Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Science Heredity And Evolution Chapter 9 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Heredity And Evolution Assignments Class 10 Science
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Define variations.
Answer : Variations are differences that occur between the organisms of the same species in spite of the same basic feature.
Question. How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer : Variations increases the adaptability of an organism to its changing environmental conditions.
Question. How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings?
Answer : 23 pairs.
Question. a. Do eyes of octopus, insect and human show relation in their evolutionary process?
b. How can we say that birds have evolved from reptiles?
Answer :
a. No, eyes of these animals do not show any evolutionary relationship as they are analogous organs.
b. The presence of feathers both in dinosaurs and birds indicate birds have evolved from reptiles.
Some organs may be adapted to perform new functions during evolution, e.g., feathers which were meant for providing insulation in cold weather, slowly became adapted for flight. Hence birds are closely related to reptile as dinosaurs had feathers, though could not fly.
Question. All the variations in a species do not have equal chances of survival. Why?
Answer : Some variations are caused by environmental changes and they do not bring out any change in DNA. Therefore, all the variations do not have equal chances of survival.
Question. Why is it that asexual reproduction produces exact copies but sometimes minor variations are also seen in next progeny?
Answer : Since no biochemical reaction is reliable, therefore, in copying of DNA, it may cause slight difference which causes these variations.
Question. How can the chromosomes be identified?
Answer : In human beings, the individual chromosomes are identified by their lengths, position of centromere and banding pattern on staining.
Question. A normal baby girl receives her X chromosome from whom : mother, father, both mother and father or either from mother or father?
Answer : From both mother and father.

Question. No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why?
Answer : All individuals have different kind of DNA. So all individuals are not alike to each other.
Question. When does the process of gene flow take place?
Answer : Gene flow or gene migration takes place in between the populations that are partly but not completely separated.
Question. How can we say that change in genes can be brought about the change in DNA?
Answer :
A gene is a segment of DNA on a chromosome occupying a specific position.
a. It provides informations from one protein to another and is responsible for its alteration.
b. It ensures the stability of the DNA of the species.
So, we can say that change in gene segment can bring about change in DNA.
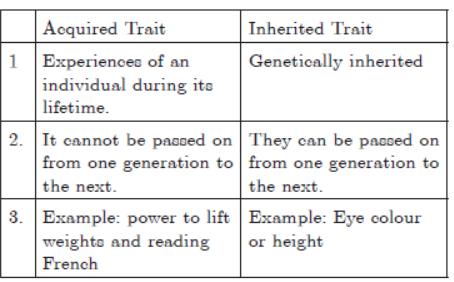
Question. State the meaning of inherited traits and acquired traits. Which of the two is not passed on to the next generation? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer :
Question. Name the term used for the traits that are exhibited externally.
Answer : Phenotype.
Question. A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in Fj progeny?
Answer : All will bear violet flowers.
Question. Write the sex of the baby that inherits Y-chromosomes from the father.
Answer : Male.
Question. a. Write full form of DNA.
b. Why are variations essential for the species?
Answer :
a. Deoxyribonucleic acid
b. Survival
Question. An organism which is a worm, has very simple ‘eyes’, that are really eye spots which detect light. Name that organism.
Answer : Planaria.
Question. How can we trace evolutionary relationships?
Answer : Evolutionary relationships can be traced by studying fossils, by studying homologous and analogous organs, by comparing the embryos of different animals and by comparing the DNA’s of different species.
Question. What is phylogeny and molecular phylogeny?
Answer : Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of an organism. Molecular phylogeny traces the evolutionary relationships by comparing the differences in the DNA of different organisms.
Question. What is adaptation?
Answer : An adaptation is characteristics feature which helps an organism to survive in its habitat in a better way.
Question. What is speciation?
Answer : Speciation is the process of formation of a new species from the already existing species by accumulation of variations, natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift, etc.
Question. What is a gene?
Answer : Gene is the unit of inheritance. It is a part of the chromosome which controls the appearance of a set of hereditary characteristics.
Question. What is the significance of studying homologous and analogous organs?
Answer : Organisms that have homologous organs show relatedness and a common ancestory.
Question. Which of the following combinations of sex chromosomes produces a male or a female child—XX or XY?
Answer : XX combination produces a female child while the XY combination produces a male child.
Question. Which is gene flow?
Answer : It is the exchange of genetic material by interbreeding between populations of the same species. Gene flow increases the variations in a population.
Question. The forelimbs of frog, reptiles, birds and arms of man show the same basic design. What kind of organs are these?
Answer : Homologous organism
Question. What is microevolutions?
Answer : Microevolutions is the evolution that takes place on a relatively small scale at the population level and can change the common characteristics of particular species.
Question. What is classification?
Answer : It is the arrangement of organism into series of groups based on the similarity of characters on physiology, anatomy, morphology and other relationships.
Question. Who is known as the ‘‘father of Genetics’’?
Answer : G.J. Mendel is called the ‘‘father of Genetics’’.
Question. What are fossils?
Answer : Fossils are preserved traces or remains of living organisms of geological past.
Question. What are the uses of fossils?
Answer : 1. Fossils helps to trace the racial history of organisms. 2. They help to analyse the past climatic conditions. 3. They help to measure the geological time.
Question. Name the scientist who put forth the theory of natural selection.
Answer : Charles Darwin.
Question. What is artificial selection?
Answer : It is the process of modification of a species by selective breeding. Animals and plants with desirable characters are selected and propagated. Artificial selection by farmers has resulted in the formation of cauliflowers, cabbage, broccoli and kohlrabi from the wild cabbage.
Question. Why evolution should not be equated with progress?
Answer : Evolution cannot be equated with progress because it seems to have just given rise to more complex body designs. For example bacteria still flourish in spite of a very simple body design while dinosaurs did not survive in spite of complex design. Thus evolution is simply the generation of diversity and shaping of diversity by environmental selection.
Short Answer Questions
Question. What is speciation? How does it occur?
Answer : Formation of new species from the existing ones over the period of time is called speciation. Speciation takes place due to gene flow, genetic drift, reproductive isolation and finally natural selection.
Question. Why are human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and looks said to belong to the same species?
Answer : Because irrespective differences in characters they have capacity of interbreeding. Interbreeding is an important criteria to categorize them as one species.
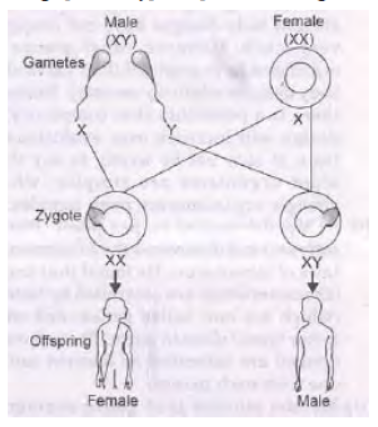
Question. “It is a matter of chance whether a couple will have a male or a female child.” Justify this statement by drawing a flow chart.
Answer : Women produce only one type of ovum (carrying X chromosome) and males produce two types of sperms (carrying either X or Y chromosome) in equal proportions. So the sex of a child is a matter of chance depending upon the type of sperm fertilizing the ovum.
Question. List three main factors responsible for the speciation and briefly describe each one of them.
Answer : Genetic Drift: Random change in the frequency of genes.
Natural Selection: Nature selects the fittest individual in a population. Reproductive Isolation: When two individuals are geographically isolated and natural selection operates upon them differently leading to inability of the individuals to interbreed.
Question. “Natural selection and speciation lead to evolution”.Justify the statement.
Answer : Natural selection: Some variations are advantageous for an organism to adapt better in the prevailing conditions of habitat. It makes it easy to obtain food and mating partner by them. In this manner they are able to propagate more, transmitting their genes to next generation and producing more individuals with similar genetic makeup and phenotype.
a. It leads to change in frequency of some genes in a population which give survival advantage to a species from elimination.
b. When most of the members of a population possess this variation, it is called its adaptation.
c. Over a period of time large numbers of adaptations are accumulated in the various populations of a species which may be physically segregated from each other.
d. Geographical barriers like mountains, rivers etc., lead to incapability to reproduce amongst themselves in the population.
e. By processes like genetic drift and natural selection combined with geographical separation, when the populations of a species become incompatible/ fail to reproduce with each other, speciation – evolution of a new species from pre-existing species – occurs.
Question. With the help of one example each, distinguish between inherited traits and acquired traits. Why are the traits acquired during the life time of an individual not inherited in the next generation? Explain the reason of this fact with an example.
or
Distinguish between inherited traits and acquired traits in a tabular form, giving one example of each.
Answer :


Question. What is evolution? How does it occur?
Answer : Organic Evolution: Gradual unfolding of organisms from pre-existing organisms through change is called evolution.
a. Evolution occurs in the form of genetic drift and natural selection combined with geographical separation.
b. Speciation – evolution of a new species from preexisting species-occurs.
c. Fossils are impressions of the body/body parts or the remains of organisms living in the past, which got preserved in sediments of earth.
d. Study of not living species but also fossils helps in working out evolutionary relationships.
e. Fossils provide one of the most acceptable evidences in support of evolution, because we can study the evolutionary past of individuals in the form of their fossils.
Question. “Two areas of study namely evolution and classification are interlinked”. Justify this statement.
Answer : All living things are identified and categorised on the basis of their body design in form and function. After a certain body design comes into existence, it will shape the effects of all other subsequent design changes simply because it already exists. So, characteristics which came into existence earlier are likely to be more basic than characteristics which have come into existence later.
This means that the classification of life forms will be closely related to their evolution. On connecting this idea of evolution to classification, it is seen that some groups of organisms with ancient body designs have not changed very much. However, other groups of organisms have acquired their particular body designs relatively recently. Because there is a possibility that complexity in design will increase over evolutionary time, it may not be wrong to say that older organisms are simpler, while younger organisms are more complex.
Question. Explain Mendel’s concept of heredity, by giving three points.
Answer :
a. Mendel worked on pea plant {Pisum sativum) and discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance. He found that traits (characteristics) are controlled by factors (which are now called genes) and each factor (gene) come in pairs. These factors (genes) are inherited as distinct units, one from each parent.
b. Mendel studied that genes segregate during the formation of gametes (sperms in males and ova in females) and they again combine in the offspring (one from each parent) and appear as dominant or recessive trait. This can be worked out by making a test cross.
c. Mendel proposed three laws, namely:
(i) Law of segregation: Each inherited trait is defined by a pair of gene. Parental genes are randomly separated to the germ-cells so that germ contain only one pair of gene.
(ii) Law of independent assortment: Genes of different traits are sorted separately from one another so that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on the inheritance of another.
(iii) Law of dominance: An organism with alternate forms of a gene will express the form that is document.
Question. From the set of figures given below, make a pair of homologous and analogous organs each and give one reason in case of both, to justify your answer.

Answer : Organs:
a. Bird wing and Bat wing – Analogous organs.
Structures are different but functions are same.
b. Human forelimb and Bird wing — Homologous organs.
Structure are same but functions are different.
Question. Why do human beings look different from each other?
What do you mean by species?
Answer : Human beings are sexually reproducing organisms.
Genetic recombination occurs during gamete formation in the sex organs followed by union of two gametes coming from two parents with different genetic combination. Thus it ensures more diversity in characteristics in terms of colour, size, and looks.
Inspite of this, they are able to reproduce among themselves to produce fertile offsprings. A species is a group of individuals which have some common characters and they are able to reproduce among themselves to produce fertile offsprings.
Question. With the help of suitable examples, explain why certain traits cannot be passed on to the next generation.
What are such traits called?
Answer :
Example: Acquiring knowledge by reading/change in body weight. Reason: Because such changes do not bring any change in the DNA of the germ cells/ such changes take place only in the non-reproductive tissues.
Traits: Acquired traits.
Question. In evolutionary terms, we can say which among bacteria, spiders, fish and chimpanzees have a better body design? Why or why not?
Answer : Evolution shows that body design changed from simple to complex. Hence, bacteria has the simplest body design and chimpanzee has the most complex and better body design.
Question. What is natural selection?
Answer : According to Darwin, natural selection is the process which brings about evolution of new species of plants and animals. It consists of the following processes: (i) He noted that the size of population tends to remain constant despite the fact that more offsprings are produced than needed. (ii) Variations provide adaptations. (iii) The best adopted survive in the changing environment (survival of the fittest). (iv) Nature selects the best organisms with better adaptations and after many generations new species are formed (natural selection).
Question. A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits–blood group A or O is dominant? Why?
Answer : The given information is not enough to tell us which of the traits-blood group A or O – is dominant. In blood heredity, bood type A is always dominant and blood type O is always recessive. Here, father’s Blood group can be IAIA (homozygous) or IAi (heterozygous) genotypically, whereas that of mother is ii.
Question. Define variation in relation to a species: Why is variation beneficial is the species.
Answer : Variations are differences that occur between the organisms of the same species in spite of the same basic features. Variation in species promotes survival of an organism in changing environment by increasing the adaptability.
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process?
Answer : If DNA copying is not perfectly accurate then the variations occurs among the species of same organisms.
Question. Describe briefly four ways in which individual with a particular trait may increase in population.
Answer : Four ways in which individual with a particular trait may increase in population are:
(a) Variations that occur in species helps in the survival of individuals.
(b) Organisms when show genetic drift which cope them to survive in the given environment.
(c) Adaptation and natural selection.
(d) Sexual reproduction results in variation.
Question. ‘‘Variations that confer an advantage to an individual organism only will survive in population’’. Justify.
Answer : Variation is the difference in the characters or traits among the individuals of a species. Sexual reproduction of organisms produces variation. The variations produced in organisms during successive generations gets accumulated in the organism. The significance of variations shows up only if it continues to be inherited by the offspring for several generation.
Question. How are the areas of study—evolution and classification—interlinked?
Answer : For c lassification of organisms we generally group the organisms of same characteristics together and those with different characteristics are grouped or classified separately. A set of characteristics tells about the level of evolution of an organism.
Question. Explain the terms analogous and homologous organs with examples.
Answer : Analogous organs—Organs with different structure and same function e.g., wings of bird, insects. Homologous organs—Organs which have same structure but different functions are called homologous organ e.g., forearm of lizard, bird and human.
Question. What are fossils? What do they tell about the process of evolution?
Answer : Fossils are preserved traces or remains of living organism of geological past. Fossils help to trace the racial history of organisms. Fossils found closer to the surface are more recent than fossils found in the deepest layers.
Question. What are fossils? What do they tell us about the process of evolution?
Answer : Preserved traces of living or dead organisms on solid hard surface is called fossil. Fossils help us to know the evolution. If a fossil is found closer to the surface of earth, then it is more recent in origin than the fossils we find in deeper layers. Fossils, like Archaeopteryx, help us to find evolutionary relation between organisms.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits–blood group A or O is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer : The given information is not enough to tell us which of the traits-blood group A or O – is dominant. In blood heredity, bood type A is always dominant and blood type O is always recessive. Here, father’s Blood group can be IAIA (homozygous) or IAi (heterozygous) genotypically, whereas that of mother is ii. For daughter to be born with blood group O, she must receive i type gene one each from father and mother. For this father must have heterozygous IAi blood group and mother must have homozygous blood group ii.
Question. How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?

Answer : In case of human beings female sex have a pair of XX chromosomes (sex) and male sex have a pair of XY sex chromosome. When the crossing of male and female gametes takes place then the sex of the child is determined as follows: This shows that the ratio of male: female sex of the child is same i.e., (1 : 1), 50% possibility of each is seen here.
Question. What are the different ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population?
Answer : The ways in which individual with a particular trait may be increased in a population are: (a) If it can survive in the adverse condition i.e., naturally selected. (b) It can also be increased by the inheritance.
Question. Why are traits acquired during the life-time of an individual not inherited?
Answer : The traits can be inherited from one generation to the other only if there is a variation/change in DNA. The traits acquired during the life-time of an individual may not bring change in the genes of DNA.
Question. Why are the small numbers of surviving tigers a cause of worry from the point of view of genetics?
Answer : The small number of tigers are causing a worry for the genetics because if they become extinct then the genes of this species will be lost forever. There will be no scope of again getting this species back to life without their genes.
Question. What factors could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer : The factors which can lead to the rise of a new species are gene flow, genetic drift, reproductive isolation and natural selection.
Question. Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species. Why or why not?
Answer : No, geographical isolation cannot be a major factor in the speciation of self-pollinating plant species. It is because such plants do not depend on other plants for its further reproduction to be carried out.
Question. Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of an organism that reproduces asexually? Why or why not?
Answer : No, because the asexually reproducing organisms does not depend on other organisms for their reproduction.
Question. Give an example of characteristics being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms.
Answer : Two organisms with similar characteristics have genes with similar DNA codes. Whereas the organisms with different characteristics will have different genes, different DNA structures.
Question. Can the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat be considered homologous organ? Why or why not?
Answer : The wing of butterfly and the wing of a bat cannot be considered homologous organs because both have different structures but same function. They have different basic structural design and developmental origin. They are analogous organism
Question. a. In which form the traits are transferred from parent to the offspring?
b. Mention the two processes that essentially J occur in sexual reproduction?
c. How the number of chromosomes is retained in a species?
Answer :
a. Chromosomes – thread like structures made up of DNA found in the nucleus.
b. Formation of gametes that involves reducing the chromosome number to half and genetic recombination.
Fusion of gametes to maintain the chromosome number characteristic of that species.
c. The original number of chromosomes becomes half during gamete formation. Hence, when the gametes combine, the original number of chromosomes gets restored in the progeny, (or same thing explained in the form of a flow chart).
Question. a. What are monohybrid and dihybrid cross?
b. How Mendel proved that tallness is the dominant trait and dwarfness is recessive in a pea plant?.
Explain with the help of a monohybrid cross.
Answer :
a. A monohybrid cross is the cross between two homozygous parents, which differ in only one contrasting trait in F2 generation ratio 3:1. A dihybrid cross is a cross between two heterozygous parents which differ in two contrasting traits. This type of cross yields a phenotypic ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 in F2 generation.
b. Mendel took pea plants with different characteristics – a tall plant and a short plant, produced progeny from them and calculated the percentage of tall or short progeny.
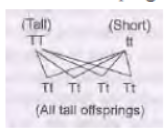
It was found that all plants were tall. This proves that tallness is the dominant trait while dwarfness is the recessive trait.
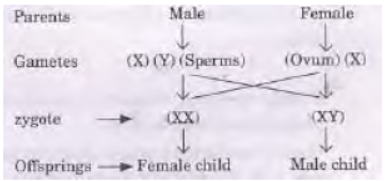
Question. Identify male and female in the figures given below.
Also fill in the blanks 3 to 8 and then clarify about the misconception that mother and not father is responsible for bearing daughters and not sons.

Answer :
1. Male 2. Female
3. X and Y 4 X and X
5. XX 6 XX
7. XY 8 XY
A child who inherits ‘X’ chromosome from father will be a girl and the one who inherits ‘Y’ chromosome from father will be a boy.
Question. What are fossils? How are they formed? Describe in brief two methods of determining the age of fossils.
State any one role of fossils in the study of the process of evolution.
Answer : Fossils are preserved remains or impressions of prehistoric organisms in the different strata of the earth’s crust.
or
Fossils are dead remains of animals and plants from remote past.
Fossils are formed when dead organisms are not completely decomposed. The organisms may get trapped in resins of tree, lava of volcanoes or hot mud which when hardens, retains the animal’s parts thus, forming fossils.
Two methods of determining the age of fossils:
a. Relative method: By estimating the age of the layer of earth’s crust where the fossil is found.
Fossils near the surface are recent and those in the deeper layers are more ancient.
b. Radio-carbon dating method: By detecting the ratios of different isotopes of carbon in the fossils.
Fossils help in determining the connecting links between various groups and their origin from their primitive ones, e.g., Archaeoptyrx.
Question. How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings? Out of these how many are sex chromosomes?
How many types of sex chromosomes are found in human beings?
“The sex of the new-born child is a matter of chance and none of the parents may be considered responsible for it”. Draw a flow chart showing determination of sex of a new-born to justify the statement.
Answer :
a. 23 pairs of chromosomes.
b. One pair, two types.
c.
Question. How do Mendel’s experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
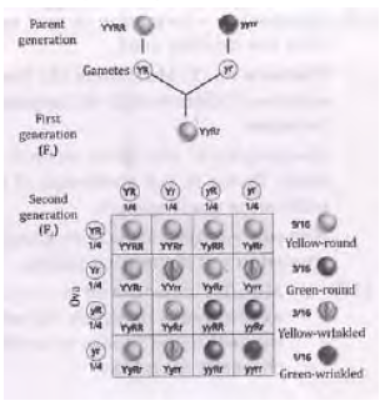
Answer : Mendel carried out dihybrid crosses by crossing two pea plants differing in contrasting traits of two characters. For example, he crossed a pea plant having yellow colour and round seed characters with another pea plant bearing green colour and wrinkled seed characters. In the F2 generation, he obtained pea plants with two parental and two recombinant phenotypes as yellow round and green wrinkled (parental) and yellow wrinkled and green round (recombinant). This indicated that traits separated from their original parental combinations and got inherited independently.
Question. a. Why do we say that homozygous plants produce pure progeny?
b. Define heterozygous.
c. Explain how the process of speciation take place.
Answer :
a. Because of presence of same set of genes.
b. Having different pair of genes.
c. (i) Natural selection.
(ii) Geographical isolation, reproductive isolation.
(iii) Genetic drift.
(iv) Accumulated variations causing changes in the DNA of germ cells to an extent, such as a change in the number of chromosomes.
Due to this, the germ cells of the two groups cannot fuse with each other. This results in the emergence of a new species.
Question. Give differences between:
a. Heredity and variations.
b. Dominant and recessive traits,
c. Natural and artificial selection.
Answer :
a. Heredity: It is the transmission of characters from parents to the next generation.
Variations: The changes that occur in the DNA of an organism because of mutations, or by chance.
b. Dominant: The trait which is able to express itself even in the presence of contrasting trait. It appears in all the progenies in Fj generation.
Recessive: The trait which can express itself only in homozygous condition. It doesn’t appear in Fj generation.
c. Natural selection: Is the gradual natural process by which any biological traits become either more or less common in a population. Example, red beetle eaten up by crow, leading to increase in the population of green beetle.
Artificial selection: It is the artificial mechanism of selecting the breeds having desirable characters to bring about major changes in plant and animals.
Example, different vegetables generated from wild variety of cabbage.
Question. a. What is geographical isolation?
b. Illustrate formation of a species with the help of an example where individuals are very different from each other and one capable of reproduction among themselves.
Answer :
a. Geographical isolation is the isolation of population by physical barriers such as stretches of water or mountain ranges.
b. There is a population of red beetles living in a mountain area covered with green bushes.
Various sub-population in the large-population exists in the neighbourhood. Individuals of a sub¬population reproduce sexually among themselves and numerous variations accumulate
in these sub-populations of red beetles.
There may be some reproduction among these sub-populations. If a beetle from one subpopulation strays into other’s area and some individuals from one sub¬population may be carried by predators to the area of other subpopulation, then random reproduction takes place. It may lead to migration of genes from one sub¬population to other.
Question. Given below is the experiment carried out by Mendel to study inheritance of two traits in garden-pea.

a. Fill in the boxes with appropriate answer.
b. Why did Mendel carry out an experiment with two traits?
c. What were his findings with respect to inheritance of traits in Fj and F2 generations?
d. What do you conclude from this experiment?
Answer :
a. Gametes – Ry, rY
F1 – RrYy
Ratio – 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
b. To study the independent inheritance of two traits in subsequent generation.
c. F1 progeny exhibited both the dominant traits.
F2 exhibited parental traits along with new mixtures/recombinants.
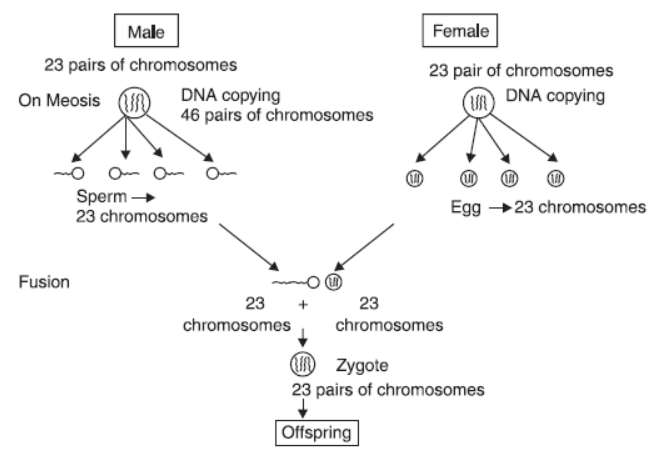
Question. Male individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes, female individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes. Then why don’t an offspring have 46 pairs of chromosomes which is obtained by the fusion of these two eggs.
Answer : Male individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes but the gamete that is formed by the meiotic cell division contain only half the number of chromosomes i.e., 23 chromosomes in male sperm and 23 chromosomes in female egg. It is the fusion of this sperm and egg which leads to an offspring with 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Question. Study the given figure and say what information it gives you.
Answer : ……………………….
Question. (i) What are traits?
(ii) Explain the inherited trait and acquired traits.
(iii) Define speciation. What are the factors which could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer : (i) Traits: A characteristic feature is called trait.
(ii) Inherited and acquired trait .
(iii) Speciation and factors .

