Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Chapter 12 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Compounds A and C in the following reaction are
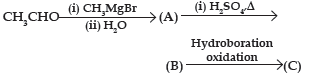
(A) identical
(B) positional isomers
(C) functional isomers
(D) optical isomers
Answer
B
Question. What kind of compounds undergo Cannizzaro reaction?
(A) Ketones with no α- hydrogen
(B) Aldehydes with α- hydrogen
(C) Carboxylic acids with α- hydrogen
(D) Aldehydes with no α- hydrogen
Answer
D
Question. Write the product(s) in the following reactions:
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution ?
(A) Butan-1-ol
(B) Butan-2-ol
(C) Both of these
(D) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The reagent which does not react with both,acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde.
(A) Sodium hydrogen sulphite
(B) Phenyl hydrazine
(C) Fehling’s solution
(D) Grignard reagent
Answer
C
Question. Write the IUPAC name of

(A) 1-Aminopropanaldehyde
(B) 2-Aminopropanal
(C) 1-Aminoethan-1-al
(D) None of the above
Answer
B
Question.
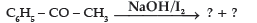
(A) C6H5COOH + CH4
(B) C6H5COONa + CHI3
(C) C6H6 + CH3COONa + HI
(D) C6H5CH2COOH
Answer
B
Question. The reaction in which the aqueous solution of sodium salt of carboxylic acids on electrolysis give alkanes:
(A) Soda lime decarboxylation
(B) Kolbe’s electrolysis decarboxylation
(C) Dry distillation of calcium formate
(D) Reduction of carboxylic acid.
Answer
B
Question. In Clemmensen reduction, carbonyl compound is treated with _________.
(A) zinc amalgam + HCl
(B) sodium amalgam + HCl
(C) zinc amalgam + nitric acid
(D) sodium amalgam + HNO3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions ?

Answer
A
Question. Complete the following reaction:

Answer
C
Question. Common name of Ethane-1,2-dioic acid is known as:
(A) Oxalic acid
(B) Phthalic acid
(C) Adipic acid
(D) Acetic acid
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following acids does not form anhydride ?
(A) Formic acid
(B) Acetic acid
(C) Propionic acid
(D) n-butyric acid
Answer
A
Question. Identify the name of the given reaction:
(A) Etard reaction
(B) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(C) Stephen reaction
(D) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Predict the product of the following reaction:
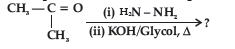
(A) CH3CH2CH3
(B) CH3CHOHCH3
(C) CH3CH2CHO
(D) CH3CONHCH3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the strongest acid?
(A) Acetic acid
(B) Phenol
(C) Methyl alcohol
(D) Water
Answer
A
Question. The carboxylic acid that does not undergo HVZ reaction is:
(A) CH3COOH
(B) (CH3)2CHCOOH
(C) CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH
(D) (CH3)3CCOOH
Answer
D
Question. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of acid strength
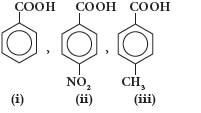
(A) (i) > (ii) > (iii)
(B) (ii) < (i) < (iii)
(C) (iii) < (i) < (ii)
(D) (iii) > (i) > (ii)
Answer
C
Question. Formaldehyde reacts with methyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis to form:
(A) Methanol
(B) Ethanol
(C) Propanol
(D) Butanol
Answer
B
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror.
Reason (R): Both aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Benzaldehyde is less reactive than ethanal towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
Reason (R): Ethanal is more sterically hindered.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Aromatic carboxylic groups do not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
Reason (R): Carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel-craft’s reaction.
Reaction (R): The carboxyl group is activating group and undergo electrophilic substitution reaction.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizzaro reaction.
Reason (R): Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Oxidation of ketones is easier than aldehydes.
Reason (R): C–C bond of ketones is stronger than C–H bond of aldehydes.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols.
Reason (R): Phenols are ortho and para directing.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Compounds containing —CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason (R): Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4.
Answer
B
Case-based MCQs
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
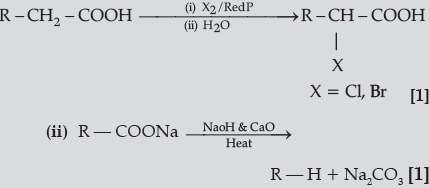
Carboxylic acids having an a-hydrogen atom when treated with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus gives a-halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
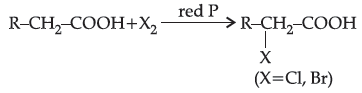
When sodium salt of carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime it loses carbon dioxide and gives hydrocarbon with less number of C-atoms.

In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is NOT correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): H.V.Z. reaction involves the treatment of carboxylic acids having a-hydrogens with Cl2 or Br2 in presence of small amount of red phosphorus.
Reason (R): Phosphorus reacts with halogens to form rhosphorus trihalides.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): (CH3)3CCOOH does not give H.V.Z. reaction.
Reason (R): (CH3)3CCOOH does not have a-hydrogen atom
Answer
A
Question.Assertion (A): On heating 3-methylbutanoic acid with soda lime, isobutane is obtained.
Reason (R): Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH + CaO in the ratio 3:1.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): C6H5COCH2COOH undergoes decarboxylation easily than C6H5COCOOH.
Reason (R): C6H5COCH2COOH is a b-keto acid.
Answer
A
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids are few of the major classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl group. Aldehydes are prepared by dehydrogenation or controlled oxidation of primary alcohols and controlled or selective reduction of acyl halides. Ketones are prepared by oxidation of secondary alcohols and hydration of alkynes.
Carboxylic acids are prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohols, aldehydes and alkenes by hydrolysis of nitriles and by treatment of Grignard reagents with carbon dioxide.
Question. How will you distinguish between aliphatic aldehydes and aromatic aldehydes ?
(A) Fehling’s test
(B) Benedict’s test
(C) Iodoform test
(D) Hinsberg reagent
Answer
A
Question. Name a method by which both aldehydes and ketones can be prepared.
(A) Reduction of carboxylic acids
(B) Ozonolysis of alkenes
(C) Oxidation of alcohols
(D) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
(A) Sodium hydrogensulphite
(B) Phenyl hydrazine
(C) Fehlings’ solution
(D) Grignard reagent
Answer
C
Question. Name the main compounds A and B formed in the following reaction:
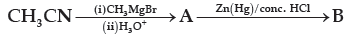
(A) CH3CH2COOH [A], CH3CH2CH3 [B]
(B) CH3CH2CHO [A], H2H4 [B]
(C) CH3COCH3 [A], CH3CH2CH3 [B]
(D) CH3COCH3 [A], C2H6 [B]
Answer
C
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Reductive alkylation is the term applied to the process of introducing alkyl groups into ammonia or a primary or secondary amine by means of an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a reducing agent. The present discussion is limited to those reductive alkylations in which the reducing agent is hydrogen and a catalyst or “nascent” hydrogen, usually from a metal acid combination; most of these reductive alkylations have been carried out with hydrogen and a catalyst. The principal variation excluded is that in which the reducing agent is formic acid or one of its derivatives; this modification is known as the Leuckart reaction. The process of reductive alkylation of ammonia consists in the addition of ammonia to a carbonyl compound and reduction of the addition compound or its dehydration product. The reaction usually is carried out in ethanol solution when the reduction is to be effected catalytically:

Since the primary amine is formed in the presence of the aldehyde it may react in the same way as ammonia, yielding an addition compound, a Schiff’s base (RCH= NCH2R) and finally, a secondary amine. Similarly, the primary amine may react with the imine, forming an addition product which also is reduced to a secondary amine Finally, the secondary amine may react with either the aldehyde or the imine to give products which are reduced to tertiary amines.
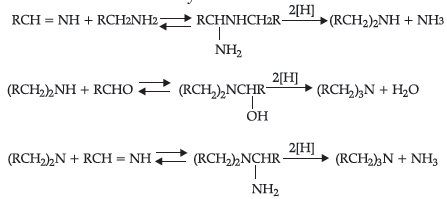
Similar reactions may occur when the carbonyl compound employed is a ketone.
Question.
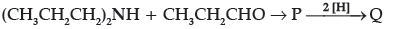
The compound Q is:
(A) (CH3CH2CH2)3N
(B) (CH3CH2CH2)2N(CH2CH3)
(C) (CH3CH2)3N
(D) (CH3CH2)2NH
Answer
A
Question. Acetaldehyde is reacted with ammonia followed by reduction in presence of hydrogen as a catalyst.The primary amine so formed further reacts with acetaldehyde. The Schiff’s base formed during the reaction is:
(A) CH3CH=NHCH3
(B) CH3CH=NHCH2CH3
(C) CH3=NHCH2CH3
(D) CH3CH2CH=NHCH3
Answer
B
Question. Ethanal on reaction with ammonia forms an amine (X) which on reaction with nascent hydrogen gives (Y). Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
(A) X is CH3CH=NH and Y is CH3NH2
(B) X is CH3CHOHNH2 and Y is CH3CH2NH2
(C) X is CH3CHOHNH2 and Y is CH3NH2
(D) X is CH3CH=NH and Y is CH3CH2NH2
Answer
D
Question. The reaction of ammonia and its derivatives with aldehydes is called:
(A) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(B) Electrophilic substitution reaction
(C) Nucleophilic addition reaction
(D) Electrophilic addition reaction
Answer
C
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Ketones are less reactive than aldehydes Why?
Answer. Ketones are less reactive than aldehydes due to following facts :
(i) Electron releasing effect
In ketones, the carbonyl carbon is attached to alkyl groups which are electron releasing in nature. These alkyl groups push electrons towards carbonyl carbon and therefore, decrease the magnitude of positive charge on it and make it less reactive toward nucleophilic attack.
(ii) Steric effect
In ketones, the presence of two bulky alkyl groups also hinders the approach of the nucleophile to the carbonyl carbon.
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of
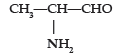
(ii) Draw the structure of 3-methylpentanal.
Answer. (i) 2-Aminopropanal.
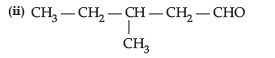
Question. (i) (CH3)3C–CHO does not undergo aldol condensation. Comment.
(ii) Out of CH3CH2COCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2 COCH3, which gives iodoform test.
Answer. (i) No a-H is present.
(ii) CH3CH2CH2COCH3 will give iodoform test as it has a terminal ketomethyl group.
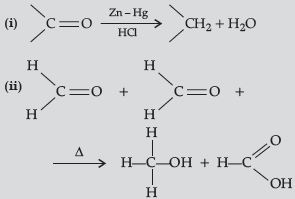
Question. Write the reactions involved in the following reaction :
(i) Clemmensen reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer.
Question. (i) Draw the resonating structures of carboxylic acid.
(ii) Carboxylic acids behave as fairly strong acids. Comment.
Answer.
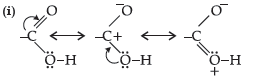
(ii) Carboxylic acids are quite strong acids due to the presence of polar O–H group. They ionize to give H+ ions and therefore, behave as acids.
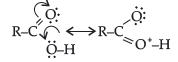
Carboxylic acids as well as carboxylate ion both are stabilised by resonance.
Question. Write structures of main compounds A and B in each of the following reactions :
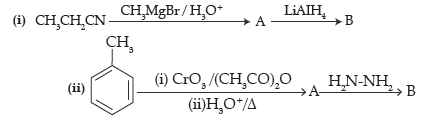
Answer. A ⇒ CH3CH2CO-CH3, B ⇒ CH3CH2–CH(OH)–CH3
A ⇒ C6H5CHO, B ⇒ C6H5–CH=N–NH2
Question. (i) What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro reaction?
(ii) An aromatic organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C8H8O gives positive DNP and iodoform tests. It neither reduces Tollens’ reagent nor does it decolourise bromine water. Write the structure of ‘A’.
Answer. (i) Having no a-hydrogen.
(ii) C6H5COCH3
Question. Write structures of main compounds A and B in each to the following reactions:
Answer. (a) A = CH3CHO B= CH3CH(OH)OCH3
(b) A and B = CHI3, C6H5COONa
Question. Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
Answer.
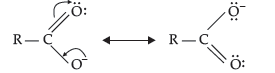

(i) Phenoxide ion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is at the lesser electronegative carbon atom whereas in case of carboxylate ion both the resonating structures are equivalent.
(ii) The negative charge is delocalised over two electronegative oxygen atoms in carboxylate ion whereas in phenoxide ion, the negative charge less effectively delocalises over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atoms. So, the carboxylate ion is more resonance stabilised than phenoxide ion. Thus, the release of proton from carboxylic acid is much easier than from phenol. Hence, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
Question. Write the equations involved in the following reactions :
(i) Wolff-Kishner reduction
(ii) Etard reaction.
Answer.

Question. Write the reactions involved in the following :
(i) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(ii) Decarboxylation reaction
Answer.(i)
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of
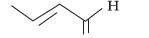
(ii) Write the IUPAC name of the following :
CH3 – CH2 – CHO
Answer.
IUPAC name = But-2-enal
(ii) Propanal.
Question. (i) What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizzaro reaction ?
(ii) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated :
(a) CH3COCH3, C6H5COCH3, CH3CHO (reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction)
(b) Cl – CH2 – COOH, F – CH2 – COOH, CH3 –COOH (acidic character)
Answer. (i) Having no a – hydrogen
(ii) (a) C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(b) CH3COOH < Cl – CH2 – COOH < F – CH2 –COOH
Question. How will you convert the following :
(a) Propanone to propan-2-ol
(b) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
Answer.

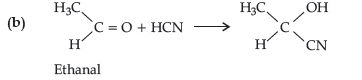
Question. Do the following conversions in not more that two steps:
(i) Propene to Acetone
(ii) Propanoic acid to 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
Answer.

Question. Write structures of compound A and B in each of the following reactions:
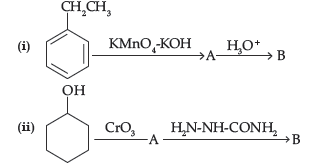
Answer.
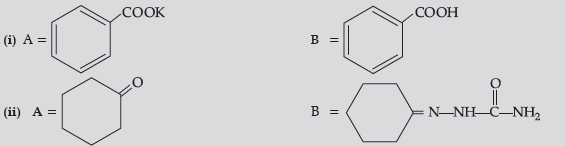
Question. Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
(b) Propanal and Propanone
Answer. (a) Benzoic acid reacts with NaHCO3 to give brisk effervescence of CO2 while benzaldehyde does not.
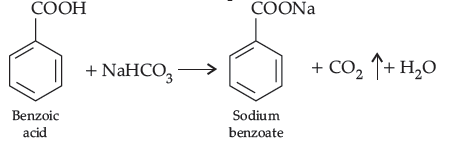
(b) Propanal being aldehyde when heated with Tollens’ reagent to give silver mirror but propanone being a ketone does not.
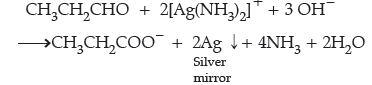
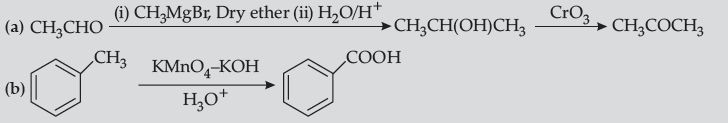
Question. How do you convert the following ?
(a) Ethanal to Propanone
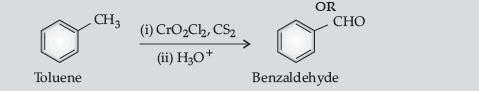
(b) Toluene to Benzoic acid
Answer.
Question. Write chemical equations for the following reactions :
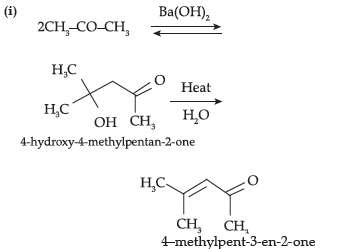
(i) Propanone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2.
(ii) Acetophenone is treated with Zn(Hg)/ Conc.
Answer.

Question. Account for the following :
(a) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(b) pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
Answer. (a) because the carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
(b) Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group (-I effect) so it stabilizes the carboxylate anion and strengthens the acid / Due to the presence of an electron withdrawing nitro group (-I effect).
Question. Write structures of main compounds A and B in each of the following reactions :

Answer. (i) A = C6H5COCl, B = C6H5CHO
(ii) A= CH3COCH3, B = CH3CH2CH3
Question. Which bond C–OH or CO–H of carboxylic acid is broken when
(i) Acid reacts with alcohol
(ii) Acid reacts with Sodium
Answer. (i) C–OH
(ii) CO–H
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Do the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Ethyl benzene to benzoic acid
(iii) Propanone to propene
Answer.

Question. (A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens’ test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens’ test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D). (a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
(b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN ?
Answer. (a) A= CH3CH2CH2CHO
B = CH3COCH2CH3
C= (CH3)2CHCHO
D= CH3CH2CH2CH3
(b) B
Question. (i) Account for the following :
(a) Cl—CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(b) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group.
(ii) Write the chemical equation to illustrate the
following name reaction :
Rosenmund reduction.
Answer. (i) (a) Cl-CH2 COOH has lower pka value than acetic acid. Also, Cl group is an electron withdrawing, creating less electron density on oxygen of carboxylic acid making the release of proton easier than acetate ion. Hence, Cl–CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(b) The carbonyl group in –COOH is inert and does not show nucleophilic addition reaction like carbonyl compound due to resonance stabilisation of carboxylate ion :
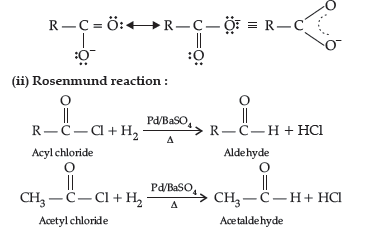
Question. Write the structures of the main products in the following reactions :
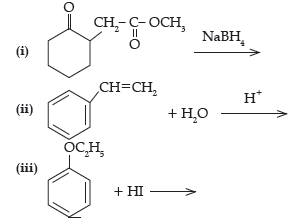
Answer.
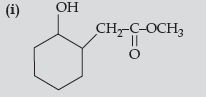
(ii) C6H5CH(OH)CH3
(iii) C2H5I + C6H5OH
Question. Complete the following reactions
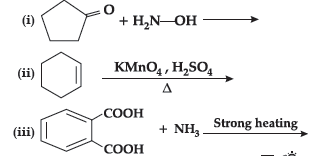
Answer.
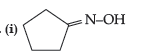

Question. How will you bring about the following conversions :
(i) Propanone to propane
(ii) Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde.
(iii) Ethanal to but-2-enal.
Answer.(i)
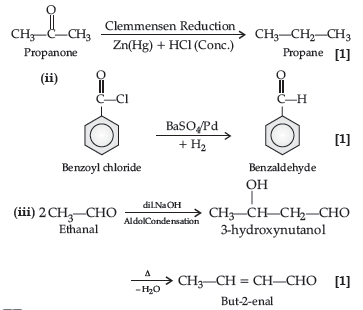
Question. Complete the following reactions :

Answer. (i) C6H5−CH(OH)−CN
(ii) 2CH3COCH2C6H5 + CdCl2
(iii) (CH3)2−C(Br)COOH
Question. (a) Give reasons :
(i) Benzoic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
(ii) Methanal is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction than ethanal.
(b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone.
Answer. (a) (i) Due to greater electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon to which carboxyl carbon is attached / Due to greater resonance stabilization of carboxylate ion with the benzene ring.
(ii) Because carbonyl carbon of methanal is more electrophilic than that of ethanol / due to + I effect of methyl group in ethanal, reactivity decreases.
(b) On heating with Tollens’ reagent / [Ag(NH3)2]+,propanal forms silver mirror whereas propanone does not.
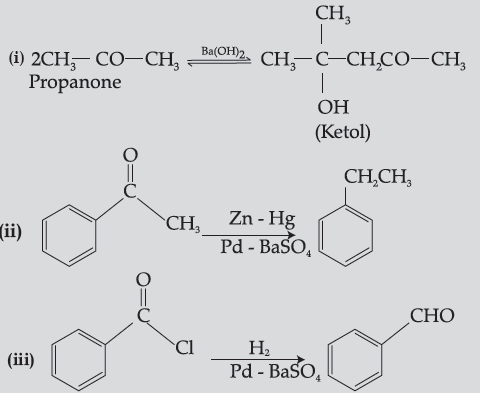
Question. Write chemical equations for the following reactions :
(i) Propanone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2.
(ii) Acetophenone is treated with Zn(Hg)/ Conc. HCl
(iii) Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in presence of Pd/BaSO4.
Answer.
Question. Write structures of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reaction :
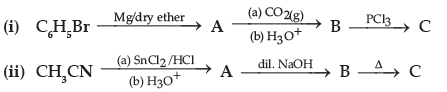
Answer. (i) A : C6H5MgBr B : C6H5COOH C : C6H5COCl
(ii) A : CH3CHO B : CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO C : CH3CH = CHCHO
Question. Predict the products of the following reactions :
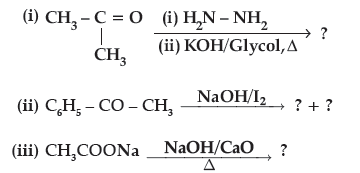
Answer. (i) CH3CH2CH3
(ii) C6H5COONa + CHI3
(iii) CH4
Question.. An alcohol A (C4H10O) on oxidation with acidified potassium dichromate gives acid B(C4H8O2). Compound A when dehydrated with conc. H2SO4 at 443 K gives compound C. Treatment of C with aqueous H2SO4 gives compound D (C4H10O) which is an isomer of A. Compound D is resistant to oxidation but compound A can be easily oxidised. Identify A, B, C and D. Name the type of isomerism exhibited by A and D.
Answer. *
Question. Predict the products of the following reactions :
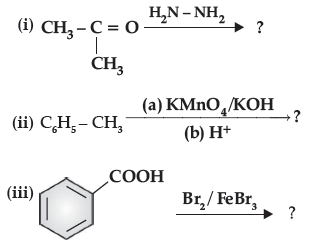
Answer. (i) (CH3)2C = N-NH
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b) Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c) Why pKa of F – CH2 – COOH is lower than that of Cl – CH2 – COOH ?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction
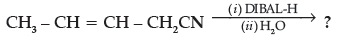
(e) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone ?
Answer.

(or any other example)
(b) CH3CH=N–NHCONH2
(c) Stronger -I effect of fluorine, stronger acid less pka / strong electron withdrawing power of fluorine.
(d) CH3CH=CHCH2 CHO
(e) Silver mirror formed on adding ammonical silver nitrate to propanal and not with propanone.
Question. (a) An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C4H8O gives orange red precipitate with 2, 4-DNP reagent. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but gives yellow precipitate of iodoform on heating with NaOH and I2. Compound (A) on reduction with NaBH4 gives compound (B) which undergoes dehydration reaction on heating with conc. H2SO4 to form compound (C). Compound (C) on ozonolysis gives two molecules of ethanal.
Identify (A), (B) and (C) and write their structures. Write the reactions of compound
(A) with (i) NaOH/I2 and (ii) NaBH4.
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Oxidation of propanal is easier than propanone.
(ii) a-hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones is acidic in nature.
Answer. (a) Compound A (C4H8O) gives positive, 2, 4-DNP test, it must be carbonyl compound. It gives iodoform test

(b) (i) Oxidation of propanal is easier than propanone because aldehydes have one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group while ketones have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the carbonyl group. Propanal easily oxidised to form acid with same number of carbon atoms whereas propanone is difficult to be oxidise and form acids with less number of carbon atoms.
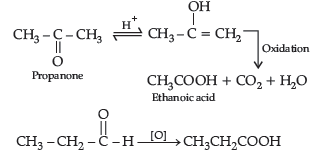
(ii) a-hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature because carbonyl group has the great electron withdrawing effect and the molecule thus formed after the removal of a-Hydrogen is resonance stabilised.
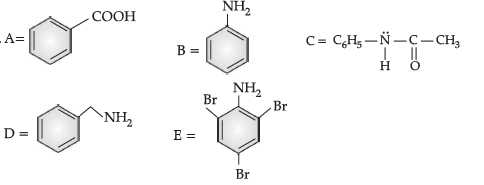
Question. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :
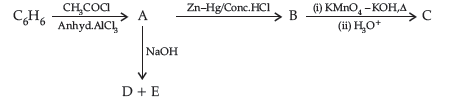
Answer. A-C6H5COCH3
B-C6H5CH2CH3
C-C6H5COOH
D ,E -C6H5COONa, CH
Question. (a) Write the products formed when benzaldehyde reacts with the following reagents :
(i) CH3CHO in presence of dilute NaOH

(iii) Conc. NaOH
(b) Distinguish between following:
(i) CH3 – CH = CH – CO – CH3 and CH3 – CH2 – CO – CH = CH2
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Answer.
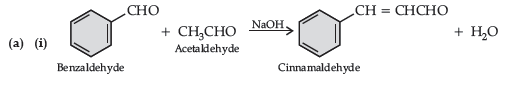
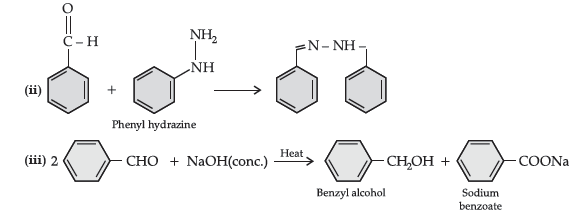
(b) (i) CH3 – CH = CH – CO – CH3 gives iodoform test while CH3 – CH2 – CO – CH = CH2 does not give.
(ii) (1) Benzaldehyde reacts with tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror. Benzoic acid does not give this reaction.
(2) With NaHCO3 benzaldehyde does not react while benzoic acid produces brisk effervescence.
Question. (a) Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions :
(b) Distinguish between :
(i) C6H5 – COCH3 and C6H5 – CHO,
(ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH.
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points :
CH3CHO, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH.
Answer. (a) (i) A : CH3CHO, B : CH3CH=N–OH
(ii) A : CH3COOH , B : CH3COCl
(b) (i) Heat both compounds with NaOH and I2, C6H5COCH3 forms yellow ppt. of CHI3 whereas C6H5CHO does not.
(ii) Add ammonical solution of silver nitrate (Tollens’ reagent) to both the compounds, HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not.
(c) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Question. (i) How will you convert:
(a) Benzene to acetophenone
(b) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
(ii) Give reasons:
(a) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid take place at meta-position.
(b) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
(c) Propanal is more reactive than propanone in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Answer. (i) (a)
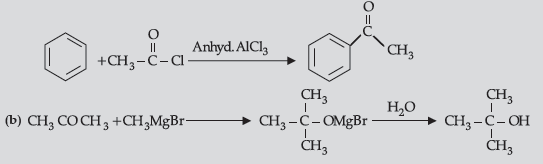
(ii) (a) Because it is a deactivating group/due to electron withdrawing carboxylic group resulting in decreased electron density at o- and p- position.
(b) Due to extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(c) Due to steric and +I effect of two methyl groups in propanone.
Question. (a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff- Kishner reduction.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction :
C6H5COCH3, CH3 – CHO, CH3COCH3
(c) Why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction.

(e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomer B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
Answer.
(b) C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Because of resonance in carboxylic group, the carbonyl group, loses a double bond character.
(d) CH3CH2CH=CH–CH2CHO
(e) A : CH3CH2CHO
B : CH3COCH3
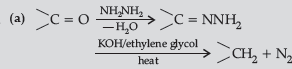
Question. (a) Write the final products in the following :
Answer.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
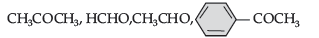
(c) Draw the structure of 2, 4 DNP derivative of acetaldehyde
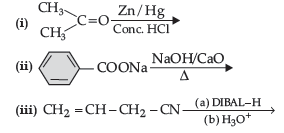
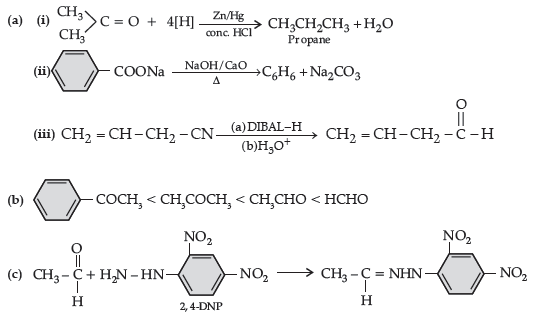
Question. (a) Write the product(s) in the following reactions:
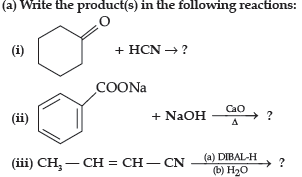
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
Answer.

(iii) CH3 — CH = CH — CHO
(b) (i) Tollen’s reagent test : Add ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) in both the solutions. Butanal gives silver mirror whereas Butan-2-one does not.
(ii) Add neutral FeCl3 in both the solutions, phenol forms violet colour but benzoic acid does not.
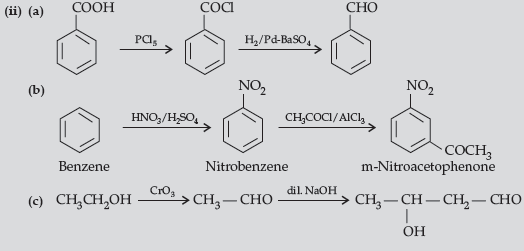
Question. (i) Describe the following giving chemical equations :
(a) Decarboxylation reaction
(b) Friedel-Crafts reaction
(ii) How will you bring about the following conversions ?
(a) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
(c) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
Answer. (i) (a) Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with sodalime (NaOH and CaO).


Question. (i) Write the chemical reaction involved in Etard reaction.
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
CH3 – CHO, C6H5COCH3, HCHO
(iii) Why pKa of Cl — CH2 — COOH is lower than the pKa of CH3COOH?
(iv) Write the product in the following reaction.
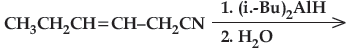
(v) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and l2, isomer A forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer B does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
Answer. (i) Etard reaction :

(ii) C6H5COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO
The reactivity of the compound towards nucleophilic addition reaction is directly proportional to electrophilic character of carbonyl carbon. In ketone, the +I group lowers the electrophilicity. Whereas, +I of methyl group in ethanal is less than that of –C6H5. Hence, ethanal is most reactive than acetophenone.
(iii) –Cl being electron withdrawing group stabilizes the ClCH2COO– anion and increases the acidic strength.
Therefore, chloroacetic acid has lower pKa value than acetic acid.
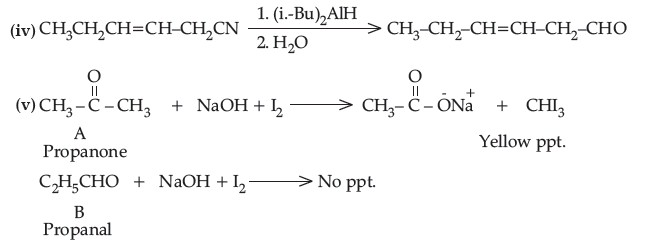
Question. (i) Describe the following reactions :
(a) Acetylation (b) Aldol condensation
(ii) Write the main product in the following equations :
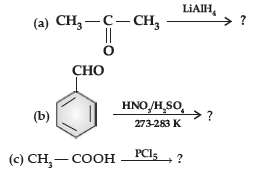
Answer. (i) (a) The acyl groups are introduced at ortho- and para- positions by reaction of chlorobenzene with acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (a Lewis acid) as catalyst.
(b) Aldehydes and ketones having at least one a-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form b-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or b-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively.*
Question. (i) Draw the structures of the following derivatives :
(a) Propanone oxime,
(b) Semicarbazone of CH3CHO.
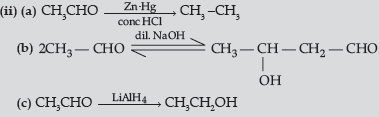
(ii) How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds ? Give the chemical equations involved.
(a) CH3—CH3

(c) CH3CH2OH
Answer.

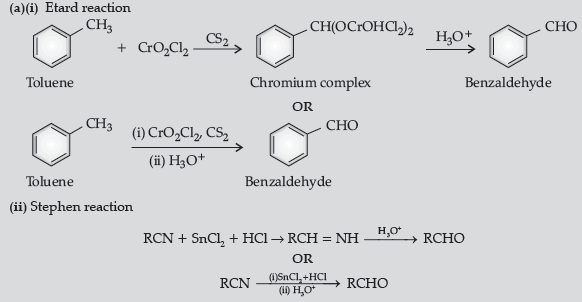
Question. (a) Write the reactions involved in the following :
(i) Etard reaction (ii) Stephen reduction
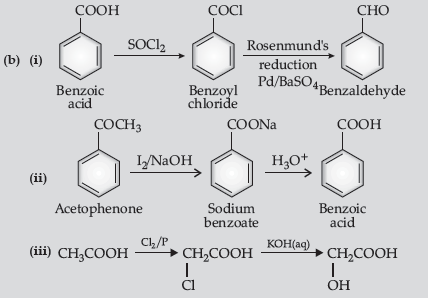
(b) How will you convert the following in not more than two steps :
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Acetophenone to benzoic acid
(iii) Ethanoic acid to 2-hydroxyethanoic acid
Answer.
Question. (i) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the pair of organic compounds :
Ethanal and Propanal.
(ii) Name and complete the following chemical reaction :

(iii) Draw the structures of the following derivatives :
(a) The 2, 4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde,
(b) Acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
(c) Cyclopropanone oxime.
Answer. (i) Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by Iodoform test.
Ethanal gives a yellow precipitate of iodoform with an alkaline solution of NaOH. Propanal does not gives this test.
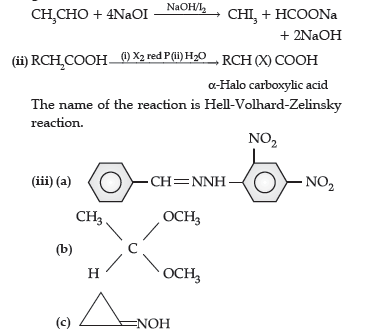
Question. (i) Complete the following equations :

(ii) Distinguish between :
Answer.

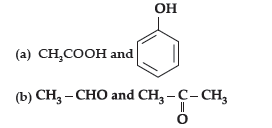
Question. (i) Account for the following :
(a) Propanal is more reactive than propanone towards nucleophilic reagents.
(b) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta-position.
(c) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group.
(ii) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Acetophenone and benzaldehyde
(b) Benzoic acid and ethylbenzoate
Answer. (i) (a) Due to steric and +I effect of two methyl groups in propanone.
(b) Because it is a deactivating group/due to electron withdrawing carboxylic group resulting in decreased electron density at o- and p- position.
(c) Due to resonance, electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon is reduced.
(ii) (a) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, acetophenone forms yellow ppt of iodoform.
(b) Add NaHCO3 solution to both the compounds, benzoic acid will give effervescence and liberates CO2.
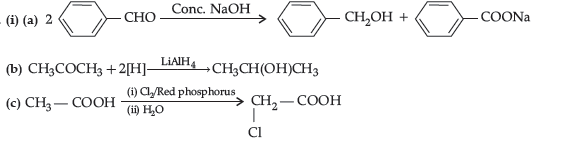
Question. An aromatic compound ‘A‘ of molecular formula C7H6O2 undergoes a series of reactions as shown below.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :

Answer.
Question. (i) Write structures of A, B, C and D in the following reaction sequence:

(ii) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points :
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3COOH
Answer. (i) A: CH3CHO; B: CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CHO;
C: CH3-CH=CH-CHO; D: CH3-CH(CH3)-OH
(ii) CH3-O-CH3<CH3H3CHO<CH3-CH2-OH < CH3-COOH
Question. (i) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following :
(a) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
(b) There are two -NH2 groups in semicarbazide.
However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(ii) Carry out the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(a) Phenyl magnesium bromide to benzoic acid.
(b) Acetaldehyde to But-2-enal.
(c) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone.
Answer.
(b) Semicarbazide has two —NH2 groups. One of them, which is directly attached to
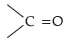
is involved in resonance. Thus, electron density on this group decreases and it does not act as a nucleophile. In contrast, the lone pair of electrons on the other —NH2 group is available for nucleophilic attack.
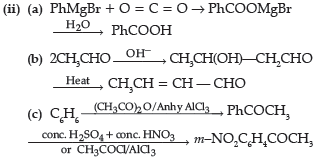
Question. (i) Write the products of the following reaction:
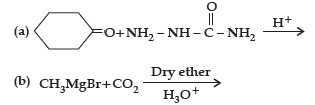
(ii) Write simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds ?
(a) Propanal and propanone
(b) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Answer. (i) (a)

(ii) (a) Add ammonical solution of silver nitrate / Tollen’s reagent to both the compounds, propanal will give silver mirror while propanone does not.
(b) Add NaHCO3 solution to both the compounds, benzoic acid will give effervescence and liberate CO2 while benzaldehyde will not.
Question. (i) Write the product(s) in the following reactions:
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Ethanol and Phenol
(b) Propanol and 2-methylpropan -2-ol
Answer.
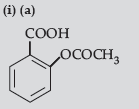
(b) (CH3)2 CHOH and CH3 CH2I
(c) CH3CH=CHCHO
(ii) (a) Add neutral FeCl3 to both the compounds, phenol gives violet complex.
(b) Add anhy ZnCl2 and conc. HCl to both the compounds, 2-methyl propan-2-ol gives turbidity immediately.
Question. (i) Give reasons :
(a) HCHO is more reactive than CH3 – CHO towards addition of HCN.
(b) pKa of O2N – CH2 – COOH is lower than that of CH3 – COOH.
(c) Alpha hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones is acidic in nature.
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Ethanal and Propanal
(b) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
Answer. (i) (a) Due to +I effect of methyl group in CH3CHO.
(b) Due to –I effect of nitro group in nitroacetic acid.
(c) Due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilisation of the conjugate base.
(ii) (a) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, ethanal gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
(b) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, pentan-2-one gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
Question. (i) Write the products of the following reactions :
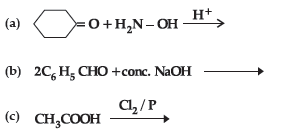
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
(b) Propanal and Propanone
Answer.
(ii) (a) NaHCO3 test.
(b) lodoform test./Fehling’s Test/Tollen’s Test
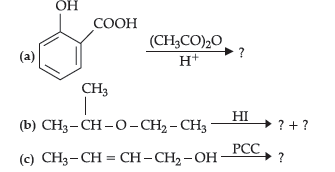
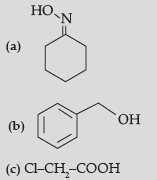
Question. (i) Write structure of the product(s) formed :
(ii) How will you bring the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(a) Propanone to propene
(b) Benzyl chloride to phenyl ethanoic acid
Answer.

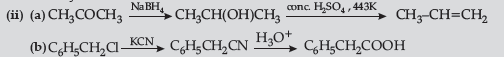
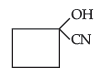
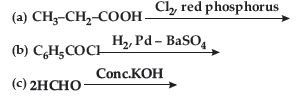
Question. (a) Draw structures of the following derivatives :
(i) Cyanohydrin of cyclobutanone
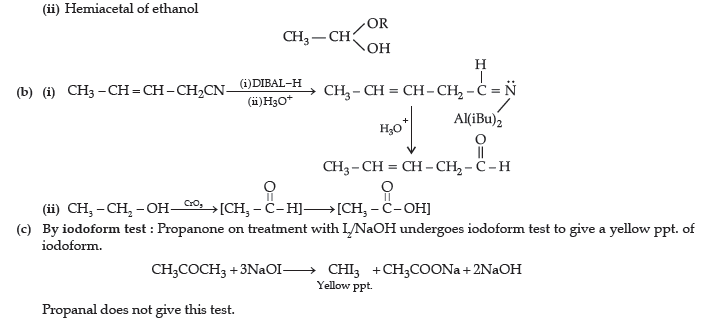
(ii) Hemiacetal of ethanal
(b) Write the major product(s) in the following :

(c) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone?
Answer. (a) (i) Cyanohydrin of cyclobutanone