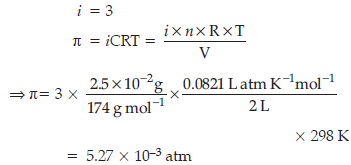See below CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Set B with solutions. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern issued by CBSE for the current academic year. All sample papers provided by our Class 12 Chemistry teachers are with answers. You can see the sample paper given below and use them for more practice for Class 12 Chemistry examination.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry Set B
Topic-1
Types of Solutions, Expression of Concentration of Solutions and Solubility
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple Choice Questions:
Question. On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid?
(a) Sugar crystals in cold water
(b) Sugar crystals in hot water
(c) Powdered sugar in cold water
(d) Powdered sugar in hot water
Answer
D
Question. The unit of ebullioscopic constant is ………….. .
(a) K kg mol–1 or K (molality)–1
(b) mol kg K–1 or K–1 (molality)
(c) kg mol–1 K–1 or K–1 (molality)–1
(d) K mol kg–1 or K (molality)
Answer
A
Question. 4L of 0.02 M aqueous solution of NaCl was diluted by adding one litre of water. The molality of the resultant solution is ………………
(a) 0.004
(b) 0.008
(c) 0.012
(d) 0.016
Answer
D
Question. Maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of a given liquid solvent does not depend upon …………… .
(a) temperature
(b) nature of solute
(c) pressure
(d) pressure of solvent
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
(a) Mole fraction
(b) Parts per million
(c) Mass percentage
(d) Molality
Answer
A
Question. A beaker contains a solution of substance ‘A’. Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is _________.
(a) saturated
(b) supersaturated
(c) unsaturated
(d) concentrated
Answer
B
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
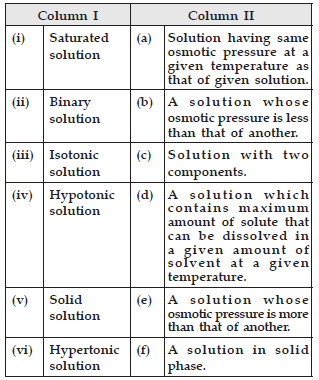
(i)-(d),(ii)-(c) ,(iii)-(a),(iv)-(b),(v)-(f),(vi)-(e)
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Calculate the molality of ethanol solution in which the mole fraction of water is 0.88.
Answer. Mole fraction of water, XH2O = 0.88
Mole fraction of ethanol, XC2H5OH = 1 – 0.88
= 0.12
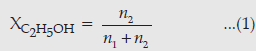
n2 = number of moles of ethanol.
n1 = number of moles of water.
Molality of ethanol means the number of moles of ethanol present in 1000 g of water.
n1 = 1000/18
= 55.5 moles
Substituting the value of n1 in equation (1)
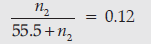
n2 = 7.57 moles ½
Molality of ethanol (C2H5OH) = 7.57 m
Alternatively,
Mole fraction of water = 0.88
Mole fraction of ethanol = 1-0.88 = 0.12
Therefore 0.12 moles of ethanol are present in 0.88 moles of water.
Mass of water = 0.88 x 18 =15.84 g of water.
Molality = number of moles of solute (ethanol)
present in 1000 g of solvent (water)
= 12 × 1000 / 15.84
= 7.57 m
Molality of ethanol (C2H5OH) = 7.57 m
Question. Explain the solubility rule “like dissolves like” in terms of intermolecular forces that exist in solutions.
Answer. A substance (solute) dissolves in a solvent if the intermolecular interactions are similar in both components. For example : polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents and non-polar solutes in nonpolar solvents thus we can say “like dissolves like”.
Question. State Henry’s law. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas in a liquid ?
Answer. The relationship between pressure and solubility is guided by Henry’s law. According to this law,
“The mass of a gas dissolved in given volume of the liquid at a constant temperature depends upon the pressure which is applied.”
It can also be stated as the partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase (p) is proportional to the molen fraction of the gas (χ) in the solution.
p = KHχ,
where KH = Henry’s constant.
Effect of Temperature on the Solubility : The solubility of a gas decreases with increase in temperature. This is because dissolution of gases in the liquids is an exothermic process. Therefore, according to Le-Chatelier’s principle, the increase in temperature results in decrease in the solubility of the gas.
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (x)
(ii) Molality of a solution (m)
Answer. (i) Mole fraction of a component = Number of moles of the component/Total number of moles of all the components
Question. State Henry’s law and mention two of its important applications.
Answer.
Applications of Henry’s Law :
(i) To increase the solubility of CO2 in soda water and soft drinks, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
(ii) At high altitude, low blood oxygen causes climber to become weak and make them unable to think clearly, which are symptoms of a condition known as anoxia.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
Answer. Let the total mass of the solution be 100 g and the
mass of benzene be 30 g.
∴ Mass of carbon tetrachloride
= (100 − 30) g = 70 g
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = (6 × 12 + 6 × 1) g mol–1 = 78 g mol–1
∴ Number of moles of C6H6 mol = 30/78
= 0.3846 mol
Molar mass of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
= 1 × 12 + 4 × 35.5 = 154 g mol–1
∴ Number of moles of CCl4 = 70/154 mol
= 0.4545 mol
Thus, the mole fraction of C6H6 is given as :
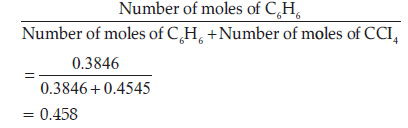
Question. The partial pressure of ethane over a saturated solution containing 6.56 × 10–2 g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution were to contain 5.0 × 10–2 g of ethane, then what will be the partial pressure of the gas ?
Answer. According to Henry’s law,
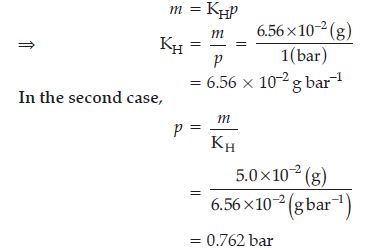
Topic-2
Vapour Pressure, Raoult’s Law, Ideal and Non-ideal Solutions
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
(a) Methanol and acetone.
(b) Chloroform and acetone.
(c) Nitric acid and water.
(d) Phenol and aniline.
Answer
A
Question. On the basis of information given below mark the correct option. Information:
(A) In bromoethane and chloroethane mixture intermolecular interactions of A–A and B–B type are nearly same as A–B type interactions.
(B) In ethanol and acetone mixture A–A or B–B type intermolecular interactions are stronger than A–B type interactions.
(C) In chloroform and acetone mixture A–A or B–B type intermolecular interactions are weaker than A–B type interactions.
(a) Solution (B) and (C) will follow Raoult’s law.
(b) Solution (A) will follow Raoult’s law.
(c) Solution (B) will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
(d) Solution (C) will show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Answer
B
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
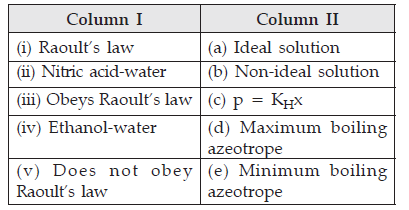
Answer. (i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(e), (v)-(b).
C. Answer the following:
Question. Some liquids on mixing form ‘azeotropes’. What are ‘azeotropes’ ?
Answer. Azeotropes : Binary mixtures having same composition in liquid and vapour phase and boil at a constant temperature.
Question. Define an ideal solution.
Answer. Solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration at specific temperature.
Question. What type of intermolecular attractive interaction exists in the pair of methanol and acetone ?
Answer. Hydrogen bonding.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. (i) Gas (A) is more soluble in water than Gas
(B) at the same temperature. Which one of the two gases will have the higher value of KH (Henry’s constant) and why ?
(ii) In non-ideal solution, what type of deviation shows the formation of maximum boiling azeotropes ?
Answer. (i) Gas B will have the higher value of KH (Henry’s constant) as lower is the solubility of the gas in the liquid higher is the value of KH.
(ii) In non-ideal solution, negative deviation shows the formation of maximum boiling azeotropes.
Question. State Raoult’s law. How is it formulated for solutions of non-volatile solutes ?
OR
Derive expression for Raoult’s law when the solute is non-volatile.
Answer. Raoult’s law for solution of non-volatile solution :
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
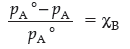
where, pA° → Vapour pressure of pure component ‘A’.
pA → Partial vapour pressure of component ‘A’
χB → Mole fraction of solute
pA° – pA → Lowering of vapour pressure
(pA° – pA)/pA° → Relative lowering of vapour pressure.
Question. State Raoult’s law for a solution containing nonvolatile solute. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by a solution of chloroform and acetone and why?
Answer. The relative lowering of vapour pressure of a solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
The vapour pressure of a solution of a non-volatile solute is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure solvent at that temperature multiplied by its mole fraction.
Negative deviation due to formation of Hydrogen bond between chloroform and acetone.
Question. Define an ideal solution and write one of its characteristics.
Answer. Solution which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration at specific temperature is known as an ideal solution.
Characteristics :
(i) ΔHmix = 0
(ii) ΔVmix = 0
Question. Explain why on addition of 1 mol of NaCl to 1 litre of water, the boiling point of water increases,while addition of 1 mol of methyl alcohol to one litre of water decreases its boiling point.
Answer. Sodium Chloride (NaCl) is a non-volatile solute, therefore, addition of NaCl to water lowers the vapour pressure of water. As a result, boiling point of water increases. Methyl alcohol on the other hand is more volatile than water, hence, its addition increases, the total vapour pressure over the solution and a decrease in boiling point of water results.
Question. What is meant by positive deviations from Raoult’s law ? Give an example. What is the sign of DmixH for positive deviation ?
Answer. In case of positive deviation from Raoult’s law, the intermolecular attractive forces between the solutesolvent molecules are weaker than those between the solute-solute and solvent-solvent molecules.
Example: Mixture of ethanol and acetone.
Sign for ΔmixH is positive
Question. State Raoult’s law for the solution containing volatile components. What is the similarity between Raoult’s law and Henry’s law ?
Answer. According to Raoult’s law for the solution containing volatile components, the partial vapour pressure of each component is directly proportional to its mole fraction.
In both case, p ∝ χ / Henry’s law is a special case of Raoult’s law.
Question. Why a mixture of Carbon disulphide and acetone shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law? What type of azeotrope is formed by this mixture?
Answer. Intermolecular forces of attraction between carbon disulphide and acetone are weaker than the pure components.
Minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B at 400 K are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively.
Find out the composition of liquid mixture if total pressure at this temperature is 600 mm Hg.
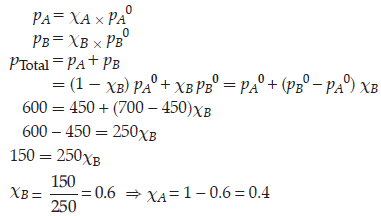
Answer.
ptotal = p1o + (p2o – p1o)x2
600 = 450 + (700 – 450) x2
x2 = 0.6
x2 = 1 – 0.6 = 0.4
Question. (a) 30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol-1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg.
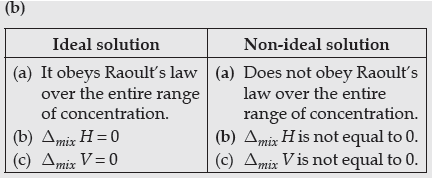
(b) Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
Answer.
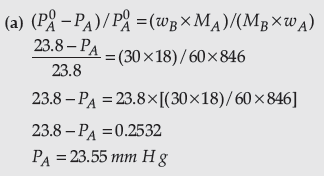
Question. Using Raoult’s law explain how the total vapour pressure over the solution is related to mole fraction of components in the following solutions.
(a) CHCl3(l) and CH2Cl2(l)
(b) NaCl(s) and H2O(l)
Answer. (a) p = p0A xA + p0B xB ; Where p0A, p0B are the vapour pressure of pure components (A) and (B) while xA xB and are the mole fractions of the components in the solution.
(b) NaCl(s) is a non-volatile solute. When it is dissolved in water, the vapour pressure is lowered. Vapour pressure of solution can be calculated using the following relations :
p = p0xa
Where, xa = mole fraction of solvent (i)
p0 = vapour pressure of pure solvent
p = vapour pressure of solution
Similarly,
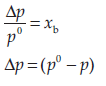
xb = mole fraction of solute (ii)
Question. Components of a binary mixture of two liquids A and B were being separated by distillation. After sometimes separation of components stopped and composition of vapour phase became same as that of liquid phase. Both the components started coming in the distillate. Explain why this happened.
Answer. Both components are appearing in the distillate and composition of liquid and vapour is same, this shows that liquids have formed azeotropic mixture.
Therefore, it cannot be separated at this stage by distillation.
Azeotropes are binary mixtures having the same composition in fluid, vapour phase and boils at a constant temperature. The components of azeotropic mixtures are separated by fractional distillation.
Topic-3
Colligative Properties, Determination of Molecular Mass, Abnormal Molecular Mass, Van’t Hoff Factor
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. We have three aqueous solutions of NaCl labelled as ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ with concentrations 0.1M, 0.01M and 0.001M, respectively. The value of van’t Hoff factor for these solutions will be in the order ………………..
(a) iA < iB < iC
(b) iA > iB > iC
(c) iA = iB = iC
(d) iA < iB > iC
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
(a) 1.0 M NaOH
(b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
(c) 1.0 M NH4NO3
(d) 1.0 M KNO3
Answer
B
Question. Colligative properties depends on ……………… .
(a) the nature of the solute particles dissolved in solution.
(b) the number of solute particles in solution.
(c) the physical properties of the solute particles dissolved in solution.
(d) the nature of solvent particles.
Answer
B
Question. An unripe mango placed in a concentrated salt solution to prepare pickle, shrivels because……………….
(a) it gains water due to osmosis.
(b) it loses water due to reverse osmosis.
(c) it gains water due to reverse osmosis.
(d) it loses water due to osmosis.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same.
(b) In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower concentration of solute to a region of higher concentration.
(c) The value of molal depression constant depends on nature of solvent.
(d) Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is a dimensionless quantity.
Answer
B
Question. The values of Van’t Hoff factors for KCl, NaCl and K2SO4, respectively are:
(a) 2, 2 and 2
(b) 2, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 1 and 2
(d) 1, 1 and 1
Answer
B
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
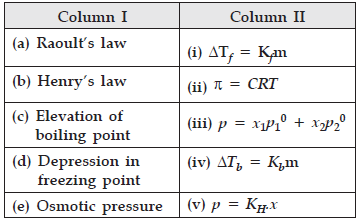
Answer. Correct option : (a)-(iii), (b)-(v), (c)-(iv),(d)-(i), (e)-(ii)
C. Answer the following :
Question. Explain boiling point elevation constant for a solvent or ebullioscopic constant.
Answer. We know that,
ΔTb = Kbm.
where m = 1, ΔTb = Kb. Thus, boiling point elevation constant is equal to the elevation in boiling point
when 1 mole of a solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. It is also called ebullioscopic constant.
Question. What is meant by term reverse osmosis ?
Answer. Reverse Osmosis : (RO) is a water purification technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove larger particles from drinking water in reverse osmosis.
Question. What are isotonic solutions ?
Answer. The solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Isotonic solutions
(ii) Van’t Hoff factor
Answer. (i) The solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
(ii) Van’t Hoff factor is expressed as :
i = Normal molecular mass/Observed molecular mass
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What are colligative properties? Write the colligative property which is used to find the molecular mass of macromolecules.
Answer. Properties that depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution.
Osmotic pressure.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Abnormal molar mass
(ii) van’t Hoff factor (i)
Answer. (i) If the molar mass calculated by using any of the colligative properties to be different than theoretically expected molar mass.
(ii) Extent of dissociation or association or ratio of the observed colligative property to calculated colligative property.
Question. Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 8.1 g of HBr in 100 g of water, assuming the acid to be 90% ionized.
[Given: Molar mass Br = 80 g/mol, Kf water = 1.86 K kg/mol]
Answer. HBr → H++ Br–
i =1 – α + nα
n = 2
i = 1 + α
ΔTf = iKfm
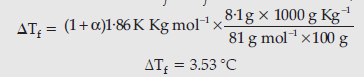
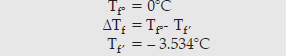
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Colligative properties
(ii) Molality (m)
Answer. (i) Properties that are independent of nature of solute and depend on number of moles of solute only.
(ii) Number of moles of solute dissolved per kg of the solvent.
Question. Explain why on addition of 1 mol glucose to 1 litre water the boiling point of water increases.
Answer. Vapour pressure of the solvent decreases in the presence of non-volatile solute (glucose) hence boiling point increases.
Question. A 1.00 molar aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid (CCl3COOH) is heated to its boiling point.
The solution has the boiling point of 100.18 °C.Determine the van’t Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. (Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1).
OR
Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor (iv) Ideal solution
Answer. ΔTb = iKbm
(373.18 – 373) K = i × 0.512 K kg mol–1 × 1 m
0.18 K = i × 0.512 K kg mol–1 × 1 m,
i = 0.35
OR
(i) Mole fraction is the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles in a mixture.
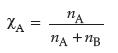
where nA = number of moles of component A.
nB = number of moles of component B.
(ii) Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor is the ratio of normal molecular mass and observed molecular mass.
(iv) Ideal solution : The solution which follows Raoult’s law over entire range of concentrations at specific temperature is called ideal solution.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Ideal solution
(ii) Molarity (M)
Answer. (i) The solution that obeys Raoults’ Law over the entire range of concentration.
(ii) Number of moles of solute dissolved per litre of
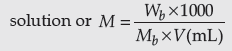
Question. What is meant by elevation in boiling point? Why is it a colligative property?
Answer. The increase in boiling point of the solvent in a solution when a non-volatile solute is added.Because it depends upon molality/the number of solute particles rather than their nature/ DTB μ m
Question. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil ?
(Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol–1, boiling point of pure water = 373.15 K)
Answer.
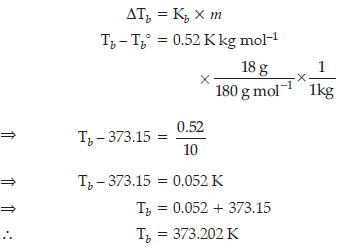
Question. Which of the following solutions has higher freezing point?
0.05 M Al2 (SO4)3, 0.1 M K3 [Fe(CN)6] Justify.
Answer. 0.05 M Al2(SO4)3 has higher freezing point.
0.05 M Al2(SO4)3 : i = 5, DTf μ No. of particles; DTf = i ´ concentration = 5´0.05 = 0.25 moles of ions
0.1 M K3[Fe(CN)6]: i = 4,
= 4 ´ 0.1 = 0.4 moles of ions
Question. Will the elevation in boiling point be same if 0.1 mol of sodium chloride or 0.1 mol of sugar is dissolved in 1L of water ? Explain.
Answer. No, the elevation in boiling point is not the same.
Elevation in boiling point is a colligative property which depends on the number of particles. NaCl is an ionic compound which dissociates in solution to give more number of particles whereas sugar is made up of covalent molecules and thus does not dissociate.
Question. Calculate the mass of compound (molar mass = 256 g mol–1) to be dissolved in 75 g of benzene to lower its freezing point by 0.48 K(Kf= 5.12 K kg mol-1).
Answer.
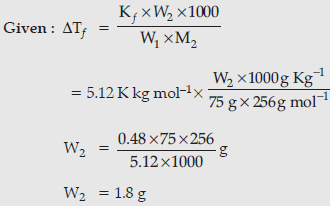
Question. Define osmotic pressure. How is the osmotic pressure related to the concentration of a solute in a solution?
Answer. The external pressure applied on the solution side to stop the flow of solvent across the semipermeable membrane i.e., osmosis is known as osmotic pressure.
The osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution i.e., π = CRT.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. 1.00 g of a non electrolyte solute when dissolved in 50 g of benzene lowered the freezing point of benzene by 0.40 K. Find the molar mass of the solute.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol–1)
Answer.
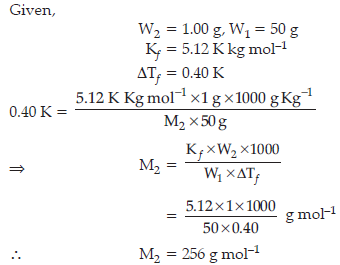
Question. Calculate the freezing point of an aqueous solution containing 10.5 g of Magnesium bromide in 200 g of water, assuming complete dissociation of Magnesium bromide. (Molar mass of Magnesium bromide = 184 g mol–1, Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1).
Answer.
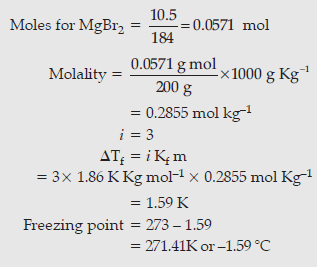
Question. Give reasons for the following :
(a) Measurement of osmotic pressure method is preferred for the determination of molar masses of macromolecules such as proteins and polymers.
(b) Aquatic animals are more comfortable in cold water than in warm water.
(c) Elevation of boiling point of 1 M KCl solution is nearly double than that of 1 M sugar solution.
Answer. (a) As compared to other colligative properties, its magnitude is large even for very dilute solutions / macromolecules are generally not stable at higher temperatures and polymers have poor solubility / pressure measurement is around the room temperature and the molarity of the solution is used instead of molality.
(b) Because oxygen is more soluble in cold water or at low temperature.
(c) Due to dissociation of KCl / KCl (aq) → K+ + Cl–, i is nearly equal to 2.
Question. The freezing point of benzene decreases by 2.12 K when 2.5 g of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) is dissolved in 25 g of benzene. If benzoic acid forms a dimer in benzene, calculate the van’t Hoff factor and the percentage association of benzoic acid. (Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1)
Answer.
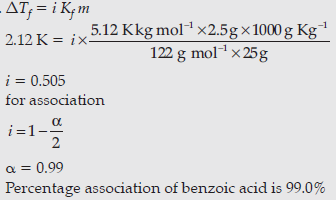
Question. A solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol-1) in water has a boiling point of 100.200C. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. Molal constants for water Kf and Kb are 1.86 K kg mol-1 and 0.512 K kg mol-1 respectively.
Answer. Given: Tb of glucose solution = 100.200C
ΔTb = Kb. m
m = 0.20/0.512
m = 0.390 mol/kg
ΔTf = Kf . m
ΔTf = 1.86 K kg/mol × 0.390 mol/kg
ΔTf = 0.725 K
Freezing point of solution = 273.15 – 0.725
= 272.425 K
Question. Give reasons for the following:
(a) When 2g of benzoic acid is dissolved in 25 g of benzene, the experimentally determined molar mass is always greater than the true value.
(b) Mixture of ethanol and acetone shows positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
(c) The preservation of fruits by adding concentrated sugar solution protects against bacterial action.
Answer. (a) Molecules of benzoic acid dimerise in benzene, the number of particles are reduced.
(b) The intermolecular interactions between ethanol and acetone are weaker/ the escaping tendency of ethanol and acetone molecules increases on mixing / the vapour pressure increases.
(c) Due to osmosis, a bacterium on fruit loses water, shrivels and dies.
Question. Calculate the amount of KCl which must be added to 1 kg of water so that the freezing point is depressed by 2 K. (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer. Since one mole of KCl gives 2 mole particles, the value of
i = 2
ΔTf = 2K
Kf = 1.86K kg mol–1
Applying equation, Tf = iKf m
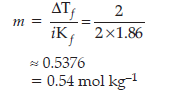
Therefore, 0.54 mole of KCl should be added to one kg of water.
Question. 45 g of ethylene glycol (C2H4O2) is mixed with 600 g of water. Calculate
(i) the freezing point depression and
(ii) the freezing point of the solution
(Given : Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer.
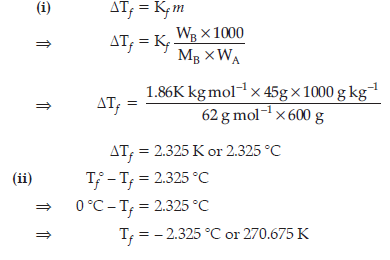
Question. At 25°C, the saturated vapour pressure of water is 3.165 k Pa (23.75 mm Hg) Find the saturated vapour pressure of a 5% aqueous solution of urea (carbamide) at the same temperature. (Molar mass of urea = 60.05 g mol–1)
Answer.
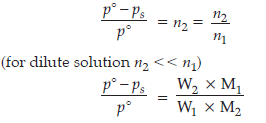
Given p° = 3.165 k Pa, W2 = 5 g, W1 = 95 g
M2 = 60.05 g mol–1, M1 = 18 g mol–1
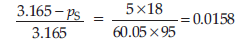
⇒ 3.165 – pS = 0.049
⇒ pS = 3.116 k Pa
Question. A 5 percent solution (by mass) of cane-sugar (M.W. 342) is isotonic with 0.877% solution of substance X. Find the molecular weight of X.
Answer.
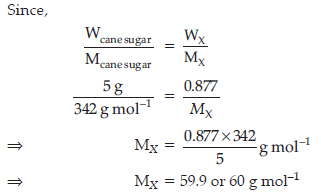
Question. Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 60 g of glucose (Molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in 250 g of water. (Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)]
Answer.
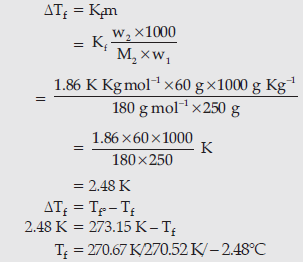
Question. A solution is prepared by dissolving 10 g of nonvolatile solute in 200 g of water. It has a vapour pressure of 31.84 mm Hg at 308 K. Calculate the molar mass of the solute.
(Vapour pressure of pure water at 308 K = 32 mm Hg)
Answer.
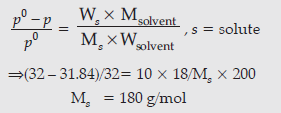
Question. 3.9 g of benzoic acid dissolved in 49 g of benzene shows a depression in freezing point of 1.62 K.
Calculate the van’t Hoff factor and predict the nature of solute (associated or dissociated).
(Given : Molar mass of benzoic acid = 122 g mol–1,Kf for benzene = 4.9 K kg mol–1)
Answer.
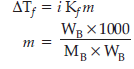
ΔTf = Depression in freezing point = 1.62
i = van’t Hoff factor
Kf = constant = 4.9
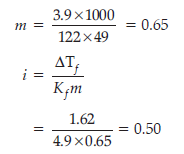
∴ i = 0.50
As the value of i < 1, the solute is associated.
Question. Calculate the boiling point of a 1M aqueous solution (density 1.04 g mL–1) of Potassium chloride (Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol–1, Atomic masses : K = 39 u, Cl = 35.5 u). Assume, Potassium chloride is completely dissociated in solution.
Answer. Molar mass of KCl = 39 + 35.5 = 74.5 g mol–1
As KCl dissociates completely, number of ions produced are 2.
Therefore, van’t Hoff factor, i = 2
Mass of KCl solution = 1000 × 1.04 = 1040 g
Mass of solvent = 1040 – 74.5 = 965.5 g = 0.9655 kg
Molality of the solution :
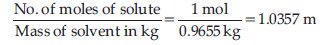
ΔTb = i × Kb × m
= 2 × 0.52 × 1.0357 = 1.078° C
Therefore, boiling point of solution
= 100 + 1.078 = 101.078°C
Question. Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 2.5 × 10–2 g of K2SO4 in 2L of water at 25°C, assuming that it is completely dissociated.
(R = 0.0821 L atm K–1 mol–1, molar mass of K2SO4 = 174 g mol–1)
Answer. When K2SO4 is dissolved in water, ions are produced.
Total number of ions produced = 3