298 K and 1 bar. Assuming that ∆H° and ∆S° do not change with temperature, temperature above which conversion of limestone to lime will be spontaneous is
(a) 1118 K
(b) 1008 K
(c) 1200 K
(d) 845 K
Answer
A
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs :
A statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Enthalpy of formation of graphite is zero but of diamond it is not zero.
Reason : Enthalpy of formation of the most stable allotrope is taken as zero.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : U is a state function.
Reason : T is an intensive property.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Entropy of system increases for a spontaneous reaction.
Reason : Enthalpy of reaction always decreases for spontaneous reaction.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The sum of q + w is a state function.
Reason : Work and heat are state functions.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Sublimation of the solid is nonspontaneous.
Reason : Sublimation is endothermic process.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Spontaneous process is an irreversible process and may be reversed by some external agency.
Reason : Decrease in enthalpy is a contributory factor for spontaneity.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Decrease in free energy causes spontaneous reaction.
Reason : Spontaneous reactions are invariable exothermic reactions.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Some salts are sparingly soluble in water at room temperature.
Reason : The entropy increases on dissolving the salts.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : The heat absorbed during the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas against vaccum is zero.
Reason : The volume occupied by the molecules of an ideal gas is zero.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Heat of neutralisation for both H2SO4 and HCl with NaOH is 53.7 kJ mol–1.
Reason : Both HCl and H2SO4 are strong acids.
Answer
A

