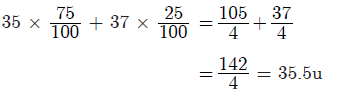Please refer to Structure Of The Atom Chapter 4 Class 9 Science Assignments below. We have provided important questions and answers for Structure Of The Atom which is an important chapter in Class 9 Science. Students should go through the notes and also learn the solved assignment with solved questions provided below. All examination and class tests questions are as per the latest syllabus and books issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have also provided Class 9 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom Class 9 Science Assignments
Question. Give the mass and charge of an electron.
Answer
(i) The mass of electron is about 9.0 × 10–31 kg.
(ii) An electron is negatively charged particle and has a charge of 1.6 × 10–19 coulomb.
Question. An uncharged particle is found in the nucleus of an atom. Identify this uncharged particle.
Answer
Neutron.
Question. Name the scientist who concluded that the size of nucleus is very small as compared to the size of atom.
Answer
Rutherford.
Question. Write the names of three elementary particles which constitute an atom.
Answer
Electron, proton and neutron.
Question. Helium atom has two electrons in its valence shell but its valency is not two. Why?
Answer
Helium atom has two electrons in its valence shell but its valency is not two as its outermost shell is completely filled, its combining capacity or valency is zero.
Question. Write the symbols of two isotopes of uranium.
Answer
Uranium 238 (92U238) and Uranium 235 (92U235).
Question. Write any two observations which support the fact that atoms are divisible.
Answer
Discovery of electrons and protons are two observations which support the fact that atoms are divisible.
Question. If an atom contains one electron and one proton, will it carry any charge or not?
Answer
It will not carry any charge because the positive charge on the proton neutralizes the negative charge on the electron.
Question. Name the scientist who discovered neutrons.
Answer
J. Chadwick.
Question. Name the particles which determine the mass of an atom.
Answer
Proton and neutron are the particles which determine the mass of an atom.
Question. Where is neutron located in an atom?
Answer
It is located in the nucleus of an atom.
Question. Helium atom has an atomic mass of 4u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons does it have?
Answer
Two.
Question. How are the canal rays different from electrons in terms of charge and mass?
Answer
Electrons are negatively charged particles, mass of which is approximately 1/2000 that of canal rays.
Question. State the charge and mass of a neutron.
Answer
Neutron has no charge and its mass is equal to that of a proton.
Question. Give two uses of isotopes in the field of medicines.
Answer
(i) An isotope of cobalt is used in the treatment of cancer.
(ii) An isotope of iodine is used in the treatment of goitre.
Question. What is meant by electronic configuration of elements?
Answer
The systematic distribution of electrons in various orbits of an atom is called electronic configuration of elements.
Question. Why do noble gases show low reactivity?
Answer
The outermost shell of the atoms of noble gases are complete. So, they show little chemical reactivity.
Question. Is an atom electrically neutral?
Answer
Yes, because number of protons (+ve charge) inside the nucleus are equal to the number of electrons (–ve charge) outside the nucleus.
Question. Give the derivative source of sodium.
Answer
The symbol of Na for sodium is derived from its Latin name ‘Natrium’.
Question. Are noble gases inert?
Answer
The outermost shell of the atoms of noble gases are completely filled. So, they do not show affinity towards chemical reactions.
Question. What is the charge and mass of alpha particle?
Answer
Charge = + 2 units
Mass = 4 units
Question. Name an element which has one electron, one proton and no neutron.
Answer
Hydrogen atom (1H1) has one electron, one proton and no neutron.
Question. Name one element, the nucleus of which does not have any neutron.
Answer
Hydrogen.
Question. Draw an atomic structure of hydrogen atom.
(a) K = 1
(b) (no neutron)
Answer

Question. Why is the valency of Na is 1 and not 7?
Answer
It is easy for Na atom to lose one electron instead of gaining seven electrons. So, valency of Na is one and not seven.
Question. How can an atom become stable by losing or gaining electrons?
Answer
For stability of an atom it must have either 2 or 8 electrons in the outermost orbit. So, by losing or gaining electrons it reaches to the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas.
Question. What is the relation between physical and chemical properties of isobars?
Answer
Isobars have different atomic numbers, so different electronic configuration and have different chemical properties. They are atoms of different elements, hence they have different physical properties.
Question. Why did Rutherford select a gold foil in his a-ray scattering experiment?
Answer
Rutherford selected a gold foil in his a-ray scattering experiment because gold has high malleability and can be hammered into thin sheet.
Question. What is the limitation of J.J. Thomson’s model of an atom?
Answer
The major limitation of J.J. Thomson’s model is that it does not explain how positively charged particles are shielded from negatively charged particles, without getting neutralized.
Question.What kind of elements have a tendency to gain electrons? What are they commonly called?
Answer
The elements having 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons have the tendency to gain electrons. They are commonly called non-metals.
Question. Is it possible for the atom of an element to have one electron, one proton and no neutron? If so, name the element.
Answer
Yes, it is true for hydrogen atom which is represented as 11H.
Question. How does an atom become a cation?
Answer
When an atom acquires positive charge by losing one or more electrons, it is called cation.
Question. What are nucleons?
Answer
Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus of an atom and are thus called nucleons.
Question. Give four characteristics of isotopes.
Answer.
All isotopes of an element consist of the same number of protons inside their nuclei. Hence, they have the same atomic number.
(i) All isotopes of an element consist of different number of neutrons in their nuclei. Hence, they have different mass number.
(ii) All isotopes of an element give identical chemical reactions.
(iii) Isotopes of an element have same electronic configuration.
Question. Write drawbacks of Thomson’s model.
Answer. Drawbacks of Thomson’s Model : It could not explain about the stability of an atom, i.e., how both positive and negative charges could remain so close together.
It could not explain the results of experiments (such as alpha ray scattering experiment) carried out by other scientists.
Question. Draw a sketch of Bohr’s model of an atom with three shells.
Answer.
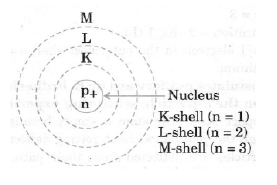
Figure: Bohr’s model of an atom
Question. What do you think would be the observation if the a -particle scattering experiment is carried out using a foil of a metal other than gold?
Answer.
If experiment is done by using a foil of some other metal, then results would not have been such as most of the particles will be deflected back. Gold can be beaten to an extremely thin sheet as it is extremely malleable metal. Rutherford could predict with the use of extremely thin gold foil that, “Most of the space inside the atom is empty and nucleus is positively
charged occupying a small volume within the atom.”
Question. State the properties of isotopes.
Answer.
Isotopes have the following uses :
Treatment of disease : Radioactive isotopes are used for the treatment of dreadful diseases like cancer. Cobalt-60 is used to kill malignant cells in patients suffering from cancer.
(i) It is used in chemical analysis.
(ii) It is used to detect disease in plants.
(iii) Dating of plants/animals being obtained by using carbon-14 after excavation.
(iv) Thyroid disorders can be treated by I-131.
(v) Leukaemia can be treated by using P-32.
(vi) Uranium-235 can produce electricity.
Question. Helium atom has an atomic mass of 4u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons it have?
Answer. Mass number = Number of protons
+ Number of neutrons
4 =2 + No. of neutrons
Number of neutrons = 4 – 2 = 2
Question. If K and L shells of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom?
Answer.
Number of electrons in full K-shell = 2
Number of electrons in full L-shell = 8
Total number of electrons in an atom is 2 + 8 = 10 electrons.
Question. If number of electrons in an atom is 8 and number of protons is also 8, then (i) what is the atomic number of the atom? And (ii) what is the charge on the atom?
Answer.
(i) Atomic number = Number of protons = 8
(ii) The charge of the atom is zero, as total number
of positive charge is equal to total number of negative charge.
Number of protons = Number of electrons
8 = 8
Question. Explain the essential features of experiment that led to the discovery of isotopes.
Answer. The e/ m values of the ionized atoms were determined by studying their deflections under the influence of electrical and magnetic fields. Ionised atoms of an element do not give a unique mass and chemical properties of these atoms are identical.
Question. Define the term “Half life”.
Answer. Radioactive elements are unstable and disintegrate with time emitting alpha and beta particles along with gamma rays. The rate of disintegration depends on the amount of substance. As the amount of the substance decreases, disintegration becomes slower.
But it takes a long time for whole of the substance to decay. Thus, the rate of radioactive decay is measured in terms of half time. The time taken by half of the atoms of radioactive element to disintegrate is called its half-time.
Question. Write three main features of Rutherford’s nucleus model of an atom.
Answer.
On the basis of a -particle scattering experiment,Rutherford proposed a model of atom. According to
him :
There is positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus which contains the whole mass of the atom.
The electrons revolve around the nucleus.
The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom.
Question. Name the three subatomic particles of an atom.
Answer.
(i) Electrons (negatively charged particles) which revolve around the nucleus.
(ii) Protons (positively charged particles) which are present in the nucleus.
(iii) Neutrons (having no charge) which are present in the nucleus.
Question. Give drawbacks of Rutherford’s model.
Answer. Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model :
(i) Unable to explain the source of energy required for movement of electrons.
(ii) Unable to explain as to why a moving charge does not lose energy and fall into the nucleus.
(iii) It could not explain about the emission of radiations of different frequencies by different atoms when heated.
(iv) It could not explain the stability of an atom when charged electrons are moving under the attractive force of positively charged nucleus.
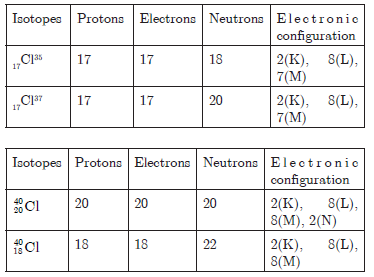
Question. Write the electronic configuration of any one pair of isotopes and isobars.
Answer.
Question. What were the drawbacks of Rutherford’s model of an atom?
Answer. The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable. Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo acceleration and the charged particles would radiate energy. Thus, the revolving electron would lose energy and finally fall into the nucleus. If this were so, the atom should be highly unstable and hence matter would not exist in the form that we know.
Question. Define isotopes. Why do isotopes have same atomic number but different mass number? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer. Atoms of the same element, having the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes.Isotopes have same atomic number but different mass number because they contain different number of neutrons.
For example : In nature chlorine occurs in two
isotopic forms; 17Cl35 and 17Cl37.Here atomic number of both the atoms is same but due to the difference in the number of neutrons, their mass number is different.
Question. Describe the essential properties of the atomic nucleus. Compare these properties with the properties of electron.
Answer. Nucleus is small positively charged centre located in a very small space. An electron is a very small negatively charged particle with well established charge to mass ratio. The charge on electron forms the smallest unit of charge on atomic particles.
Question. What are canal rays? Who discovered them? What is the charge and mass of canal ray?
Answer. New radiations in a gas discharge tube which are positively charged are known as canal rays. They were discovered by E. Goldstein. Charge on canal rays is positive and its mass is one unit.
Question. An element 12X24 loses two electrons to form a cation which combines with the anion of element 17Y35 formed by gaining an electron.
(i) Write the electronic configuration of element X.
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of the anion of element Y.
(iii) Write the formula for the compound formed by combination of X and Y.
Answer.
(i) X = 2, 8, 2
(ii) Y = 2, 8, 8
(iii) XY2
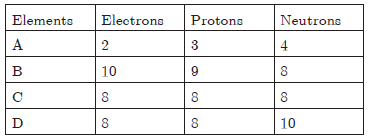
Question. Number of electrons, protons and neutrons in chemical species A, B, C and D is given below :
Now, answer the following questions :
(a) What is the mass number of A and B?
(b) What is the atomic number of B?
(c) Which two elements represent a pair of isotopes and why?
(d) What is the valency of element C?
Also, justify your answers.
Answer.
(a) Mass number of A = 3 + 4 = 7
Mass number of B = 9 + 8 = 17
(b) Atomic number of B = Number of protons = 9
(c) Elements C and D represent a pair of isotopes because their atomic numbers are the same.
(d) Electronic configuration of C (8) = 2, 6. So, its valency is 2.
Question. Explain Rutherford’s atomic model.
Answer. Rutherford purposed a model of an atom on the basis of a-particles scattering experiment. This is known as Rutherford’s nuclear model of atom.
(i) An atom consist, a heavy positively charged core called nucleus.
(ii) Nucleus is surrounded by electrons.
(iii) Electrons and nucleus are held together by electrostatic force of attraction.
(iv) Size of nucleus is very small as compared to the size of atom.
(v) Almost the entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Question. Give reasons :
(i) Mass number of an atom excludes the mass of an electron.
(ii) Nucleus of an atom is charged.
(iii) Alpha-particle scattering experiment was possible by using gold foil only and not by foil of any other metal.
Answer.
(i) Mass number of an atom excludes the mass of an electron because electrons have negligible mass in comparison to protons and neutrons.
(ii) Nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles.So, the nucleus of an atom is charged.
(iii) Because an extremely thin film was required for the experiment and it was only possible by using gold, as gold is a highly malleable metal.
Question. Chlorine occurs in nature in two isotopic forms with masses 35u and 37u in the ratio of 3 : 1. What should be the mass of chlorine atom?
Answer.