Please refer to Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Neural Control and Coordination
Objective Questions
Question. Which of the following is not a major part of brain?
(a) CNS
(b) Forebrain
(c) Hind brain
(d) Mid brain
Answer
A
Question. The name of nervous band connecting the cerebral hemisphere
(a) Corpus albicans
(b) Corpus callosum
(c) Corpus striatum
(d) Corpus spongiosum
Answer
B
Question. Association areas in cerebral cortex are
(a) Sensory areas
(b) Motor areas
(c) Responsible for intersensory associations, memory, and communications
(d) None of the above is correct
Answer
C
Question. Myelinated fibres of the tract forms
(a) White matter
(b) grey matter
(c) both
(d) Red matter
Answer
A
Question. Hypothalamus does not
(a) Control thermoregulation
(b) Control urge for eating and drinking
(c) Produces hormones that regulate the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormone
(d) Control creative thinking and consciousness
Answer
D
Question. Along with hypothalamus, limbic system is involved in the _____
(a) Regulation of sexual behaviour
(b) Expression of emotional reaction (e.g. excitement pleasure, rage and fear)
(c) Motivation
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Brain stem includes
(a) Mid brain only
(b) Hind brain only
(c) Mid brain and hind brain only
(d) Fore brain and hind brain only
Answer
C
Question. A. Cerebellum has very convoluted surface in order to provide the additional space for more neurons
B. The medulla is connected to the spinal cord
C. Medulla contains controlling centres for respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretion
Options :
(a) All are correct
(b) Only A is correct
(c) Only A and C are correct
(d) Only B is correct
Answer
A
Question. Reflex action is controlled by
(a) CNS
(b) PNS
(c) ANS
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. In reflex action, the reflex arc is formed by
(a) Muscle, receptor, brain
(b) Brain, spinal cord, muscle
(c) Receptor, spinal cord, muscle
(d) Muscle, spinal cord, receptor
Answer
C
Question. The nerves carrying impulses to CNS are known as
(a) motor
(b) efferent
(c) afferent
(d) mixed
Answer
C
Question. A bipolar neuron has
(a) 2 dendrites and 1 axon
(b) 2 axons and 1 dendrite
(c) 1 dendrite and 1 axon
(d) 2 axons and 2 dendrites
Answer
C
Question. During conduction of nerve impulse
(a) Na+ moves into axoplasm
(b) Na+ moves out of axoplasm
(c) K+ moves into axoplasm
(d) Ca++ moves into axoplasm
Answer
A
Question. Action potential of nerve cell is
(a) – 60 mV
(b) –80 mV
(c) +20 mV
(d) +30 mV
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following ions are required for nerve conduction ?
(a) Ca++, Na+ and K+
(b) Ca++ and Mg++
(c) Mg++ and K+
(d) Na+ and K+
Answer
A
Question. A typical value of resting membrane potential is
(a) – 40m V
(b) – 60m V
(c) – 70m V
(d) – 80m V
Answer
C
Question. The resting potential occurs because
(a) of reduced energy production by mitochondria.
(b) the action potential depletes transmitter substance.
(c) of the different concentrations of ions across the cell.
(d) the action potential causes axoplasmic transport back towards the cell body.
Answer
C
Question. The secretion of gastric juice is controlled by
(a) cerebellum
(b) ANS
(c) cerebrum
(d) medulla
Answer
D
Question. Purkinje cells are found in
(a) cerebellar cortex
(b) mammalian heart
(c) voluntary cells
(d) semicircular canal
Answer
C
Question. Part of mammalian brain controlling muscular coordination is
(a) cerebrum
(b) corpus callosum
(c) medulla oblongata
(d) cerebellum
Answer
D
Question. Part of brain responsible for hearing is
(a) cerebellum
(b) cerebrum
(c) medulla
(d) hypothalamus
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following cell in the central nervous system functionally equivalent to a Schwann cell?
(a) astrocyte
(b) neuron
(c) oligodendrocyte
(d) microglial cell
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a thin middle layer of cranial meninges?
(a) Duramater
(b) Arachnoid
(c) Piamater
(d) Optic nerve
Answer
B
Question. Which is not a reflex action?
(a) Swallowing of food
(b) Shivering in cold
(c) Salivation at choicest food
(d) Closure of eyelid by flashing light
Answer
B
Question. The thinned-out portion of retina where only cones are densely packed is called
(a) blind spot
(b) corpus luteum
(c) macula lutea
(d) fovea
Answer
D
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Electrical synapses are more common in our neural system than chemical synapses.
(b) The new potential in post-synaptic neuron may be either excitatory or inhibitory.
(c) Hypothalamus is the major coordination centre for sensory and motor signaling.
(d) The tracts of nerve fibres that connect two cerebral hemispheres are called corpora bigemina.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) The ear ossicle attached to tympanic membrane is malleus.
(b) Opsin (of rhodopsin) develops from vitamin A.
(c) The pressure on ear drum is equalized by Eustachian tube.
(d) Otolith organ consists of saccule and utricle.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is an example of conditioned reflex?
(a) Hand took up when piercing with a needle.
(b) Driving a vehicle.
(c) Eyes closed when any thing enter into it.
(d) In digestion food goes forward in alimentary canal.
Answer
B
Question. During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
(a) Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid.
(b) K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid.
(c) Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid.
(d) K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid.
Answer
A
Question. Which statement regarding ‘stapes’ is correct?
(a) It lies in the auditory meatus.
(b) It fits onto the oval window.
(c) It conducts sound vibrations to fenestra rotundus.
(d) It is analogus to columella auris.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is correct regarding a myelinated nerve fibre?
(i) It is always associated with an axon.
(ii) It allows rapid conduction of nerve impulses.
(iii) It allows slow conduction of nerve impulses.
(iv) It has nodes of Ranvier.
(a) Only (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (i), (ii), and (iii)
(c) Only (i), (ii), and (iv)
(d) Only (i), (iii), and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is correct about rods compared to cones?
(i) Rods are most numerous in the fovea.
(ii) Rods contain rhodopsin.
(iii) Rods produce general outlines of objects rather than sharp images.
(iv) Rods produce black and white but not colour images.
(a) (i), and (ii) only
(b) (ii), and (iiii) only
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) only
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The space within cochlea called scala media is filled with endolymph.
(b) The vestibular apparatus is composed of two semicircular canals and the otolith organ consisting of
the saccule and utricle.
(c) The external auditory meatus helps in equalizing the pressures on either sides of the ear drum.
(d) The membranes constituting cochlea, the reissner’s and basilar, divide the surrounding perilymph filled
bony labyrinth into an upper scala tympani and a lower scala vestibuli.
Answer
C
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The following diagram represent the reflex arc. Identify the parts labelled as A, B, C, D, E, F and G and choose the correct option

(a) A – sense organ; B – sensory nerve; C – dorsal horn; D – interneuron; E – ventral horn; F – motor nerve ; G – effector
(b) A – sense organ; B – sensory nerve; C – ventral horn; D – interneuron; E – dorsal horn; F – motor nerve; G – effector
(c) A – effector; B – motor nerve; C – dorsal horn; D – interneuron; E – ventral horn; F – sensory nerve; G – effector
(d) A – effector; B – motor nerve; C – ventral horn; D – interneuron; E – dorsal horn; F – sensory nerve; G – sense organ.
Answer
A
Question. In the given diagram which stage of conduction of nerve impulse through nerve fibre is observed?

(a) Polarization
(b) Resting potential
(c) Repolarization
(d) Depolarization
Answer
B
Question. The given diagram chows the axon terminal and synapse with few part labelled as A, B, C & D. Choose the correct combination of labelling from the given options.

(a) A- Synaptic vesicle, B- Axon terminal, C- Synaptic cleft, D- Postsynaptic membrane
(b) A- Axon terminal, B- Synaptic vesicle, CPostsynaptic membrane, D- Synaptic cleft.
(c) A- Synaptic vesicle, B- Synaptic cleft, C- Axon terminal, D- Post synaptic membrane
(d) A- Post synaptic membrane, B- Axon terminal, C- Synaptic vesicle, D- Synaptic cleft
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following options correctly represents the name of 1, 2, 3 and 4 is the given diagram of neuron?

(a) 1- Axon, 2- Dendrites, 3- Node of Ranvier, 4- Myelin sheath
(b) 1- Dendrites, 2- Axon, 3- Node of Ranvier, 4- Myelin sheath
(c) 1- Dendrites, 2- Cell body, 3- Myelin sheath, 4- Node of Ranvier
(d) 1- Axon, 2- Cell body, 3- Dendrites, 4- Node of Ranvier
Answer
C
Question. Refer the given figure of ear with few structure marked as I, II, III & IV. Which labelled structure converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
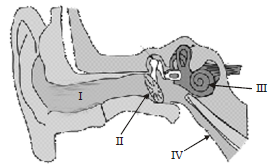
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is/are functions of structure labelled as ‘X’ in the given diagram of eye?

I. It provides attachment points for muscles that move the eye.
II. It maintains the shape of the eye ball.
III. It helps during accomodation.
IV. It is responsible for eye colour.
(a) I and II
(b) I, II and IV
(c) II, III and IV
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. The primary function of the structure labelled as X in the given figure is
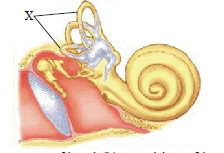
(a) movement of head
(b) position of head
(c) hearing
(d) vision
Answer
A
Directions : Refer the given figure of neuron structure with few parts labelled as 1, 2, 3, and 4 and answer the questions.

Question. Identify the part along which the sequence of impulse generation is repeated.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. Refer the given figure of eye in which few parts are labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4. Select the option which shows the correct identification of the part with its characteristics.

(a) 1 : Choroid, it contains ganglion cells, bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells.
(b) 2 : Iris, it is responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil and thus the amount of light reaching the retina.
(c) 3 : Blind spot, it is a yellowish pigmented spot called macula lutea with a central pit called the fovea.
(d) 4 : Cornea, it is a transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber.
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. For sound (good) reflex actions we require intact
(a) spinal cord
(b) cerebellum
(c) hypothalamus
(d) medulla oblongata
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is an example of a simple reflex ?
(a) Closing of eyes if an object suddenly approaches them.
(b) Climbing stairs in dark.
(c) Watering of mouth at the sight of delicious food.
(d) Tying laces while talking to and looking at another person.
Answer
A
Question. An example of autonomous nervous system is
(a) swallowing food
(b) pupillary reflex
(c) peristalsis of intestine
(d) knee-jerk response
Answer
C
Question. A person feels no sensation when he puts his hand over flame. The part of the brain which has damaged is
(a) cerebellum
(b) medulla oblongata
(c) diencephalon
(d) hypothalamus
Answer
D
Question. Sequence of meninges from inner to outside is
(a) Duramater – Arachnoid – Piamater
(b) Duramater – Piamater – Arachnoid
(c) Arachnoid – Duramater – Piamater
(d) Piamater- Arachnoid – Duramater
Answer
D
Question. You are watching a horror movie and you notice your heart is beating fast and mouth is dry. It is because of
(a) fight and flight response
(b) sympathetic nervous system
(c) parasympathetic nervous system
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. A person entering an empty room suddenly finds a snake right in front on opening the door. Which one of the following is likely to happen in his neuro-hormonal control system?
(a) Hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic division of brain.
(b) Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal cortex.
(c) Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal
medulla.
(d) Neurotransmitters diffuse rapidly across the cleft and transmit a nerve impulse.
Answer
C
Question. The part of an eye which acts like diaphragm of a photographic camera, is
(a) pupil
(b) iris
(c) lens
(d) cornea
Answer
B
Question. A person is wearing spectacles with concave lenses for correcting vision. While not using the glasses, the image of a distant object in his case will be formed
(a) on the blind spot.
(b) behind the retina.
(c) on the yellow spot.
(d) in front of the retina.
Answer
D



