Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements – I Class 11 Accountancy with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 11 Accountancy issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Accountancy for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 9 Financial Statements – I in Class 11 Accountancy provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 9 Financial Statements – I MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 9 Financial Statements – I MCQ Questions Class 11 Accountancy with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 9 Financial Statements – I Class 11 Accountancy
Question. Liability which is payable on the happening of an event is
(a) contingent liability
(b) fluctuating liability
(c) current liability
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Consider the following statement.
(i) Balance sheet contains only the balances of personal and real accounts.
(ii) Assets side of balance sheet is always equal to capital side.
(iii) Drawings are not shown in the balance sheet as it is a personal expense of the owner.
Alternatives
(a) Only (i) is correct
(b) Only (ii) and (iii) is correct
(c) All are correct
(d) All are incorrect
Answer
A
Question. Ram is the owner of a firm. He brought additional capital of ₹ 1,00,000 to the firm. The receipt of money in business is ……… .
(a) revenue receipt
(b) capital receipt
(c) revenue expenditure
(d) capital expenditure
Answer
B
Question. Capital expenditure ………. the earning capacity or ………. the operating expenses of a business.
(a) increases, reduces
(b) reduces, increases
(c) maintain, reduces
(d) reduces, maintain
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
(i) Revenue expenditure gives benefit within the accounting period.
(ii) Revenue expenditures are non-recurring in nature.
Alternatives
(a) Both (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (i)
(c) Only (ii)
(d) Neither (i) nor (ii)
Answer
B
Question. While calculating operating profit, the following are not taken into account
(a) normal transactions
(b) abnormal items
(c) expenses of a purely financial nature
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Profit and loss account is prepared ……… .
(a) for the whole year
(b) for a particular period
(c) on a particular date
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Operating profit earned by Harshad Mehta in 2020-21 was ₹ 8,50,000. His non-operating incomes were ₹ 75,000 and non-operating expenses were ₹ 1,87,500. Calculate the profit earned during the year.
(a) ₹ 7,37,500
(b) ₹ 9,62,500
(c) ₹ 5,87,500
(d) ₹ 11,12,500
Answer
A
Question. Match the following.
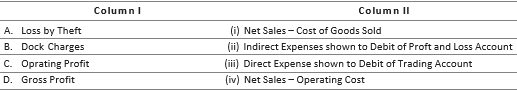
Codes
A B C D
(a) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(b) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
(c) (ii) (iii) (i) (iv)
(d) (iii) (ii) (i) (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Depreciation or the expired cost of fixed assets will be
(a) revenue expenditure
(b) capital expenditure
(c) deferred revenue expenditure
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The financial statements consist of
(a) trial balance
(b) profit and loss account
(c) balance sheet
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is correct?
(a) Net Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales − Sales Return
(b) Net Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales + Sales Return
(c) Net Sales = Total Sales − Credit Sales
(d) Net Sales = Sales + Credit Sales
Answer
A
Question. Opening Stock = ₹ 9,60,000
Purchases = ₹ 27 ,20,000
Sales = ₹ 39,00,000
Gross Profit is 30% on cost
Which of the following will be the amount of closing stock?
(a) ₹ 7,80,000
(b) ₹ 6,80,000
(c) ₹ 47,60,000
(d) ₹ 12,40,000
Answer
B
Question. Choose the correct chronological order of ascertainment of the following profits from the profit and loss.
(a) Operating Profit, Net Profit, Gross Profit
(b) Operating Profit, Gross Profit, Net Profit
(c) Gross Profit, Operating Profit, Net Profit
(d) Gross Profit, Net Profit, Operating Profit
Answer
C
Question. On which assumption the expenditure is classified as capital and revenue expenditure?
(a) Going concern assumption
(b) Accrual assumption
(c) Money measurement assumption
(d) Consistency assumption
Answer
A
Assertion-Reasoning MCQs :
There are the two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the
statements and choose the appropriate option from the options given below.
(a) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is wrong
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct
(c) Assertion (A) is wrong, but Reason (R) is correct
(d) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are wrong
Question. Assertion (A) Heavy advertising to launch a new product is deferred revenue expenditure.
Reason (R) Deferred revenue expenditure is a revenue expenditure that is incurred during an accounting period but its benefit extends beyond that accounting period.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A) Warehousing expenses, export duties, royalty, etc are shown to debit side of trading account.
Reason (R) Direct expenses are shown to debit side of trading account.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A) ₹ 10,000 spent on installing the machine is capital expenditure.
Reason (R) Capital expenditure increase the value of fixed assets and its benefits extend upto one accounting period.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A) Loan taken by Anuj Enterprises from SBI is revenue receipt.
Reason (R) Revenue receipts are those receipts which arise in normal course of business.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A) Closing stock is valued at cost or net realisable value whichever is higher.
Reason (R) According to conservatism principle, all prospective losses are taken into consideration butnot the prospective profits.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A) Advertising, packing expenses, interest paid on loan, legal expenses are shown to debit side of profit and loss account.
Reason (R) All indirect expenses are shown to debit side of profit and loss account.
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs :
Shamita studies in class 11th in Happy Public School. She comes from a CA family. She has two CA sisters and her father CA Arjun owns his firm at Darya Ganj.
She spent most of her day reading novels and devote very less hours for study. As a result, she scored very less marks in Ist term exam in accountancy. Ms Ritika Sachdeva, her accountancy teacher has now decided to give remedial classes to all weak students. Her father is also giving his time to teach her. One day, her teacher introduced the chapter financial statements in class but Shamita found it very hard. She asked her sister CA Isha to teach her financial statements. Isha showed financial statements of their father’s firm which aroused her curiosity. She even grasped the concept quickly of trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Isha realised that Shamita can only progress if she is shown visual aids, real objects, things, etc. She teaches her with this method and is successful as Shamita got good marks.
Question. Freight inward of ₹ 5,600 is outstanding at the end of year. Where it is recorded in final accounts?
(a) Trading account and balance sheet
(b) Profit and loss account and balance sheet
(c) Trading account and profit and loss account
(d) Trading account (debit) and balance sheet (assets)
Answer
A
Question. Trading account is a
(a) personal account
(b) real account
(c) nominal account
(d) asset account
Answer
C
Question. What is prepared in sole proprietorship business with the objective of calculating gross profit or gross loss of the business?
(a) Trading account
(b) Profit and loss account
(c) Balance sheet
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Closing stock is given outside of the trial balance with book value ₹ 60,000 and market value of ₹ 80,000 as on 31st March, 2020. It will be recorded in balance sheet at which amount?
(a) ₹ 60,000
(b) ₹ 80,000
(c) ₹ 20,000
(d) ₹ 1,40,000
Answer
A
Aditi is an engineer, who is working as a content developer and educator at ABC Limited. Along with her job, she is also preparing for various competitive exams.
During weekend, Aditi was studying about financial statements. After doing all the theory, she tried to attempt a question but she got struck as her balance sheet total didn’t agree. Immediately, she called her friend Shweta and asked her to find her mistakes.
Shweta found her conceptual errors and also sent her correct solution for the same.
Following trading account and profit and loss account as on 31st March, 2020 and balance sheet as at that date were prepared by Aditi from the balances as on 31st March, 2020 given in her book.
Question given in Aditi’s book
From the following balances, as on 31st March, 2020, prepare trading and profit and loss account and the balance sheet.

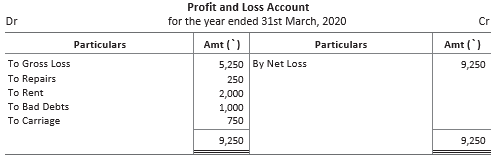
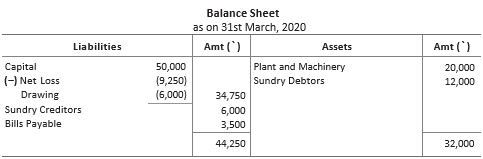
Question. Total of balance sheet is ……… .
(a) ₹ 94,250
(b) ₹ 44,250
(c) ₹ 84,250
(d) ₹ 74,250
Answer
B
Question. Opening Stock + Purchases − Purchases Return + Direct Expenses − Closing Stock =……… .
(a) Cost of Raw Material
(b) Gross Profit
(c) Closing Capital
(d) Cost of Goods Sold
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is correct amount of gross profit/gross loss?
(a) Gross profit ₹ 2,500
(b) Gross loss ₹ 2,500
(c) Gross profit ₹ 5,000
(d) Gross loss ₹ 5,000
Answer
B
Question. Which of the undermentioned net profit/net loss is correct?
(a) Net loss ₹ 9,250
(b) Net profit ₹ 9,250
(c) Net profit ₹ 10,000
(d) Net loss ₹ 10,000
Answer
A


