Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation Class 10 Mathematics with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 10 Mathematics issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 10 Mathematics for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation in Class 10 Mathematics provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation MCQ Questions Class 10 Mathematics with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation Class 10 Mathematics
Question. Equation ax2 + 2x + 1 has one double root if :
(a) a = 0
(b) a = − 1
(c) a = 1
(d) a = 2
Answer
C
Question. Solve for x : (x + 2) (x − 5) (x − 6) (x + 1) = 144
(a) −1, −2, −3
(b) 7, − 3, 2
(c) 2, − 3, 5
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The value of k (k > 0) for which the equations x2 + kx + 64 = 0 and x2 − 8x + k = 0 both will have real roots is :
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) − 64
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. If the roots, x1 and x2, of the quadratic equation x2 −2x + c = 0 also satisfy the equation 7x2 − 4×1 = 47, then which of the following is true ?
(a) c = −15
(b) x1 = 5, x2 = 3
(c) x1 = 4.5, x2 = − 2.5
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Solve : √2x + 9 − √x −4 = 3
(a) 4, 16
(b) 8, 20
(c) 2, 8
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. If the roots of the equation x2 −bx/ac−c =m−1/m+1 are equal and of opposite sign, then the value of m will be :
(a) a−b/a+b
(b) b−a/a+b
(c) a+b/a−b
(d) b+a/b−a
Answer
A
Question. If a, b are the roots of the equation x2 + 2x + 4 = 0, then 1/α3+1/β3 is equal to :
(a) − 1/ 2
(b) 1/ 4
(c) 32
(d) 1/ 32
Answer
B
Question. Solve for x : 2[x2 +1/x2] −9[x−1/x] +14 = 0 :
(a) 1/ 2 , 1, 2
(b) 2, 4, 1/ 3
(c) 1 /3 , 4, 1
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. Solve for x : √x2 + x−6−x2 + 2 = √x2 −7x + 10, + x ∈ R :
(a) 2, 6, 10 − 3
(b) 2, 6
(c) −2, −6
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. If the equation (3x)2 + (27 × 31/k − 15) x + 4 = 0 has equal roots, then k =
(a) − 2
(b) −1/2
(c) 1/ 2
(d) 0
Answer
B
Question. What does the following graph represent ?

(a) Quadratic polynomial has just one root.
(b)Quadratic polynomial has equal roots.
(c)Quadratic polynomial has no root.
(d) Quadratic polynomial has equal roots and con- stant term is non-zero.
Answer
D
Question. If the roots of the equations (c2−ab)x2−2(a2−bc)x+(b2−ac)=0 for a ∈ 0 are real and equal, then the value of a3+b3+c3 is
(a) abc
(b) 3abc
(c) zero
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. If, α, β are the roots of X2 − 8X+P=0 and α2+β2 =40. then the value of P is
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 14
Answer
C
Question. Consider a polynomial ax2 + bx + c such that zero is one of it’s roots then
(a) c = 0, x = −b a satisfies the polynomial equation
(b) c ¹ 0, x = −a b satisfies the polynomial equation
(c) x = −b a satisfies the polynomial equation.
(d) Polynomial has equal roots.
Answer
A
Question. Consider a quadratic polynomial f(x) = ax2 − x + c such that ac > 1 and it’s graph lies below x-axis then:
(a) c=0,x=−b/a
(b) c≠0,x=−a/b
(c) x=−b/a
(d) x=−b/a
Answer
B
Question. If both the roots of the equations x2 + mx + 1 = 0 and (b − c) x2 + (c − a) x + (a − b) = 0 are common, then :
(a) m = − 2
(b) m = − 1
(c) m = 0
(d) m = 1
Answer
A
Question. If α,β are the roots of a quadratic equation x2 − 3x + 5 = 0 then the equation whose roots are (a2 − 3a + 7) and (b2 − 3b + 7) is :
(a) x2 + 4x + 1 = 0
(b) x2 − 4x + 4 = 0
(c) x2 − 4x − 1 = 0
(d) x2 + 2x + 3 = 0
Answer
B
Question. If α, β are the roots of the equation x2 + 7x + 12 = 0, then the equation whose roots are (α + β)2 and (α − β)2 is :
(a) x2 + 50x + 49 = 0
(b) x2 − 50x + 49 = 0
(c) x2 − 50x − 49 = 0
(d) x2 + 12x + 7 = 0
Answer
B
Question. The expression a2x2 + bx + 1 will be positive for all x ∈ R if :
(a) b2 > 4a2
(b) b2 < 4a2
(c) 4b2 > a2
(d) 4b2 < a2
Answer
B
Question. For what value of a the curve y = x2 + ax + 25 touches the x-axis :
(a) 0
(b) ± 5
(c) ± 10
(d) None
Answer
C
Question. If a, b are roots of the quadratic equation x2 + bx − c = 0, then the equation whose roots are b and c is
(a) x2 + ax − b = 0
(b) x2 − [(α + β) + ab] x − αβ (α + β) = 0
(c) x2 + (αβ + α + β) x + αβ (α + β) = 0
(d) x2 + (αβ + α + β) x − αβ (α + β) = 0
Answer
C
Question. The number of real solutions of x −1/x2 −4 =2 −1/x2 −4 is :
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) Infinite
Answer
A
Question. Solve for x : x6 − 26x3 − 27 = 0
(a) − 1, 3
(b) 1, 3
(c) 1, − 3
(d) −1, −3
Answer
A
Question. The value of the expression x2 + 2bx + c will be positive for all real x if :
(a) b2 − 4c > 0
(b) b2 − 4c < 0
(c) c2 < b
(d) b2 < c
Answer
C
Question. If the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are imaginary then for all values of a, b, c and x ∈ R, the expression a2x2 + abx + ac is
(a) Positive
(b) Non-negative
(c) Negative
(d) May be positive, zero or negative
Answer
D
Question. The coefficient of x in the equation x2+px+p=0 was wrongly written as 17 in place of 13 and the roots thus found were −2 and −15. The roots of the correct equation would be
(a) −4, −9
(b) −3, −10
(c) −3, −9
(d) −4, −10
Answer
B
Question. If a and b are the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, then the value of α2/β+β2/α is
(a) 2bc−a3/b2c
(b) 3abc−b3/a2c
(c) 3abc−b2/a3c
(d) ab−b2c/2b2c
Answer
B
Question. If the equations x2 + bx + c = 0 and x2 + cx + b = 0, (b ∈ c) have a common root then :
(a) b + c = 0
(b) b + c = 1
(c) b + c + 1 = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If both the roots of the equations k(6x2 + 3) + rx + 2x2 − 1 = 0 and 6k (2x2 + 1) + px + 4x2 − 2 = 0 are common, then 2r − p is equal to :
(a) 1
(b) − 1
(c) 2
(d) 0
Answer
D
Question. If the ratio between the roots of the equation lx2+mx + n= 0 is p:q, then the value of √p/ q +√q/p+√n/l is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 0
(d) −1
Answer
A
Question. The integral values of k for which the equation (k − 2) x2 + 8x + k + 4 = 0 has both the roots real, distinct and negative is :
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) − 4
Answer
C
Question. Solve : √2x + 9 + x = 13 :
(a) 4, 16
(b) 8, 20
(c) 2, 8
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Find the root of the quadratic equation bx2−2ax+a=0
(a) √b/√b±√a−b
(b) √a/√b±√a−b
(c) √a/√a±√a−b
(d) √a/√a±√a+b
Answer
C
Question. The equation √x + 1− √x −14 = √4x −1 + -=- has :
(a) No solution
(b) One solution
(c) Two solutions
(d) More than two solutions
Answer
A
Question. The number of real roots of the equation (x − 1)2 + (x − 2)2 + (x − 3)2 = 0 :
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 6
Answer
A
Question. If 4 is a solution of the equation x2+3x+k=10, where k is a constant, what is the other solution ?
(a) −18
(b) −7
(c) −28
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. If x2 − ax − 21 = 0 and x2 − 3ax + 35 = 0 ; a > 0 have a common root, then a is equal to :
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer
C
Question. The adjoining figure shows the graph of y = ax2 + bx + c. Then which of the following is correct :

(i) a > 0 (ii) b > 0
(iii) c > 0 (iv) b2 < 4ac
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) & (iv)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The values of a for which the quadratic equation (1 − 2a) x2 − 6ax − 1 = 0 and ax2 − x + 1 = 0 have at least one root in common are :
(a) 1/ 2 , 2/ 9
(b) 0, 1/ 2
(c) 2/ 9
(d) 0, 1/ 2 , 2/ 9
Answer
C
Question. If the quadratic equation 2x2 + ax + b = 0 and 2x2 + bx + a = 0 (a ∈ b) have a common root, the value of a + b is :
(a) − 3
(b) − 2
(c) − 1
(d) 0
Answer
B
Question. The roots of the equation |x2 − x − 6| = x + 2 are
(a) − 2, 1, 4
(b) 0, 2, 4
(c) 0, 1, 4
(d) −2, 2, 4
Answer
D
Question. If, l, m, n are real and l=m, then the roots of the equations (l−m)x2−5(l+m)x−2(l−m)=0 are
(a) Real and Equal
(b) Complex
(c) Real and Unequal
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. In a family, eleven times the number of children is greater than twice the square of the number of children by 12. How many children are there ?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 5
Answer
B
Question. Find all the integral values of a for which the quad- ratic equation (x a) (x 10) + 1 = 0 has integral roots :
(a) 12, 8
(b) 4, 6
(c) 2, 0
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. The equation x − 2/x−1 = 1− 2/x−1 has
(a) Two roots
(b) Infinitely many roots
(c) Only one root
(d) No root
Answer
D
Question. The value of x which satisfy the expression : (5 + 2√)x2−3 = 10
(a) ± 2, ±√ 3
(b) ± √2 , ± 4
(c) ± 2, ±√ 2
(d) 2,√ 2 , √3
Answer
C
Question. Graph of y = ax2 + bx + c is given adjacently. What conclusions can be drawn from the graph?
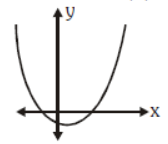
(i) a > 0 (ii) b < 0
(iii) c < 0 (iv) b2 − 4ac > 0
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) & (iv
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
Answer
B
Question. The value of k, so that the equations 2x2 + kx − 5 = 0 and x2 − 3x − 4 = 0 have one root in common is :
(a) − 2, − 3
(b) − 3, −27 /4
(c) − 5, − 6
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. If x2 − (a + b) x + ab = 0, then the value of (x − a)2 + (x − b)2 is
(a) a2+b2
(b) (a+b)2
(c) (a−b)2
(d) a2−b2
Answer
C
Question. If the expression x2 − 11x + a and x2 − 14x + 2a must have a common factor and a ∈ 0, then the common factor is :
(a) (x − 3)
(b) (x − 6)
(c) (x − 8)
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. If the equation x2 + bx + ca = 0 and x2 + cx + ab = 0 have a common root and b ∈ c, then their other roots will satisfy the equation :
(a) x2 − (b + c) x + bc = 0
(b) x2 − ax + bc = 0
(c) x2 + ax + bc = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The value of m for which one of the roots of x2 − 3x + 2m = 0 is double of one of the roots of x2 − x + m = 0 is :
(a) 0, 2
(b) 0, − 2
(c) 2, − 2
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. The sum of the roots of 1/x+a + 1/x + b =1/c is zero.The product of the roots is
(a) 0
(b) 1/2(a+b)
(c) −1/2(a2+b2)
(d) 2(a2 + b2)
Answer
C
Question. The sum of all the real roots of the equation lx −2l2 +lx−2 l−2= 0 is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. For the equation 3x2 + px + 3 = 0, p > 0, if one of the roots is square of the other, then p =
(a) 1/ 3
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 2/ 3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a quadratic equation?
(a) x2 + 2x + 1 = (4 – x)2 + 3
(b) – 2x2 = (5 – x) (2x – 2/5)
(c) (k + 1) x2 + 3/2 x = 7 (where k = – 1)
(d) x3 – x2 = (x – 1)3
Answer
D
Question. The degree of quadratic equation is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 5
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following equations has 2 as a root?
(a) x2 – 4x + 5 = 0
(b) x2 + 3x – 12 = 0
(c) 2x2 – 7x + 6 = 0
(d) 3x2 – 6x – 2 = 0
Answer
C
Question. The roots of the quadratic equation x2 – 0.04 = 0 are
(a) ± 0.2
(b) ± 0.02
(c) 0.4
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question. In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): The equation x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2 is a quadratic equation.
Reason (R): Any equation of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0 where a π 0, is a quadratic equation.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): (2x – 1)2 – 4x2 + 5 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
Reason (R): x = 0, 3 are the roots of the equation 2x2 – 6x = 0.
Answer
B
Question. The roots of the equation 4/3 x2 – 2x + 3/4 = 0 are
(a) 2/3 , 3/2
(b) 3/4 , 3/4
(c) 1/2 , – 1/2
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The required solution of 4x2 – 25x = 0 are
(a) x = 0, x = 12/7
(b) x = 0, x = 25/4
(c) x = 1, x = 5/9
(d) x = 1, x = 12/7
Answer
B
In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): When the quadratic equation 6x2 – x – 2 = 0 is factorised, we get its roots as 2/3 and − 1/2 ,
Reason (R): 6x2 – x – 2 = 0 ⇒ 2x(3x – 2) + (3x – 2) = 0 ⇒ (3x – 2) (2x + 1) = 0 ⇒ x= 2/3 , – 1/2
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): If x2 x − (√3 + 1) + √3 = 0, then x2 – √3x – x + √3 = 0
⇒ x(x − √3) − 1(x − √3) = 0 ⇒ (x − √3) (x − 1) = 0 ⇒ x = √3 , 1
Reason (R): If we can factorise ax2 + bx + c, a π 0 into a product of two linear factors, then the roots of the quadratic
equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 can be found by equating each factor to zero.
Answer
A
Question. The discriminant of the quadratic equation 4x2 – 6x + 3 = 0 is:
(a) 12
(b) 84
(c) 2 3
(d) –12
Answer
D
Question. The roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are given by -b ± √b2 – 4ac/2ac if b2 – 4ac .
(a) < 0
(b) ≤ 0
(c) > 0
(d) ≥ 0
Answer
D
Question. The quadratic formula was given by an ancient Indian mathematician.
(a) Sridharacharya
(b) Aryabhata
(c) Brahmagupta
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The area of a rectangular cardboard is 2 80 cm . If its perimeter is 36 cm, find its length.
(a) 40 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 8 cm
Answer
B
Question. If the product of the roots of x2 – 3x + k = 10 is – 2, what is the value of’ k’?
(a) -2
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d)-8
Answer
B
Question. When are the roots of a quadratic equation real and equal?
(a) When the discriminant is positive.
(b) When the discriminant is zero.
(c) When the discriminant is negative.
(d) When the discriminant is non-negative.
Answer
B
Question. Identify the correct statement.
(a) The roots of the quadratic equation 2y2 + 9y = 0 0 are 0 and -9/2 .
(b) The value of ‘k’ for which 4m2 + k -15 = 0 has a root m = 3 is 7.
(c) The quadratic equation (4x – 11)2 = 0 has two distinct roots.
(d) 7x2 – 12x – 18 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
Answer
A
Question. If α and β are the roots of the equation x2 -3x + 2 = 0 , which of the following is the equation whose roots are (α +1) and (β +1) ?
(a) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
(b) x2 – 5x – 6 = 0
(c) x2 – 5x – 6 = 0
(d) x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
Answer
D
Question. Find the roots of 3x2 -2√6x + 2 = 0 .
(a) 2/√3 , 2/√3
(b) √2/√3 , √2/√3
(c) √2/3 , √3/2
(d) √2/3 , √3/3
Answer
B
Question. If 2a2 + a – 2 = 1 and a >0, find ‘a’.
(a) 3/2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) -1
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a quadratic equation?
(a) x – 5/x = x2
(b) x2 + 2/x2 = 1
(c) 2x2 + 3√x + 4 = 0
(d) x2 – 1 = 2x2 + 4
Answer
D
Question. The quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has no real root. Which of the following is true?
(a) b2 – 4ac < 0
(b) b2 – 4ac + 0
(c) b2 – 4ac > 0
(d) b2 + 4ac < 0
Answer
A
Question. The perimeter and area of a rectangular park are 80 m and 400 m2 . What is its length?
(a) 20m
(b) 15m
(c) 30m
(d) 40m
Answer
A
Question. The discriminant of the equation 9x2 + 6x + 1 = 0 is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
A
Question. If D is the discriminant of the equation x2 + 2x – 4, then 2D is:
(a) 20
(b) 40
(c) 60
(d) 80
Answer
B
Question. In the following question, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(1) Assertion (A): The values of x are – a/2 , a for a quadratic equation 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0.
Reason (R): For quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, x = -b ± √b2 – 4ac/2ac
Answer
D

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 4 Quadratic Equation Class 10 Mathematics with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.

