Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry The Solid State Chapter 1 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 1 The Solid State Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
The Solid State Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following cannot be regarded as molecular solid ?
(i) SiC (Silicon carbide) (ii) AlN
(iii) Diamond (iv) I2
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. The edge lengths of the unit cells in terms of the radius of spheres constituting fcc, bcc and simple cubic unit cell are respectively ________.
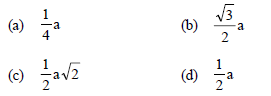
Answer
A
Question. Crystals can be classified into basic crystal units, equal to
(a) 7
(b) 4
(c) 14
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question. How many three dimensional crystal lattice are possible?
(a) 20
(b) 7
(c) 14
(d) 10
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following arrangements octahedral voids are formed ?
(i) hcp (ii) bcc
(iii) simple cubic (iv) fcc
(a) (i), (ii)
(b) (i), (iv)
(c) (iii) (d) (ii), (iv)
Answer
B
Question. In face-centred cubic lattice, a unit cell is shared equally by how many unit cells
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not the characteristic of ionic solids?
(a) Very low value of electrical conductivity in the molten state.
(b) Brittle nature.
(c) Very strong forces of interactions.
(d) Anisotropic nature.
Answer
A
Question. A ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field because ________.
(a) all the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field.
(b) all the domains get oriented in the direction opposite to the direction of magnetic field.
(c) domains get oriented randomly.
(d) domains are not affected by magnetic field.
Answer
A
Question. Tetragonal crystal system has the following unit cell dimensions
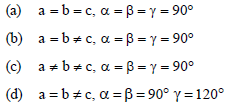
Answer
C
Question. The number of atoms contained in a fcc unit cell of a monoatomic substance is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
C
Question. In face-centred cubic lattice, a unit cell is shared equally by how many unit cells
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer
C
Question. The number of atoms per unit cell of bcc structure is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
B
Question. Silicon doped with electron – rich impurity forms _______.
(a) p-type semiconductor
(b) n-type semiconductor
(c) intrinsic semiconductor
(d) insulator
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following oxides behaves as conductor or insulator depending upon temperature ?
(a) TiO
(b) SiO2
(c) TiO3
(d) MgO
Answer
C
Question. When molten zinc is converted into solid state, it acquires hcp structure. The number of nearest neighbours of Zn will be
(a) 6
(b) 12
(c) 8
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. In which of the following crystals alternate tetrahedral voids are occupied?
(a) NaCl
(b) ZnS
(c) CaF2
(d) Na2O
Answer
B
Question. Schottky defect generally appears in :
(a) NaCl
(b) KCl
(c) CsCl
(d) all of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a crystalline solid?
(a) KCl
(b) CsCl
(c) Glass
(d) Rhombic S
Answer
C
Question. Which defect causes decrease in the density of crystal
(a) Frenkel
(b) Schottky
(c) Interstitial
(d) F – centre
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following metal(s) show(s) hexagonal close packed structure (hcp) and which show face centred cubic (fcc) structure?
hcp fcc
(a) Ag, Zn Mg, Cu
(b) Mg, Zn Ag, Cu
(c) Cu, Fe Al, Sn
(d) Na, Li Zn, Cu
Answer
B
Question. Silver crystallises in f.c.c. Lattice. It edge length of the unit cells is 4.07 × 10–8 cm density and is 10.5g cm–3. Calculate the atomic mass of silver.
(A) 144 g/mol
(B) 125 g/mol
(C) 106.6 g/mol
(D) 213 g/mol
Answer
C
Question. Graphite cannot be classified as __________.
(A) Conducting solid
(B) Network solid
(C) Covalent solid
(D) Ionic solid
Answer
D
Question. Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are dropped under the curved lattice of metals. Whether the following is not the characteristics property of interstitial compounds?
(A) They have high melting points in to pure metals
(B) They are very hard
(C) They retain metallic Conductivity
(D) They are chemically very reactive
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
(A) Graphite (G)
(B) Quartz glass (SiO2)
(C) Chrome alum
(D) Silicon carbide (SiC)
Answer
B
Question. The sharp melting point of crystalline solids is due to ___________.
(A) a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a short distance in the crystal lattice.
(B) a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a long distance in the crystal lattice.
(C) same arrangement of constituent particles in different directions.
(D) different arrangements of constituent particles in different directions.
Answer
B
Question. Solid A is very hard electrical insulator in solid as well as in molten state and melts at an extremely high temperature. What type of solid is it?
(A) Ionic solid
(B) Molecular solid
(C) Covalent solid
(D) Metallic solid
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following conditions favours the existence of a substance in the solid state?
(A) High temperature
(B) Low temperature
(C) High thermal energy
(D) Weak cohesive forces
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a network solid?
(A) SO2 (solid)
(B) I2
(C) Diamond
(D) H2O (ice)
Answer
C
Question. What is the coordination number in a square close packed structure in two dimensions?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 6
Answer
C
Question. The total number of tetrahedral voids in the face centred unit cell is _____.
(A) 6
(B) 8
(C) 10
(D) 12
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not true about the ionic solids?
(A) Bigger ions form the close packed structure.
(B) Smaller ions occupy either the tetrahedral or the octahedral voids depending upon their size.
(C) Occupation of all the voids is not necessary.
(D) The fraction of octahedral or tetrahedral voids occupied depends upon the radii of the ions occupying the voids.
Answer
B
Question. The lattice site in a pure crystal cannot be occupied by…………………..
(A) Molecule
(B) Ion
(C) Electron
(D) Atom
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not true about the hexagonal close packing?
(A) The coordination number is 12.
(B) It has 74% packing efficiency.
(C) Tetrahedral voids of the second layer are covered by the spheres of the third layer.
(D) In this arrangement spheres of the fourth layer are exactly aligned with those of the first layer.
Answer
D
Question. Examine the given defective crystal
A+ B– A+ B– A+
B– 0 B– A+ B–
A+ B– A+ 0 A+
B– A+ B– A+ B–
How is the density of the crystal affected by this defect?
(A) Density increases
(B) Density decreases
(C) No effect on density
(D) Density first increases then decreases
Answer
B
Question. In which of the following structures coordination number for cations and anions in the packed structure will be same?
(A) Cl– ion form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all octahedral voids of the unit cell.
(B) Ca2+ ions form fcc lattice and F– ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
(C) O2– ions form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
(D) S2– ions form fcc lattice and Zn2+ ions go into alternate tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
Answer
A
Question. A compound is formed by two elements M and N. The element N forms ccp lattice and atoms of M occupy two atoms an Mercury 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound
(A) MN2
(B) M2N3
(C) M3N2
(D) M2N2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is not true about amorphous solids?
(A) On heating they may become crystalline at certain temperature.
(B) They may become crystalline on keeping for long time.
(C) Amorphous solids can be moulded by heating.
(D) They are anisotropic in nature.
Answer
D
Question. The crystal showing defect is:


Answer
A
Question. The correct order of the packing efficiency in different types of unit cells is ________.
(A) fcc < bcc < simple cubic
(B) fcc > bcc > simple cubic
(C) fcc < bcc > simple cubic
(D) bcc < fcc = simple cubic
Answer
B
Question. The lattice site in a pure crystal cannot be occupied by __________.
(A) Molecule
(B) Ion
(C) Electron
(D) Atom
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following Defects is also known as dislocation defect?
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Schottky defect
(C) Non-stoichiometric defect
(D) Simple interstitial defect
Answer
A
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false and R is True
Question. Assertion (A): Total number of octahedral voids present in unit cell of cubic packing including the one that is present at the body centre is four.
Reason (R): Besides the body centre these is one octahedral void present at the centre of each of the 4 faces of the unit cell and each of which is shared between two adjacent unit cells.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Amorphous solids possess a longrange order in the arrangement of their particles.
Reason (R): The formation of amorphous solids involves very rapid cooling.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Schottky defect arises when a non-ionic solid is heated.
Reason (R): It happens because some of the lattice sites are vacant in the crystal.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Density of the crystal decreases in Frenkel defect.
Reason (R): In this defect, one of the ion is missing from lattice position and occupies interstitial site.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Graphite is a good conductor of electricity; however, diamond belongs to the category of insulators.
Reason (R): Graphite is soft in nature, on the other hand diamond is very hard and brittle.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): The packing efficiency of simple cubic lattice is 52.4%.
Reason (R): The number of atoms per unit cell is 2.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Most of the solids possess high melting point.
Reason (R): They have strong intermolecular forces of attraction.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): A two dimensional arrangement where each sphere is in contact with four of its neighbour and has a 2-D coordination number 4 is square close packing arrangement.
Reason (R): In such arrangement, if centres of the neighbouring spheres are joined, a square is formed.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature.
Reason (R): Some of their physical properties show same electrical and optical properties in different directions in the same crystal.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): The packing efficiency is maximum for the fcc structure.
Reason (R): The coordination number is 12 in fcc structure.
Answer
B
CASE-BASED MCQs
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice.
Question. Name the non-stoichiometric point defect responsible for colour in alkali metal halides.
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Interstitial defect
(C) Schottky defect
(D) F-centres
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements not true for the amorphous and crystalline solids?
(A) Amorphous solids are isotropic and crystalline solids are anisotropic.
(B) Amorphous solids are short range order and crystalline solids are long range order.
(C) Amorphous solids melt at characteristic temperature while crystalline solids melt over a range of temperature.
(D) Amorphous solids have irregular shape and crystalline solids have a geometrical shape.
Answer
C
Question. What type of structure is formed by this arrangement?
(A) ccp
(B) hcp
(C) ccp/fcc
(D) none of the above
Answer
C
Question. What is the total volume of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell of a metal? (r is atomic radius).
(A) 16/3 pr3
(B) pr3
(C) 24/3 pr3
(D) 12/3 pr3
Answer
A
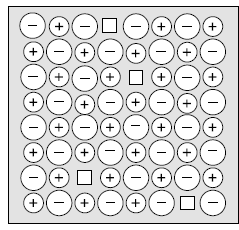
2. Study the diagram given below and answer the following questions:
In these questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false and R is True
Question. Assertion (A): AgCl shows Frenkel defect while NaCl does not.
Reason (R): Frenkel defect is shown when anionic vacancies are occupied by unpaired electrons.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): LiCl Crystal is pink.
Reason (R): Pink colour of LiCl crystal is due to excess Lithium.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): The diagram shows Schottky defect.
Reason (R): Schottky defect occurs in ionic solids.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): The crystal lattice density increases due to the defect shown in the diagram.
Reason (R): Tetrahedral voids are surrounded by 4 constituent particles.
Answer
D
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. A solid with high electrical and thermal conductivity is
(a) Si
(b) Li
(c) NaCl
(d) Ice
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following type of solid has high melting point and do not conduct electricity but its aqueous solution and melt conduct electricity ?
(a) Covalent
(b) Ionic
(c) Molecular
(d) Metallic
Answer
B
Question. A substance AxBy crystallizes in a face centred cubic (fcc) lattice in which atoms ‘A’ occupy each corner of the cube and atoms ‘B’ occupy the centres of each face of the cube. Identify the correct composition of the substance AxBy
(a) AB3
(b) A4B3
(c) A3B
(d) Composition can’t be specified
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following features are not shown by quartz glass ?
(i) This is a crystalline solid.
(ii) Refractive index is same in all the directions.
(iii) This has definite heat of fusion.
(iv) This is also called super cooled liquid.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) only
Answer
A
Question. If ‘a’ stands for the edge length of the cubic systems : simple cubic, body centred cubic and face centred cubic, then the ratio of radii of the spheres in these systems will be respectively,
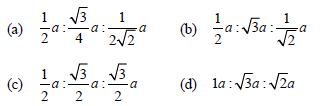
Answer
A
Question. Na and Mg crystallize in bcc and fcc type crystals respectively, then the number of atoms of Na and Mg present in the unit cell of their respective crystal is
(a) 4 and 2
(b) 9 and 14
(c) 14 and 9
(d) 2 and 4
Answer
D
Question. In a cubic lattice A atom occupy all the corners. If B atom occupy one of the opposite face, and atom C occupy the remaining faces. The simplest formulae of the compound is
(a) ABC3
(b) ABC2
(c) ABC
(d) AB2C
Answer
B
Question. A group 1 hydride crystal when heated in presence of its constituent metal vapour shows pink color. This metal can be
(a) Na
(b) K
(c) Rb
(d) Li
Answer
D
Question. A solid has a structure in which ‘W’ atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice ‘O’ atoms at the centre of edges and Na atoms at the centre of the cube. The formula for the compound is
(a) Na2WO3
(b) Na2WO2
(c) NaWO2
(d) NaWO3
Answer
D
Question. Al (at. wt 27) crystallizes in the cubic system with a cell edge of 4.05 Å . Its density is 2.7 g per cm 3 . Determine the unit cell type calculate the radius of the Al atom
(a) fcc, 2.432 Å
(b) bcc, 2.432 Å
(c) bcc, 1.432 Å
(d) fcc, 1.432 Å
Answer
D
Question. Potassium crystallizes with a
(a) body-centred cubic lattice
(b) face-centred cubic lattice
(c) simple cubic lattice
(d) orthorhombic lattice
Answer
A
Question. In a compound, atoms of element Y form ccp lattice and those of element X occupy 2/3rd of tetrahedral voids. The formula of the compound will be
(a) X4Y3
(b) X2Y3
(c) X2Y
(d) X3Y4
Answer
A
Question. A compound MpXq has cubic close packing (ccp) arrangement of X. Its unit cell structure is shown below. The empirical formula of the compound is
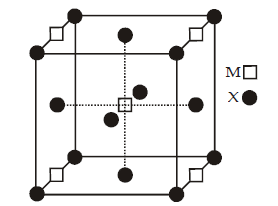
(a) MX
(b) MX2
(c) M2X
(d) M5X14
Answer
B
Question. The number of carbon atoms per unit cell of diamond unit cell is :
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 1
(d) 4
Answer
A

