Please refer to the Accounting for Share Capital Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 12th Accountancy book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 12 Accountancy as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 1 Accounting for Share Capital
Students of Class 12 Accountancy will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 12 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Meaning & Features of Company
It is an artificial person, created by law, having separate legal identity, with a perpetual succession and a common seal.
It is an artificial person, created by law, having separate legal identity, with a perpetual succession and a common seal.
Features:
(1) Incorporated under law (Companies Act, 2013 or under any previous Companies Acts)
(2) Separate legal entity
(3) Artificial person
(4) Perpetual existence
(5) Limited liability of members (to the extent of unpaid amount on shares)
(6) Common seal
(7) Transferability of shares – Shares of Public Companies are freely transferable.
(8) May sue or be sued
(9) Can enter into contracts in its own name
Types of Companies
(A) On the basis of liabilities of members:
(i) Companies Limited by Shares
(ii) Companies Limited by Guarantee
(iii) Unlimited Companies (i.e. unlimited liabilities of members – only theoretical
concept)
(B) On the basis of number of members:
(i) Public Company – A public company means a company which
(a) is not a private company;
(b) is a company which is not a subsidiary of a private company.
(ii) Private Company – A private company is one which by its Articles of
Association:
(a) Restricts the right to transfer its shares;
(b) A private company must have at least 2 members, except in case of one person company;
(c) Limits the number of its members to 200 (excluding its employees);
(d) Prohibits any invitation to public to subscribe for any securities of the company.
(iii) One Person Company (OPC) – Sec. 2(62) of the companies Act, 2013, defines OPC as a “company which has only one person as a member”.
Rule 3 of the Companies (Incorporation) Rules, 2014 provides that:
(a) Only a natural person being an Indian citizen and resident in
India can form one person company,
(b) It cannot carry out non-banking financial investment activities.
(c) It cannot be formed for charitable purpose
(d) Directors: Minimum 1 & Maximum 15
(e) Paid-up share capital: Minimum Rs. 1 lakh & Maximum ₹50 Lakhs
(f) Its average annual turnover of three years does not exceed ₹2 Crores.
Prospectus
It is a document issued by a public company, before issue of securities (like shares) to the public, which contains terms & conditions of the issue and other relevant details like purpose for which proceeds of the issue will be used.
Incorporation of Company – PROCESS
1. Promotion
2. Registration – Certificate of Incorporation
3. Capital Subscription
4. Commencement of business – Company has to obtain Commencement of business Certificate within 180 Days of its incorporation
Minimum Subscription
♦ It is the minimum amount stated in the prospectus, that must be subscribed & the application money on such minimum subscription must be received.
♦ As per SEBI Regulations – Minimum Subscription = 90% of the shares issued
♦ Shares cannot be allotted unless minimum subscription is received within the prescribed time.
♦ If minimum subscription is not received, then application money shall be refunded to the applicants within 15 days from closure of the issue
♦ In case of Delay in above – Interest @ 15% p.a. will be charged
Preliminary Expenses
Expenses incurred for incorporation / registration of the company. For example: Legal fees, registration fees, stamp duty, printing cost, share issue expenses etc.
Share Capital
♦ Amount received towards “Share Capital” of the company. In simple words, capital of the shareholders / members (i.e. owners of the company) is collectively known as share capital.
♦ Shares – It is the unit in which share capital (i.e. ownership) of a company is divided. It is a fractional part of the share capital and forms the basis of ownership interest in a company. Each share has its nominal (face) value.
Types of Shares
(i) Preference Share – Shares which carries preferential right over equity shares to:
(a) received dividend; and
(b) received repayment of capital at the time of winding up of the company.
(ii) Equity Shares – Shares other than preference shares. These carry maximum risk & reward, and voting rights.
Types of Preference Shares
1. With Reference to Dividend
• Cumulative
• Non Cumulative
2. With reference to Participation in Surplus profits
• Participating
• Non participating
3. With Reference to Convertibility
• Convertible
• Non convertible
4. With Reference to Redemption
• Redeemable
• Irredeemable (Not practical)
Dividend
It is the part of profits that are distributed amongst the shareholders.
Types of Share Capital
(1) Authorised / Nominal / Registered Capital
It is the amount of share capital which a company is authorised to issue by its Memorandum of Association. The company cannot raise more than the amount of capital as specified in the Memorandum of Association.
(2) Issued Capital
It is that part of the authorised capital which is actually issued to the public for subscription including the shares allotted to vendors and the signatories to the company’s memorandum. It cannot be more than Authorised Capital.
(3) Subscribed Capital
It is that part of the issued capital which has been actually subscribed by the public. Subscribed capital is further categorised as:
(i) Subscribed & Fully Paid-up i.e. where total face value has been called &
received.
(ii) Subscribed but not Fully paid-up i.e. where:
• Total face value has been called but not received; or
• Total face value has not yet been called; or
• Combination of both
(4) Called-up Capital
It is that part of the subscribed capital which has been called up on the shares, i.e.,
what the company has asked the shareholders to pay.
(5) Paid-up Capital
It is that portion of the called-up capital which has been actually received from the shareholders.
Other Important Terms
(1) Calls-in-Arrears
Part of called-up capital that has not been received from the shareholders.
Calls-in-Arrears = Called-up Capital (-) Paid-up Capital.
(2) Calls-in-Advance
Amount received in advance from shareholders against calls yet to be made. It is
shown under the head Current Liabilities (Other Current Liabilities).
(3) Reserve Capital
It is the part of uncalled capital, that the company decides not to call except at the time of winding-up of the company.
(4) Capital Reserve
It is a reserve created out of capital profits, that is not available for distribution as dividend. It is shown under the head “Reserves & Surplus” in the Balance Sheet.
Initial Public Offer (IPO)
When shares are issued (for cash) to the public for the first time, it is known as IPO. In India, IPO is applied using a system known as “Application Supported by Blocked Amount (ASBA)”.
Important Steps for Issue of Shares
1. Issue of prospectus
2. Receipt of applications
3. Allotment of shares (provided minimum subscription is received)
Minimum application money:
As per Companies Act, 2013 – 5% of Face Value
As per SEBI – 25% of Issue Price
Rights Issue of Shares
It is an issue of shares in which the existing shareholders have a right to subscribe for the new shares.
Provisions w.r.t. Calls
Calls are made as per AoA of the Company.
If no AoA (or if AoA is silent) Table F of Companies Act, 2013 applies, which provides:
(i) Minimum time gap between two calls – 1 month
(ii) Amount of one call cannot be more than 25% of the nominal (face) value
(iii) Notice of 14 days to be given to shareholders to pay the amount
(iv) Calls should be made on uniform basis on all shares of the same class.
(v) Interest on Calls in Arrear – 10% p.a.
(vi) Interest on Calls in Advance – 12% p.a.
Utilisation of Securities Premium Reserve [Sec. 52(2) of Companies Act, 2013]
Securities Premium Reserve can be used only for the following five purposes:
(a) to issue fully paid bonus shares to the extent not exceeding unissued
share capital of the company;
(b) to write-off preliminary expenses of the company;
(c) to write-off the expenses of, or commission paid, or discount allowed on any
securities of the company;
(d) to pay premium on the redemption of preference shares or debentures of the
company.
(e) Purchase of its own shares (i.e., buy back of shares)
Preferential Allotment of Shares
It means an allotment that is made at a predetermined price to certain identified people, such as promoters, venture capitalists, financial institutions, major customers or suppliers, who wish to take a strategic stake in the company.
Private Placement of Shares (Sec. 42 of Companies Act, 2013]
It is an offer of securities or invitation to subscribe securities to a select group of persons through issue of private placement offer letter.
Employee Stock Option Plan [ESOPs]
♦ A company may offer option to its employees and employee directors to subscribe shares of the company at lower than its market value or fair value at a future date. This is known as Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP).
♦ It is a category of Sweat Equity (Sweat Equity being a wider term)
♦ An employee may or may not exercise the right to subscribe.
♦ A company issuing the options has to fulfil following prescribed conditions:
♦ these shares are of the same class of shares already issued;
♦ it is authorised by a special resolution passed by the company;
♦ the resolution specifies the number of shares, the current market price, consideration, if any, and the class or classes of directors or employees to whom such equity shares are to be issued;
♦ not less than one year has, at the date of issue, elapsed since the date on which the company had commenced business; and
♦ these shares are issued in accordance with SEBI regulations, if the shares are listed.
♦ Important terms:
♦ Grant: It means giving an option to the Employees to subscribe to the shares of the company at the pre-determined price.
♦ Grant Date: It is the date of agreement between the enterprise and its employees to the terms of Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP).
♦ Vesting: A process to give right to employees to apply for shares of the company.
♦ Vesting Date: It is the date on which the employee becomes entitled to apply for the shares once he has satisfied the vesting conditions.
♦ Vesting Period: The period between the grant date and the date on which all the specified vesting conditions of an Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP) need to be satisfied.
♦ Exercise: It means applying by the employee for issue of shares against the option vested in him.
♦ Exercise Period: Period after vesting within which the employee must exercise the right to apply for shares against the option vested in him in pursuance of the Employees Stock Option Plan.
♦ Exercise Price: The price payable by the employee for exercising the option granted in pursuance of the Employees Stock Option Plan.
♦ Value of Option: Difference between the market price and the issue price of the security.
MCQs Questions Accounting for Share Capital Class 12 Accountancy
Question: A company invited applications for 25,000 equity shares of 10 each and received 30,000 applications along with the application money of 4 per share. Which of the following alternatives can be followed?
I. Refund the excess applications
II. Make pro rata allotment to all the applicants, and refund the excess application money
III. Not to allot any shares to some applicants, full allotment to some of the applicants and pro rata allotment to the rest of the applicants.
IV. Not to allot any shares to some applicants & make pro rata allotment to other applicants.
V. Make pro rata allotment to all the applicants and adjust the excess money received towards call money.
(a) Only (II) above
(b) Both (I) and (IV) above
(c) All (I), (II), (III), (IV) and (V) above
(d) Only (III) above
Answer
C
Question: Arrange the following sentences in sequence:
(i) Receiving calls amount
(ii) Receiving applications
(iii) Issuing prospectus
(iv) Allotment of shares
(a) I, ii, iii ,iv
(b) ii, iii, iv, I
(c) iii, ii, iv, i
(d) iii,iv, ii, i
Answer
C
Question: 4,000 Equity Shares of Rs. 10 each were issued at 8% premium to the promoters of a company for their services. Goodwill Account/ incorporation Cost Account will be debited with ?
(a) Rs.40,000
(b) Rs.43,200
(c) Rs.3,200
(d) Rs.36,800
Answer
B
Question: At the time of forfeiture of shares which were originally issued at a discount, the accounting entry involves _______________.
I. A debit to Share Capital Account with the called up value of shares forfeited
II. A credit to Share Forfeiture Account with the amount received on forfeited shares
III. A credit to discount on issue of shares with the amount of discount allowed on forfeited shares
IV. A credit to calls in arrears with the amount due but not paid on forfeited shares
(a) Both (I) and (IV) above
(b) Both (IV) and (III) above
(c) Both (I) and (II) above
(d) (I), (II), (III) and (IV) above
Answer
D
Question: If a share of Rs.10 issued at a premium of Rs.3 on which the full amount has been called and Rs.8 (including premium) paid is forfeited the capital account should be debited with:
(a) Rs.5
(b) Rs.8
(c) Rs.10
(c) Rs.13
Answer
C
Question: The subscribed capital of a company is Rs.80,00,000 and the nominal value of the share is 100 each. There were no calls in arrear till the final call was made. The final call made was paid on 77,500 shares only. The balance in the calls in arrear amounted to 62,500. Calculate the final call on share.
(a) 27
(b) 22
(c) 20
(c) 25
Answer
D
Question: A Company invited applications for 1,00,000 shares and it received applications for 1,50,000 shares. Applications for 30,000 shares were rejected and the remaining were allotted shares on prorata basis. How many shares an applicant for 3,000 shares will be allotted
(a) 2,500 Shares
(b) 4,500 Shares
(c) 3,600 Shares
(d) 2,000 Shares
Answer
A
Question: A Company issued 50,000 shares of 20 each at 5% premium,10 were payable on application and balance on allotment. What will be the allotment amount?
(a) Rs.500,000
(b) Rs.4,75,000
(c) Rs.550000
(d) Rs.5,25,000
Answer
C
Question: According to Section 52 of the Companies Act, the amount in the Securities Premium Account cannot be used for the purpose of:
(a) Issue of fully Paid Bonus Shares
(b) Writing Off Losses of the Company
(c) Writing off Preliminary Expenses
(d) Writing Off Commission or Discount on Issue of Shares.
Answer
B
Question: If vendors are issued fully paid shares of Rs. 1,00,000 in consideration of net assets of Rs. 1,20,000 the balance of Rs. 20,000 will be credited to :
(a) Goodwill Account
(b) Securities premium account
(c) Vendor’s Account
(d) Profit & Loss Account
Answer
B
Question: Match the following
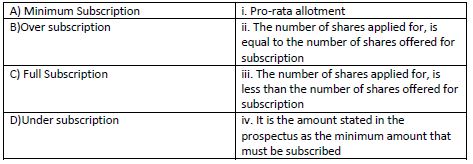
(a) A-iv, B-ii, C-iii D-i
(b) A-ii, B-i, C-iv D-iii
(c) A-iii, B-ii, C-i D-iv
(d) A-iv, B-i, C-ii D-iii
Answer
D
Question: A company is registered with a share capital of Rs. 1,00,000 divided into Rs. 10,000 shares of Rs. 10 each. Of these shares 9,990 shares are held by Rajeev and 10 Shares are held by Sanjay. In the eye of law it is treated as:
(a) Partnership
(b) Private Company
(c) Public Company
(d) Government Company
Answer
B
Question: A company purchased a machinery of Rs.2,75,000 from a vendor and issued shares of Rs.10 each to the vendor. Match the following:
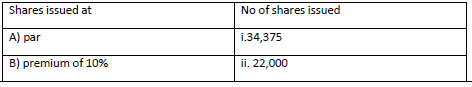

(a) -iii, B-iv, C-i, D-ii
(b) A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-ii
(c) A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
(d) A-iii, B-i, C-ii, D-iv
Answer
A
Question: Rights Issue are the shares, which :
(a) Are issued to the Direction of the company
(b) Are issued to existing shareholders of the company
(c) Are issued to promoters in consideration of their services
(d) Are issued to the vendors for purchasing assets.
Answer
B
Question: MATCH THE FOLLOWING:
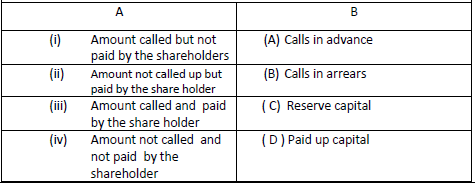
• Choose the correct option:
1. (i)-(B), (ii) -(A), (iii)-(D), (iv)-(C)
2. (i)-(A), (ii) -(B), (iii)-(C), (iv)-(D)
3. (i)-(D), (ii) -(C), (iii)-(A), (iv)-(B)
4. (i)-(B), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(A)
Answer
1.
Question: Match the following:
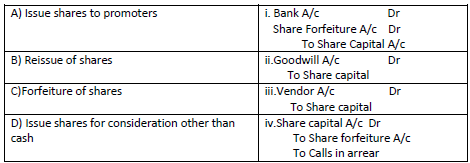
(a) A-i,B-ii,C-iii,D-iv
(b) A-ii,B-i,C-iv,D-iii
(c) A-ii,B-iv,C-i,D-iii
(d) A-ii,B-iii,C-iv,D-i
Answer:
B
Question: A company issued 10000 shares of Rs.10 each payable Rs.3 on application, Rs.4 on allotment, Rs.3 on first call and the balance on final call.
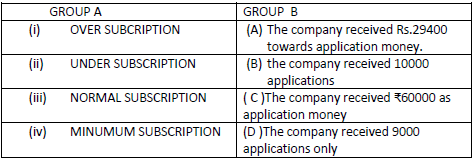
Choose the correct option:
1. (i)-(C), (ii) -(A), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(D)
2. (i)-(A), (ii) -(B), (iii)-(C), (iv)-(D)
3. (i)-(D), (ii) -(C), (iii)-(A), (iv)-(B)
4. (i)-(B), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(A)
Answer:
1.
Question: B Limited was registered with the share capital of Rs. 1 crore divided into equity shares of Rs. 10 each. It issued 9,00,000 equity shares to the general public at par payable as to Rs.3 an application Rs.3 allotment and balance in two equal calls.. The public had subscribed for 8, 50,000 shares. Till 31st March 2021 only first call had been made. All the money on the shares were received except from Mr. C a holder of 25,000 shares who did not pay call.
MATCH THE FOLLOWING:
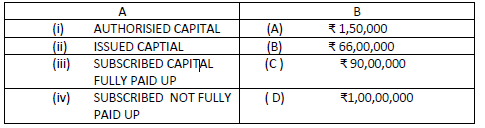
Choose the correct option:
1. (i)-(D), (ii) -(C), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(A)
2. (i)-(A), (ii) -(B), (iii)-(C), (iv)-(D)
3. (i)-(D), (ii) -(C), (iii)-(A), (iv)-(B)
4. (i)-(B), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(A)
Answer
1.
Question: MATCH THE FOLLOWING
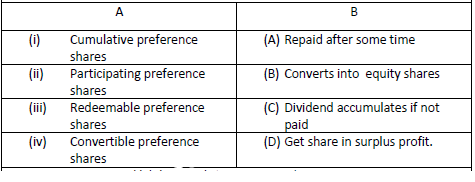
1. (i)-(B), (ii) -(A), (iii)-(C), (iv)-(D)
2. (i)-(C), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(A), (iv)-(B)
3. (i)-(C), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(B), (iv)-(A)
4. (i)-(B), (ii) -(D), (iii)-(C), (iv)-(A)
Answer
2.
Question: If the shareholder fails to pay the call money then his/her shares will be forfeited and the Directors after passing a resolution in the board meeting the forfeited shares can be reissued if authorized by its Articles of Association of the company.
1. Forfeited shares can be reissued at discount
2. Forfeited shares can be reissued at premium
3. Forfeited shares can be reissued at par
4. Forfeited shares cannot be reissued
a. All 1,2,3 and 4 are correct
b. 1,2,3 are correct and the 4 is incorrect.
c. Only 1 and 2 are correct remaining 3 and 4 are incorrect
d. Only 2 and 3 are correct remaining are incorrect
Answer
B
Question: If the applications are oversubscribed then allotment can be made as follows:
1. Excess application will be rejected.
2. Excess application will be fully adjusted towards allotment and calls
3. Excess applications will be partially rejected and partially adjusted towards allotment and calls.
4. Excess applications will be allotted in full without rejecting.
a. All 1,2,3 and 4 are correct
b. 1,2,3 are correct and the 4 is incorrect.
c. Only 1 and 2 are correct remaining 3 and 4 are incorrect
Only 2 and 3 are correct remaining are incorrect
Answer
A
Question: What is the correct sequence of events?
1. The company forfeited shares for non-payment of final call.
2. The company allotted the shares on pro rata basis.
3. The company reissued the forfeited shares at discount/par/premium.
4. The company issued equity shares of Rs.10 payable as follows: application (A) Rs.2, allotment (A) Rs.3 and the balance on calls.
(a) 4,2,1,3
(b) 1,2,3,4
(c) 3,2,1,4
(d) 1,3,4,1
Answer
A

