Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Science Human Eyes and Colourful World Chapter 11 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Human Eyes and Colourful World Assignments Class 10 Science
Very Short Type Questions
Question. Name the transparent membrane through which light enters first in the eye.
Answer : Cornea.
Question. What are light sensitive cells?
Answer : Rods and cones.
Question. What type of image is formed on the retina?
Answer : Real, inverted image.
Question. Define angle of prism.
Answer : The angle formed due to two lateral faces of the prism is called the angle of prism.
Question. What is presbyopia?
Answer : It is the defect of eye in which one cannot see nearby as well as far objects clearly.
Question. What type of lens should be used to correct the presbyopia?
Answer : Bi-focal lens. Concave-convex lens. (iMG 185)
Question. What is spectrum?
Answer : The band of seven colours obtained due to the dispersion of white light is called spectrum.
Question. In visible spectrum which colour has longest wavelength.
Answer : Red.
Question. Why is inverted image formed on the retina of human eye?
Answer : The inverted image is formed due to the eye lens which is convex in shape. Through it the light rays enters to form the real, inverted image.
Question. What type of signals are generated and sent to the brain by light sensitive cells of retina?
Answer : Electrical signals.
Question. Which part of the human eye controls the amount of light entering the eye?
Answer : Pupil.
Question. What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
Answer : The ability of the eye to focus the distant objects as well as the nearby objects on the retina by changing the focal length of the eye lens is called power of accommodation.
Question. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Answer : A person with a myopic eye can use concave lens to restore proper vision.
Question. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Answer : The far point is infinity and the near point is 25 cm of the human eye with normal vision.
Question. What is the function of crystalline lens of human eye?
Answer : The crystalline lens provides the proper focal length required to focus objects at different distances on the retina.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why doesn’t planets appear to be twinkling?
Answer : Planets are big enough and quite closer to the earth, due to these two properties the planets do not appear to be twinkling.
Question. A short-sighted person cannot see clearly beyond 5 cm. Calculate the power of lens required to correct his vision to normal?
Answer : f = – 5 cm
P= 1/f = 1/-5 = 0.20
Power = 0.2 Dioptre
Question. What is hypermetropia? How can it be corrected?
Answer : Hypermetropia is an eye defect also called as long-sightedness. Person can see a far off objects but cannot see nearby objects. It is because the image is formed beyond retina.
Cause – (a) The focal length of the eye lens is too long.
(b) The eyeball has become too small.
Correction: It can be corrected by using convex lens of appropriate power.
Question. What is presbyopia? How can it be corrected?
Answer : Presbyopia is caused due to decrease in the power of accommodation of the eyes due to ageing and weakening of ciliary muscles diminishing flexibility of eye lens. A person with this defect cannot see nearby as well as far off objects clearly.
Correction: It can be corrected by using bi-focal lens with both concave and convex lens in it.
Question. Why does the sky appears blue during day time, red during sunrise and sunset and black to an astronaut.
Answer : Sky appears blue during day time because the light of sun gets scattered and the most scattered light is blue, so the sky appears blue.
During evening and early morning when the sun is not over head but it is below the horizon, the only light that reaches our eye is red and hence the sky appear to be reddish in colour.
For an astronaut the sky appears to be black because there is no atmosphere that can refract the light.
Question. Give the difference between myopia and hypermetropia.
Answer :
| S.No. | Myopia | Hypermetropia |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. | Short-sightedness—can see nearby object but cannot see far off objects. Image is formed in front of retina. The size of eyeball increases. Focal length of eye lens decreases. Corrected by using concave lens. | Long-sightedness—can see far off objects but cannot see nearby objects. Image is formed beyond retina. The size of eyeball decreases. Focal length of eye lens increases. Corrected by using convex lens. |
Question. Why does a ray of light splits into different colours on passing through a glass prism?
Answer : When light rays enter the glass prism the angle at which it bends makes the light split into its seven components because the speed of each component of light is different and due to the bending every component shows its different ability to pass through it.
Question. In dispersion of white light through prism, which colour deviates most and which colour the least? Why do they deviate differently?
Answer : The colour of light that deviates least is red and violet deviates the maximum. The difference in deviation is due to the difference in wavelength and speed of each colour of light, also due to different bending ability when it passes through the prism.
Question. Give one main difference between the lens of human eye and lens of camera.
Answer : Lens of human eye has flexible aperture, its focal length can be changed. In camera focal length can not be changed for a lens.
Question. The near point of hypermetropic eye is 80 cm. What is the nature and power of the lens required to enable him to read a book placed at 25 cm from the eyes?
Answer : Near point = 80 cm
Object distance u = – 25 cm
ν= – 80 cm (convex lens in case of hypermetropia)
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
= 1/(-80) – 1/(-25)
1/f = -1/80 + 1/25 = (-5+16)/400
1/f = +11/400
f = 400/11 = 36.36 cm
f = 0.36 m
Power of lens P =1/f = 1/0.36 = 2.7D
Question. Why danger signals are red?
Answer : Danger signals are of red colour, as it scatters the least and can be seen from the
maximum distance.
Question. Why do you take time to see objects when you enter a dim lighted room from outside in the sun?
Answer : In the sun light the size of pupil, is small but when one enters the dim light, it takes some time for iris to adjust the size of pupil and the light sensitive cells take some time to get activated.
Question. A person needs a lens of power –5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length
of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
Answer : The focal length of a lens is given by
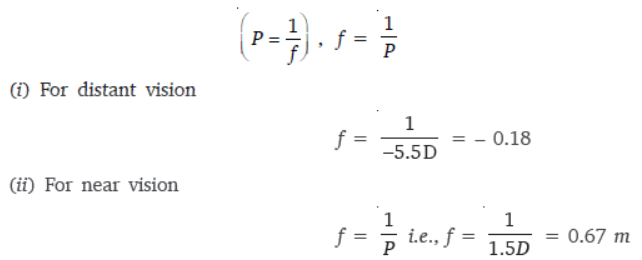
Question. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
Answer : Ciliary muscles can contract the lens of human eye to a certain limit because of which a person with normal vision can see the nearby objects clearly only if placed at 25 cm but if the object is placed closer to the eye than it cannot see the objects clearly.
Question. What is meant by dispersion of white light? Draw a ray diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism. Give reason why do we get different colours of light?
Answer : Dispersion of light: The splitting of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like glass prism is called dispersion of light.
Diagram : Dispersion of light
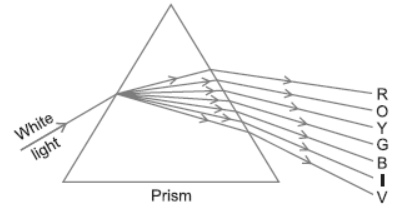
We get different colours because each colour of light has different bending ability when they pass through the glass prism.
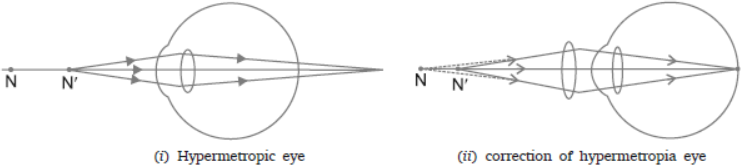
Question. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect?
Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Answer :
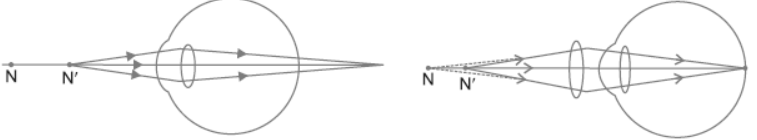
(a) The hypermetropic eye, and (b) correction for hypermetropia with a convex lens
u = –25 cm, ν = –1 m = –100 cm
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
= 1/-100 – 1/(-25) = 1/100 + 1/25
= -1+4 /100 = 3/100 or f = 1/3m
P = 1/f 1/(1/3) = 3D (convex lens)
Question. A student can see objects clearly only when the objects are lying at distances between 60 cm and 320 cm from the eye.
(a) What kind of eye defect he is suffering from?
(b) What kind of lens will be required to increase his range from 25 cm to infinity?
Explain briefly.
Answer : Student is suffering from myopia. It can be corrected by using concave lens of appropriate focal length and power. The light rays meet before retina and hence
concave lens will help the rays to diverge further and help them in meeting on retina.
Question. When we see any object through the hot air over the fire, it appears to be wavy, moving slightly. Explain.
Answer : The objects beyond the hot air appears to be wavy because the medium for light to pass through changes, the light passes from denser to rarer and then again to denser medium thereby causing refraction in the air. Moreover the refractive index of the hot air keeps changing which leads to give the wavy appearance of the object.
Question. What is the direction of rainbow formation? What is the position of red colour in rainbow?
Answer : Rainbow is always formed in the direction opposite to sun. The position of red colour in the rainbow is at the top.
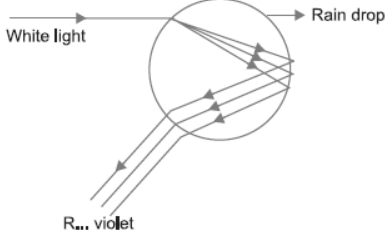
Question. (a) What is meant by dispersion of white light? Describe the formation of rainbow in the sky with the help of a diagram.
(b) What is hypermetropia? Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation of an objects by
(i) hypermetropic eye
(ii) Correction made with a suitable lens for hypermetropic eye.
Answer : (a) The splitting of white light into its constituent seven colours is called dispersion of light.
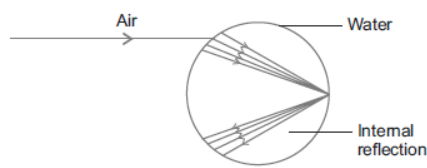
Rainbow formation in the sky: The water droplets suspended in the atmosphere after rain causes the splitting of sunlight by acting as small prism.
The light enters the water droplets, refracts, splits and shows internal reflection.
The red colour band is wider than violet or blue colour.
(b) Hypermetropia: Also called long-sightedness. Person can see long distant objects but cannot see nearby objects distinctly. This is because the eye ball becomes smaller, focal length increases. It can be corrected by using converging lens called convex lens.
Question. What is internal reflection?
Answer : When a light rays enters from one medium to another (e.g., rarer to denser i.e., air to water droplet) then a ray of light instead of passing through it reflects in the second medium then it is said to be internal reflection of light.
Question. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that it follows:
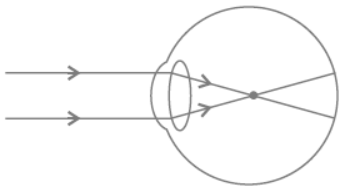
(a) Name the defect and give reason.
(b) Give 2 causes for this defect.
(c) Give the correction – draw diagram for the same.
Answer : (a) The defect is myopia, short-sightedness
(b) It is caused due to the decrease in the focal length of the eye lens and increase in
the size of the eye ball.
(c) The defect can be corrected by using the concave lens.
Question. In the given diagram label A, B, C and D and give the function of B and D.
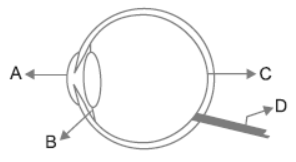
Answer : A= Cornea
B= Ciliary muscles
C= Retina
D= Optic nerve
Function of B and D are:
B : Ciliary muscles: It helps in holding the eye lens and changing or adjusting the focal length of the lens.
D : Optic nerve: It sends the electrical signal from retina to the brain.
Question. Near point of a hypermetropic eye is at 1 m. Find the focal length, power and nature of lens used to correct this defect.
Answer : Near point of hypermetropic eye is 1 m i.e., 100 cm. The eye cannot see objects between 100 cm and 25 cm.
u = – 25 cm
ν = – 1 m = – 100 cm
1/f = 1/v-1/u
= -1/100 – 1/(-25)
= -1/100 + 1/25
1/f = -1+4/100 = 3/100
f = 100/3 cm = 1/3 m
p = 1/f = 1/(1/3 )m
P = + 3 Dioptre
Convex lens of power 3D is used to correct this defect.
Question. Why do stars twinkle?
Answer : Stars twinkle due to atmospheric refraction of light from the stars and changing density of air around the earth.
Question. Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Answer : Planets are much closer to earth and behave like extended source.
Question. Draw a labelled diagram of rainbow formation. Also explain the phenomenon of rainbow formation.
Answer :

When sun light splits due to water drops suspended in air, causing the band of seven colours is called rainbow.
Water droplets acts as tiny prism in the sky. The sunlight when enters these tiny droplets undergo internal reflection and also refract these rays which are dispersed causing a band of seven colours called rainbow.
Rainbow is always formed in the direction opposite to the sun.
Question. Why is red colour selected for danger signal lights?
Answer : Red colour light has maximum wavelength, it does not scatter due to atmosphere and reaches our eyes, travels fast and hence used for danger signals.
Question. Why does sky look blue on a clear day?
Answer : White light scatters due to atmospheric refraction. White light is made up of seven colours out of which, blue light scatters the most hence the sky looks blue.
Question. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer : The image distance in the eye remains the same. On increasing the distance of an object from the eye, the focal length of the eyes changes due to ciliary muscles which helps an eye to focus the object image on retina.
Question. Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer : When the sun rises early in the morning (or set in the evening), the light from sun travels through the thicker layer of air and larger distance of the atmosphere surrounding the earth. Hence the blue light scatters the most but red light does not scatters and reaches our eyes.
Question. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer : In space there are no particles, air, gases, water droplets etc., present to scatter the light. So when the astronauts look at the sky in the space, there is no light entering our eyes, hence it appears dark.
Question. What is hypermetropia? State the two causes of hypermetropia. With the help of ray diagram show:
(i) the eye defect hypermetropia.
(ii) correction of hypermetropia by using a lens.
Answer : Hypermetropia: Defect of a vision in which a person can see distant objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects clearly.
Causes: (a) Focal length of the eye lens is too large.
(b) Eye ball has become too small.
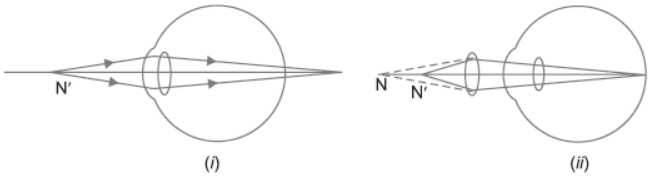
Question. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer : For the myopic eye
u = – ∝
ν = –80 cm
1/v – 1/u = 1/f lens formula
1/-80cm = 1/-∝ = 1/f
∴ f = –80 cm = –0.80 m
Power of the lens is P = 1/f
∴ p = 1/-0.80 m = –1.25 D
A concave lens; P = –1.25 D
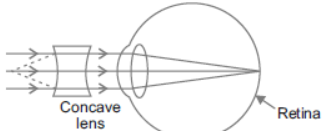
Question. (a) What is myopia? State the two causes of myopia and with the help of a labelled ray diagrams show:
(i) the eye defect myopia.
(ii) correction of myopia using a lens.
(b) Why is the normal eye unable to focus on an object placed within 10 cm from the eye?
Answer : (a) Myopia or short-sightedness—Eye can see objects at short distance. Inability of the eye in viewing long distant objects. The image falls before retina.
Causes: (i) Elongation of eye ball.
(ii) Excessive curvature in cornea.
Correction: By using concave lens (diverging lens), which shifts the image to the retina by diverging the rays further.

(b) The near point of human eye is 25 cm which cannot be changed further hence the objects within 10 cm of the eye cannot be viewed.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) What is dispersion of white light? What is the cause of such dispersion? Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
(b) A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain why?
Answer : (a) Dispersion of white light is splitting of light into its seven constituent colours forming a band of VIBGYOR called spectrum.
Cause: White light is made up of seven colours, each colour has different speed in different media. Due to different speed, the bending ability varies and the colours split/separate.
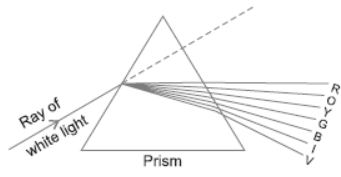
(b) Dispersion does not take place in glass slab as two refracting surfaces are parallel. The light does not split into its constituent colours.
Question. (a) What is hypermetropia?
(b) What are the two causes of the defect of vision?
(c) How can this defect of the eye be corrected? Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams to show the formation of image by
(i) a hypermetropic eye
(ii) a hypermetropic eye corrected with a suitable lens.
Answer : (a) Hypermetropia: It is also called long-sightedness. The person with this eye defect can see far off objects but cannot see nearby objects clearly. The image is formed beyond retina.
(b) Two causes
(i) Focal length of the lens increases
(ii) Eye ball becomes smaller
(c) Correction: It can be corrected by using a convex lens. It is a converging lens which shifts the image of the object on the retina.
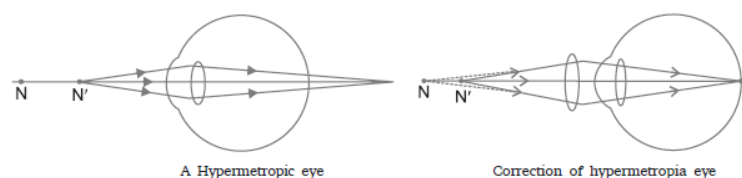
Question. Study the diagram given below and answer the question that it follows:
(a) Which defect of vision is represented in this case? Give reason for your answer.
(b) What could be the two causes of this defect?
(c) With the help of a diagram show how this defect can be corrected by the use of a suitable lens.
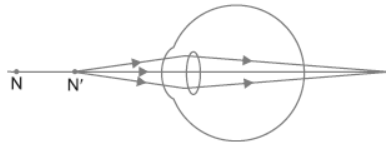
Answer : (a) The defect is hypermetropia, as the image of near point is formed beyond retina.
(b) Two causes of the defect are:
(i) Size of eye ball decreases.
(ii) Focal length of the lens increases.
(c) This defect can be corrected by using a convex lens of suitable focal length.
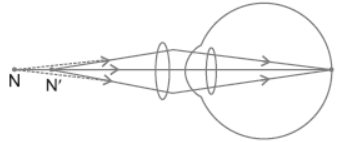
Question. Name three refractive defects of vision with the help of diagram. Explain the reasons and correction of these defects.
Answer : The three refractive defects of vision are
(I) Myopia
(II) Hypermetropia
(III) Presbyopia
(I) Myopia is short-sightedness, the image is formed in front of retina due to the
elongation of the eye ball or due to decrease of focal length.
Correction – Using concave lens.

Person cannot see nearby objects clearly.
(a) Normal eye.
(b) Myopic eye, the image is formed in front of retina.
(c) Concave lens is used to correct the defect.
(II) Hypermetropia is long-sightedness, the image is formed behind the retina due to shortening of eyeball or due to increase in the focal length of the lens of eye.
Correction: Using convex lens.
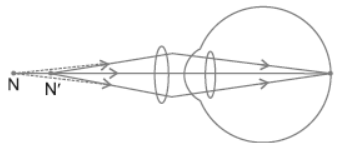
Fig. (a) Normal eye, (b) Hypermetropia eye, (c) Convex lens is used to correct the defect.
(III) Presbyopia: It is the defect of an eye in which the power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases with ageing. Near point changes as well as the far off objects are also not visible clearly. It is caused due to the weakening of ciliary muscles and the reduced flexibility of eye lens.
Such a defect in which a person suffers from both myopia and hypermetropia is called presbyopia. It is corrected by using bifocal lens.
QUESTIONS ON HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILLS (HOTS)
Question. How does the size of particles present in medium produce different colours of light by its scattering property?
Answer : The colour of the scattering light in a medium depends on the size of the scattering particles.
(i) If the size of particles is very small, it will scatter mainly blue light.
(ii) If the size of particles is larger then it will scatter light of longer wavelength i.e., red.
(iii) If the size of scattering particles is larger enough, the light appears to be white.
Question. Give one use of the following properties of light:
(i) Scattering of light (ii)Persistence of vision
(iii) Power of accommodation (iv) Refraction of light
(v) Reflection of light
Answer : (i) Due to scattering of light we can see the different colours of sky and rainbow formation.
(ii) Used in cinematography.
(iii) Eye can see both nearby and far off objects from same point.
(iv) We can see through lenses, eye defects can be corrected, we can see under water.
(v) Our eyes can see object only due to reflection of light by the object into our eyes.
Question. To correct myopia why we use concave lens and to correct hypermetropia, why do we use convex lens? Why can’t we do vice-versa?
Answer : Myopia is a defect in which the image is formed in front of retina. We need to use diverging lens so that it can further diverge the light rays before it enters our eye and make it possible to meet on the retina.
In case of hypermetropia, the image is formed beyond retina, we need to use convex lens so as to converge the rays and make it possible for the rays to meets on the retina.
Question. Why does light splits into spectrum when it passes through prism only and does not split when it passes through glass slab?
Answer : Rectangular glass slab has parallel refracting surfaces, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. It slightly gets displaced laterally. While in case of prism the surface
is not parallel and the light ray gets deviated at larger angle due to which it splits into its constituent colour.
Question. Rohan’s father is an eye surgeon. He persuaded his father to put a camp in his society for educating people on eye-donation. Rohan made a banner. One donation can give eye-vision to two blind persons.
(a) Name the part of the eye that is used during eye transplant.
(b) Name the defect that can be corrected by this transplant.
(c) What value of Rohan is reflected?
Answer : (a) Cornea is used for eye transplant.
(b) Defects caused due to cornea can be corrected by eye donation.
(c) Rohan shows sympathy, compassion and empathy in his behaviour.
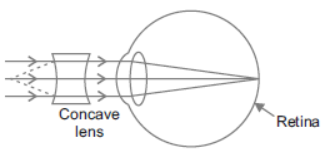
Question. (a) Draw a diagram to show the formation of image of a distant object by a myopic eye.
How can such an eye defect be remedied?
(b) State two reasons due to which this eye defect may be caused.
(c) A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond a distance of 1.5 m. What would be the power of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Answer : (a) Object at infinity, image is formed in front of retina.
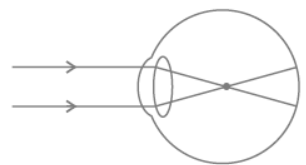
Corrected by concave lens
(b) Myopia is caused due to:
(i) Elongation of eye ball
(ii) Excessive curvature in cornea, focal length decreases.
(c) Far point of myopic eye is 1.5 m = u
to change far point to infinity = ν
focal length of power → P = ?, F = ?
1/f = 1/v – 1/u (Lens formula)
1/f = 1/-1.5 – 1/-∞ = 1/1.5 m
f = – 1.5 m
P = 1/f = 1/-1.5 = 0.67 dioptre.


