Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 12 Chemistry issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements in Class 12 Chemistry provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Chemistry
Question. In blast furnace, maximum temperature is in
(a) zone of fusion
(b) zone of combustion
(c) zone of slag combustion
(d) zone of reduction
Answer
B
Question. When 1.164 g of a certain metal sulphide was roasted in air, 0.972 g of the metal oxide was formed. If the oxidation number of the metal is +2, calculate the molar mass of the metal.
(a) 25.67 g
(b) 31.56 g
(c) 47.35 g
(d) 65 g
Answer
D
Question. Among the following statement, the incorrect one is
(a) calamine and siderite are carbonates
(b) argentite and cuprite are oxides
(c) zinc blende and pyrites are sulphides
(d) malachite and azurite are ores of copper
Answer
B
Question. In the process of extraction of gold,
Roasted gold ore + CN− + H2O →O2 [X ] + OH−
[X] + Zn→[Y] + Au
Identify the complexes [X ] and [Y ].
(a) X = [Au(CN)2]−,Y = [Zn(CN)4]2−
(b) X = [Au(CN)4]3−,Y = [Zn(CN)4]2−
(c) X = [Au(CN)2]−,Y = [Zn(CN)6]4−
(d) X = [Au(CN)4]−,Y = [Zn(CN)4]2−
Answer
A
Question. Which ore contains both iron and copper?
(a) Cuprite
(b) Chalcocite
(c) Chalcopyrite
(d) Malachite
Answer
C
Question. Cassiterite is concentrated by
(a) levigation
(b) electromagnetic separation
(c) floatation
(d) liquefaction
Answer
B
Question. The methods chiefly used for the extraction of lead and tin from their ores are respectively
(a) self reduction and carbon reduction
(b) self reduction and electrolytic reduction
(c) carbon reduction and self reduction
(d) cyanide process and carbon reduction
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following benefaction processes is used for the mineral, Al2O3 ⋅2H2O?
(a) Froth floatation
(b) Leaching
(c) Liquation
(d) Magnetic separation
Answer
A
Question. Which metal can’t be obtained from electrolysis?
(a) Ca
(b) Mg
(c) Cr
(d) Al
Answer
C
Question. Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching the metal with CN− ion. The metal is recovered by
(a) displacement of metal by some other metal from the complex ion
(b) roasting of metal complex
(c) calcination followed by roasting
(d) thermal decomposition of metal complex
Answer
A
Question. Which series of reactions correctly represents chemical relations related to iron and its compound?
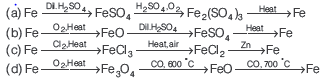
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following metals is obtained by electrolytic reduction process?
(a) Fe
(b) Cu
(c) Ag
(d) Al
Answer
D
Question. Use the relationship, ΔG° = −nFE °cell to estimate the minimum voltage required to electrolyse Al2O3 in the Hall-Heroult process
ΔfG°(Al2O3 ) = −1520 kJ mol−1
ΔfG°(CO2 ) = −394 kJ mol−1
(a) 0.8 V
(b) 1.60 V
(c) 2.8 V
(d) 3.0 V
Answer
B
Question. Zone-refining is based on the principle that
(a) impurities of low boiling metals can be separated by distillation
(b) impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal
(c) different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent
(d) vapours of volatile compound can be decomposed into pure metal
Answer
B
Question. Which method of purification is represented by the following equation?
Ti(s) + 2I2(g) →523 K
TiI4(g) →1700 K Ti(s) + 2I2(g)
(a) Zone-refining
(b) Cupellation
(c) Polling
(d) van-Arkel
Answer
D
Question. Match the following and choose the correct options.
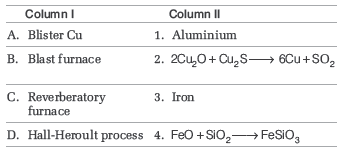
Codes
A B C D
(a) 4 3 1 2
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 4 1 3 2
(d) 2 4 3 1
Answer
B
Question. In Goldschmidt aluminothermic process which of the following reducing agent is used?
(a) Calcium
(b) Coke
(c) Al powder
(d) Sodium
Answer
C
Question. Electrolytic refining is used to purify, which of the following metals?
(a) Cu and Zn
(b) Ge and Si
(c) Zr and Ti
(d) Zn and Hg
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following does not represent correct method?
(a) TiCl2 + 2Mg → Ti + 2MgCl2 : Kroll
(b) Ni(CO)2 → Ni + 4CO : Mond
(c) Ag2CO3 → 2Ag + CO2 + 1/2 O2 : van-Arkel
(d) ZnI4 → Zn+ 2I2 : van-Arkel
Answer
C
Question. During the process of electrolytic refining of copper, some metals present as impurity settle as ‘anode mud’. These are
(a) Fe and Ni
(b) Ag and Au
(c) Pb and Zn
(d) Se and Ag
Answer
B
Question. An impure metal is allowed to react with carbon monoxide at 50°C and the volatile gas thus, formed is collected and heated further to about 200°C. This process gives the metal of 99.99% purely. What is the metal?
(a) Fe
(b) Cr
(c) Co
(d) Ni
Answer
D
Question. Of the following reduction processes,
I. Fe2O3 + 3C(s) → Fe + 3CO
II. ZnO + C(s) → Zn + CO
III. Ca3(PO4)2 + C(s) → P
IV. PbO + C(s) → Pb + CO
Correct processes are
(a) All of these
(b) All but III
(c) All but IV
(d) Both II and IV
Answer
A
Question. Calcination is the process in which
(a) removal of water takes place
(b) decomposition of carbonates takes place
(c) oxidation of sulphides takes place
(d) All of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following reactions is an example of auto-reduction?
(a) Fe3O4 + 4C→ 3Fe + 4CO2
(b) Cu2O + C → 2Cu + CO
(c) Cu2+ (aq)+ Fe (s) → Cu(s)+ Fe2+ (aq)
(d) Cu2O +1/2Cu2S → 3Cu +1/2 SO2
Answer
D
Question. In the context of the Hall-Heroult process for the extraction of Al, which of the following statement is false?
(a) CO and CO2 are produced in this process
(b) Al2O3 is mixed with CaF2 which lowers the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity
(c) Al3+ is reduced at the cathode to form Al
(d) Na3AlF6 serves as the electrolyte
Answer
D
Question. Bauxite ore is made up of Al2O3 + SiO2 + TiO2 + Fe2O3. This ore is treated with conc. NaOH solution at 500 K and 35 bar pressure for few hours and filtered hot. In the filterate, the species present are
(a) NaAl(OH)4
(b) Na2Ti(OH)6
(c) Na[Al(OH)4] and Na2SiO3
(d) Na2SiO3
Answer
C
Question. Consider the following reactions:
Ag2S +NaCN → (A)
(A) + Zn → (B)
(B) is a metal. Hence (A) and (B) are
(a) [Na2Zn(CN)4], Zn
(b) Na [Ag(CN)2], Ag
(c) Na2[Ag(CN)4], Ag
(d) Na3[Ag(CN)4], Ag
Answer
B
Question. When copper ore is mixed with silica in a reverberatory furnace, copper matte is produced. The copper matte contains
(a) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (II)
(b) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (III)
(c) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (II)
(d) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (III)
Answer
A
Question. Extraction of zinc from zinc blende is achieved by
(a) electrolytic reduction
(b) roasting followed by reduction with carbon
(c) roasting followed by reduction with another metal
(d) roasting followed by self reduction
Answer
B
Question. The major role of fluorspar (CaF2 ) which is added in small quantities in the electrolytic reduction of alumina dissolved in fused cryolite (Na3AlF6) is
(a) that of a catalyst
(b) to make the fused mixture very conducting
(c) to lower the temperature of the melt
(d) to decrease the rate of oxidation of carbon at anode
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements about the advantage of roasting of sulphide ore before reduction is not true?
(a) ΔfG° of the sulphide is greater than those of CS2 and H2S
(b) ΔfG° is negative for roasting of sulphide ore to oxide
(c) Roasting of sulphide to oxide is thermodynamically feasible
(d) Carbon and hydrogen are suitable reducing agents for metal sulphides
Answer
D
Question. From the Ellingham graph on carbon, which of the following statements is false?
(a) CO reduces Fe2O3 to Fe at temperature less than 983 K
(b) CO is less stable than CO2 at temperature more than 983 K
(c) CO reduces FFe2O3 to Fe in the reduction zone of blast furnace.
(d) CO2 is more stable than CO at temperature less than 983 K
Answer
B
Question In the Baeyer’s process,
(a) Al2O3 goes into solution as soluble Al(OH)4− , while other basic oxides as TiO2 and Fe2O3 remain insoluble.
(b) Al2O3 changes to AlN which in turn decomposed by H2O
(c) Al2O3 changes to Al2 (CO3)3 which changes to AlCl3
(d) None of the above is correct
Answer
A
Question. In the metallurgy of sodium by electrolysis, excess of calcium chloride is mixed with sodium chloride to
(a) make the latter a good conductor
(b) make the latter soft
(c) generate more energy for the electrolytic cell
(d) assist liquefaction of the later much lower temperature
Answer
D
Question. In the electrolytic method for obtaining aluminium from purified bauxite, cryolite is added to
(a) minimise the heat loss due to radiation
(b) protect aluminium produced from oxygen
(c) dissolve bauxite and increases its conductivity
(d) lower the melting point of bauxite
Answer
C
Question. The value of ΔfG° for the formation of Cr2O3 is –540 kJ mol−1 and that of Al2O3 is –827 kJ mol−1. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 with Al is feasible reaction?
(a) The data is incomplete
(b) The reaction is feasible
(c) The reaction is not feasible
(d) The reaction may or may not be feasible
Answer
B
Question. When copper pyrites is roasted in excess of air, a mixture of CuO + FeO is formed. FeO is present as impurities. This can be removed as slag during reduction of CuO. The flux added to form slag is
(a) SiO2, which is an acidic flux
(b) limestone, which is a basic flux
(c) SiO2, which is a basic flux
(d) CaO, which is a basic flux
Answer
A
Question. In the extraction of nickel by Mond’s process, the metal is obtained by
(a) electrochemical reduction
(b) thermal decomposition
(c) chemical reduction by aluminium
(d) reduction by carbon
Answer
B
Question. Froth-floatation process is used for the concentration of sulphide ore. Which of the following processes is correct?
(a) It is based on the difference in wettability of different minerals
(b) In this process sodium ethyl xanthate, C2H5OCS2Na is used as collector
(c) In this process NaCN is used as depressant in the mixture of ZnS and PbS when ZnS forms soluble complex and PbS forms froth
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Refining of impure copper with zinc impurity is to be done by electrolysis using electrodes as
Cathode Anode
(a) Pure copper Pure zinc
(b) Pure zinc Pure copper
(c) Pure copper Impure copper
(d) Pure zinc Impure zinc
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following ores is best concentrated by froth floatation method?
(a) Siderite
(b) Galena
(c) Malachite
(d) Magnetite
Answer
B
Question. The process of converting hydrated alumina into anhydrous alumina is called
(a) roasting
(b) smelting
(c) dressing
(d) calcination
Answer
D

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Chemistry with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.


