Please refer to Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Objective Questions
Question. Photosynthesis is a/an
(a) physio-chemical process.
(b) physical process.
(c) chemical process.
(d) energy wasting process.
Answer
A
Question. Half leaf experiment proves that
(a) light is essential for photosynthesis.
(b) CO2 is essential for photosynthesis.
(c) O2 releases during photosynthesis.
(d) chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
Answer
B
Question. Contribution of Ingen-Housz in elucidation of process of photosynthesis is that
(a) only green parts of plants exposed to light can convert foul air (CO2) into pure air (O2).
(b) green plants convert light energy into chemical energy
(c) plants have the capacity to purify foul air.
(d) sunlight is the ultimate source of energy for plants and animals.
Answer
A
Question. Which one represents the correct empirical equation of photosynthesis?
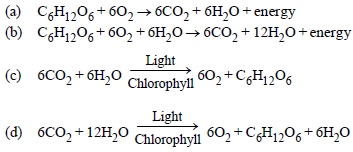
Answer
D
Question. What is/are the function(s) of accessory pigments?
(a) They enable a wider range of wavelength of incoming light to be utilized for photosynthesis.
(b) They absorb light and transfer the energy to reaction centre.
(c) They protect reaction centre from photo-oxidation.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. In a plant cell, which of the following pigments participates directly in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
(a) Chlorophyll a
(b) Chlorophyll b
(c) Chlorophyll d
(d) Carotenoids
Answer
A
Question. An energy diagram for the transfer of electrons in the light reactions of photosynthesis in plants is
(a) cyclic photo-phosphorylation
(b) Z-band
(c) Z-Scheme
(d) non-cyclic photo-phosphorylation
Answer
C
Question. Splitting of water is related with
(a) photosystem I
(b) photosystem II
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) cyclic photo-phosphorylation
Answer
B
Question. The chemiosmotic mechanism mediates
(a) ATP synthesis.
(b) splitting of water.
(c) reduction of NADP+.
(d) flow of electrons from PS – II to PS – I
Answer
A
Question. In photosynthesis, protons accumulate in the
(a) inner membrane space of mitochondria.
(b) matrix of mitochondria.
(c) lumen of thylakoid.
(d) stroma of thylakoid.
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about RuBisCO?
(a) It catalyzes the fixation of CO2.
(b) It has oxygenation & carboxylation both activity.
(c) It is the most abundant protein on earth.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statement is incorrect in relation to photorespiration?
(a) It is a characteristic of C3 plants.
(b) The RuBP binds with O2 to form one molecule of phosphoglycerate and phosphoglycolate.
(c) There is synthesis of ATP or NADPH.
(d) It occurs in daytime only.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements (i-iv) regarding “Splitting of water” is/are correct.
(i) It is photolysis of water which provides H+ ions for synthesis of NADPH.
(ii) It provides electrons for photophosphorylation & activation of NADP+.
(iii) O2 is evolved during this process.
(iv) It replenishes O2 consumed by living beings and combustion.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Why C4 plants are special ? Because,
(i) they have a special type of leaf anatomy.
(ii) they tolerate higher temperatures.
(iii) they show a response to high light intensities.
(iv) they lack a process called photorespiration.
(v) they have greater productivity of biomass.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : 6 molecules of CO2 and 12 molecules of NADPH+ + H+ and 18 ATP are used to form one hexose molecule.
Reason : Light reaction results in formation of ATP and NADPH2.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Mitochondria helps in photosynthesis
Reason : Mitochondria have enzymes for dark reaction.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: Six molecules of CO2 and twelve molecules of NADPH+ + H+ and 18 ATP are used to form one hexose molecule.
Reason: Light reaction results in the formation of ATP and NADPH2.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : C4 photosynthetic pathway is more efficient than the C3 pathway.
Reason : Photorespiration is suppressed in C4 plants.
Answer
A
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match the scientists given in column-1 with their work, given in column-II & select the correct answer using the codes given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Priestley | I. Determined the action spectrum of chlorophyll |
| B. Jan Ingenhousz | II. Provided evidence that in green parts of plant glucose is made & stored as starch |
| C. Sachs | III. Plants purify air only in the presence of light |
| D. Engelmann | IV. Demonstrated that photosynthesis is essentially a light-dependent reaction |
| E. Niel | V. Revealed the essential role of air in the growth of plants |
(a) A – V; B – III; C – II; D – I; E – IV
(b) A – V; B – I; C – II; D – III; E – IV
(c) A – V; B – I; C – IV; D – III; E – II
(d) A – V; B – I; C – III; D – IV; E – II
Answer
A
Question. Match the column-1 with column II and choose the correct answer using the codes given below.
| Column -I | Column -II |
| A. Emerson effect | I. C4 cycle |
| B. Hill reaction | II. Photolysis |
| C. Calvin cycle | III. C3 cycle |
| D. Hatch & Slack cycle | IV. Photosystem I & II |
(a) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – I; B – III; C – IV; D – I
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
(d) A – IV; B – II; C – III; D – I
Answer
D
Question. Match the parts given in column I with the events given in column II and choose the correct combination from the options given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Grana of chloroplast | I. Kreb’s cycle |
| B. Stroma of chloroplast | II. Light reaction |
| C. Cytoplasm | III. Dark reaction |
| D. Mitochondrial matrix | IV. Glycolysis |
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(b) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following pair is not correctly matched ?
(a) C3 plant – Maize
(b) C4 plant – Kranz anatomy
(c) Calvin cycle – PGA
(d) Hatch and Slack pathway – Oxaloacetic acid
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. In non-cyclic reactions of photosynthesis, electrons from chlorophyll molecules in photosystem-I are used in the formation of NADPH. What is the source of such electrons?
(a) Light
(b) NADPH
(c) Photosystem-I
(d) Photosystem-II, which splits water molecule
Answer
D
Question. To make 100 molecules of glucose, how many molecules of ATP & NADPH are required?
(a) 1800 and 1200 respectively.
(b) 1200 and 1800 respectively.
(c) 1800 and 600 respectively.
(d) 200 and 600 respectively.
Answer
A
Question. The correct sequence of Calvin cycle is
(a) Decarboxylation → Oxidation → Regeneration
(b) Decarboxylation → Regeneration → Oxidation
(c) Carboxylation → Reduction → Regeneration
(d) Carboxylation → Reduction → Regeneration
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following combination is correct for C4 plants?

Answer
A
Question. Which of the following plant species have highest photosynthetic yield?
(a) Species that perform photorespiration
(b) Species possessing C3 pathway
(c) Species possessing C4 pathway
(d) Same for all
Answer
C
Question. During monsoon, the rice crop of eastern states of India shows lesser yield due to limiting factor of
(a) CO2
(b) light
(c) temperature
(d) water
Answer
B
Question. Under water stress, the rate of photosynthesis declines because of
(a) stomatal closure leading to decrease in CO2 supply.
(b) reduced water potential that decreases leaf surface areas for photosynthesis.
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) turgidity of leaf.
Answer
C
Question. What will happen if the supply of oxygen is decreased to an illuminated wheat plant?
(a) Its photosynthesis would decrease.
(b) Its respiration process would stop.
(c) All physiological process would stop.
(d) Its photosynthesis would increase.
Answer
D
Question. The electrons that are released by the photolysis of water during non-cyclic photophosphorylation, ultimately end up in
(a) glucose
(b) ATP
(c) H2O
(d) NADPH
Answer
D
Question. During light reaction, as electrons move through photosystems, protons are transported across the
membrane. This happens because of
(a) the primary acceptor of e– (located towards the outer surface of the membrane) transfers its electron not to an e– carrier but to H carrier.
(b) the primary acceptor of e– transfers only its e– to e– carrier.
(c) the primary acceptor of e– transfers only H+ to the next carrier.
(d) NADP – reductase is present in grana.
Answer
A


