Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal Class 11 Economics with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 11 Economics issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal in Class 11 Economics provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal MCQ Questions Class 11 Economics with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal Class 11 Economics
Question. —– refers to disposal of equity of public sector units in the market
a) Globalization
b) Privatization
c) Liberalization
d) Disinvestment
Answer
D
Question. Outsourcing is good for India because
a) It provides employment to large number of unemployed
b) It provides excellence in a particular field
c) Both a and b
d) Neither a nor b
Answer
C
Question. The highest GST rate applicable now is
a) 28%
b) 12%
c) 18%
d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. It refers to contracting out some of its activities to a third party which were earlier performed by the organization
a) Globalization
b) Outsourcing
c) Privatization
d) Liberalization
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a policy initiated under New Economic Policy?
a) Liberalization
b) Privatization
c) Globalization
d) Licensing
Answer
D
Question. Quantitative restrictions on imports of manufactured consumer goods and agricultural products were also fully removed from
a) 1980
b) 1991
c) 2001
d) 1995
Answer
C
Question. Reforms have not been able to benefit agriculture because of
a) Public investment in agriculture sector especially in infrastructure has fallen
b) Rise in subsidy
c) Rise in import duties on agriculture products
d) Shift from production of cash crops to food crops
Answer
A
Question. On which date did PM Narendra Modi address the Indian people announcing the demonetization of RS 5OO AND RS 1000
a) 8 Oct 2017
b) 8 Nov 2016
c) 8 Nov 2017
d) 8 Oct 2016
Answer
B
Question. GST was introduced in India with effect from
a) 1/7/2017
b) 1/7/2016
c) 1/7/2018
d) 1/7/2019
Answer
A
Question. When was the New Economic Policy announced?
a) June 1991
b) July 1991
c) May 1991
d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. At present how many industries are exclusively reserved for the public sector in India?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Answer
B
Question. When was WTO founded?
a) 1948
b) 1951
c) 1991
d) 1995
Answer
D
Question. Which Act has been enacted in place of MRTP Act ?
a) Competition Act
b) Monopoly Act
c) Licensing Act
d) Foreign Exchange Act
Answer
A
Question. Trade between two countries is known as
a) Bilateral Trade
b) Multi lateral Trade
c) Both a and b
d) Neither a nor b
Answer
A
Question. What is the other name of World Bank?
a) World Health Organization
b) World Trade Organization
c) International Monetary Fund
d) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
Answer
D
Question.Which of the organization replaced General Agreement on Trade and Tariff
a) International Monetary Fund
b) United Nations Organization
c) World Trade Organization
d) World Health Organization
Answer
C
Question. GATT was established in the year:
a) 1958
b) 1948
c) 1968
d) 1995
Answer
B
Question. Financial sector reforms mainly relate to :
a) Banking sector
b) Foreign Exchange Market
c) Both a and b
d) Insurance sector
Answer
C
Question. At present how many member countries WTO has?
a) 150
b) 164
c) 159
d) 190
Answer
B
Question. —refers to the transfer of assets or services function from public to private ownership?
a) Globalization
b) Privatization
c) Disinvestment
d) Liberalization
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns:
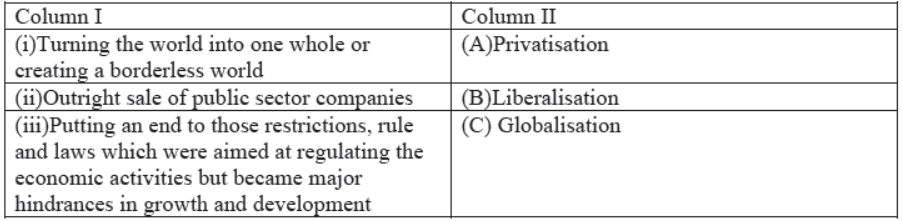
a) (i)-(A), (ii)-(B), (iii)-(C)
b) (ii)-(A), (i)-B, (iii)-(C)
c) (i)-(C) , (ii)-(A), (iii) –(B)
d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. In 1991, an immediate measure to resolve the balance of payments crisis was:
a) To free the determination of rupee value in the foreign exchange market from government control.
b) Devaluation of rupee against foreign currencies.
c) Removing the trade barriers-quotas and tariffs.
d) Simplification of export and import procedures.
Answer
B
Question. Goods and Services Tax Act, 2016 which came into effect from July 2017, is expected to:
a) Generate additional revenue for the government
b) Reduce tax evasion
c) Create ’one nation, one tax and one market’
d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Government taxation and expenditure policy is known as
a) Trade policy
b) Monetary policy
c) Fiscal policy
d) Taxation policy
Answer
C
Question. The government has made efforts to improve the efficiency of PSU’s by giving them ______ in taking managerial decisions.
a) Money
b) Financial Assistance
c) Autonomy
d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Name the successor organization on General Agreement on Trade and Tariff (GATT)
a) World Bank
b) International Monetary Fund
c) Food and Agricultural Organisation
d) World Trade Organisation
Answer
D
Question. The origin of the financial crisis in India in the 1980s can be traced from the _______.
a) Challenges like unemployment, poverty and population explosion
b) Insufficient revenue generation from internal sources such as taxation.
c) Sharp rise in the prices of essential goods.
d) Inefficient management of the Indian economy.
Answer
D
Question. The opening up of Indian Economy has led to
a) Fall in foreign exchange and rise in FDI
b) Rise in foreign exchange and fall in FDI
c) Rise in foreign exchange and rise in FDI
d) Fall in foreign exchange and fall in FDI
Answer
C
Question. Aim of demonetization not included :
a) Form a cashless economy
b) Check on tax evasion
c) It will lead to money supply contraction in the form of cash
d) Adding savings into the formal financial system
Answer
C
Question. ___________ have been removed to increase the competitive position of Indian goods in the international markets.
a) Import licensing
b) Quantitative restrictions
c) Export duties
d) Tariffs
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the reason for the decelerating growth rate of agriculture during the reform period?
a) Public investment in agriculture sector especially infrastructure has fallen in the reform period.
b) Removal of fertilizer subsidy has led to increase in the cost of production.
c) Due to number of policy changes such as reduction in import duties on agricultural products, etc.
Indian farmers now have to face increased international competition.
d) All of the above
Answer
D
Assertion-Reasoning Questions :
Question. Assertion (A): Launch of LPG policies has caused a significant shift in the structure of the Indian markets they are now increasingly shedding their monopoly nature and becoming more competitive in nature.
Reason: (R) Equity limit of foreign capital investment has been raised from the initial 40, it now ranges between 51-100%
Alternatives
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is true,
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Demonetisation refers to withdrawal of the status of “legal tender ‘to the currency in circulation.
Reason (R): Demonetisation notes of Rs. 500 & Rs. 1000 with immediate effect on 08 Nov.2015.
Alternatives
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is true,
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Huge reforms have been made in indirect taxes to facilitate establishment of common national market for goods and services.
Reason (R): In order to encourage better compliance on the part of taxpayers, many procedures have been simplified.
Alternatives
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is true,
Answer
A

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 3 Liberalisation Privatisation and Globalisation: An Appraisal Class 11 Economics with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.


