Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 Chemistry with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 11 Chemistry issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques in Class 11 Chemistry provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following mentioned is a type of hydrocarbon?
(a) Saturated hydrocarbon
(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
(c) Aromatic hydrocarbon
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Name of following compound according to IUPAC nomenclature is
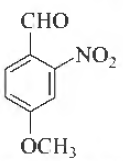
(a) 4-methox y-2-ni trobenzaldehyde
(b) 4-formyl-3-nitroanisole
(c) 4-methoxy-6-nitrobenzaldehyde
(d) 2-formyl-5-methylnitrobenzene
Answer
A
Question. IUPAC name of CH2 = CH-CH(CH2CH3) C = CH2
l
Br
is
(a) 4-bromo-3-ethyl-1, 4-pentadiene
(b) 2-bromo-3-ethy 1-1 ,4-pentadiene
(c) 2-bromo-3-ethyl-1 ,5-pentadiene
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. IUPAC name of the following compound is
CH3
I
CH3—CH2—CH—CH2—CH CH2—CH2—CH3
l
CH
/ \
CH3 CH3
(a) 4-isopropyl-6-methyloctane
(b) 3-methyl-5-(1-methyl ethyl)octane
(c) 3-meth y 1-5-isopropy !octane
(d) 6-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl) octane
Answer
B
Question.

Answer
C
Question. Give the correct IUPAC name for
CH3
I
CH3 ·CH2OCH·CH2 ·CH2 ·CH2CI
(a) 2-ethoxy-5-chloropentane
(b) l-chloro-4-ethoxy-4-methylbutane
(c) 1-chloro-4-ethoxypentane
(d) Ethyl-1-chloropentylether
Answer
A
Question.

(a) bicyclo (2, 1, 0) pentane
(b) 1, 2-cyclopropyl-cyclobutane
(c) 1, 2-methylene cyclobutane
(d) cyclopentane-( 4, 3)-annulene
Answer
A
Question.
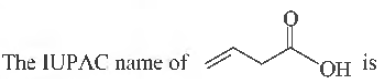
(a) but-3-enoic acid
(b) but-1-enoic acid
(c) pent-4-enoic acid
(d) prop-2-enoic acid
Answer
A
Question. The IUP AC name of the following compounds is
CH2—CH—CH2
I I I
CH CN CN
(a) 1, 2, 3-tricyanopropane
(b) propane-1, 2, 3-trinitrile
(c) 3-cyanopentane-1, 5-dinitrile
(d) 1, 3, 5-pentanetrinitrile
Answer
A
Question. TheIUPAC nan1e of the compound
CH2 = CH-CH(CH3)2 is
(a) 1,1-dimethy-1-2-propene
(b) 2-vinyl propane
(c) 3-methy-1-butene
(d) 2-vinyl propene
Answer
C
Question. What is the IUP AC name of isopropylamine?
(a) Propan-2-amine
(b) Ethanamine
(c) 2-aminotoluene
(d) Propan-1-amine
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound,
C2H5—C—CH2OH is
II
CH2
(a) 2-ethylprop-2-en-1-ol
(b) 2-hydrox ymethylbutan-1-o I
(c) 2-methylenebutan–o 1
(d) 2-ethyl-3-hydroxyprop–en
Answer
A
Question. Propanal and propanone are
(a) functional isomers
(b) enantiomers
(c) chain isomers
(d) structural isomers
Answer
A
Question. How many structural isomers are possible for C4H9Cl?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 10
Answer
B
Question. The number of optical isomers of CH3CH(OH) CH(OH)CHO is
(a) zero
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
(e) 6
Answer
D
Question. How many optically active stereoisomers are possible for butane-2, 3-diol ?
(a) o
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
(e) 4
Answer
C
Question. Pick out the alkane which differs from the other members of the group.
(a) 2,2-dimethyl propane
(b) Pentane
(c) 2-methyl butane
(d) 2,2-dimethyl butane
Answer
D
Question. The isomers which are interconverted through rotation around a single bond are
(a) conformers
(b) diastereomers
(c) enantiomers
(d) position isomers
Answer
A
Question. 2-pentanone and 3-methyl-2-butanone is a pair of isomers.
(a) functional
(b) chain
(c) positional
(d) stereo
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a dynamic isomerism?
(a) Metamerism
(b) Geometrical isomerism
(c) Tautomerism
(d) Coordinate isomerism
Answer
C
Question. The reason for the loss of optical activity of lactic acid when —OH group is changed by H is that
(a) chiral centre of the molecule is destroyed
(b) molecules acquires asymmetry
(c) due to the change in configuration
(d) structural changes occur
Answer
A
Question. Which type of isomerism is shown by 2, 3-dichlorobutane ?
(a) Structural
(c) Optical
(b) Geometric
(d) Diastereomer
Answer
C
Question. The IUP AC name of neopentane is
(a) 2-methylbutane
(b) 2,2-dimethylpropane
(c) 2-methylpropane
(d) 2,2-dimethylbutane
Answer
B
Question. IUPAC name of (CH3)3 CCI is
(a) n-butylchloride
(b) 3-chlorobutane
(c) 2-chloro- 2-methyl propane
(d) t-butyl chloride
Answer
C
Question. Pick out the correct statement from the following and choose the correct answer from the codes given below.
I. Hexa-1, 5-diene is a conjugated diene.
II. Prop-I, 2-diene is conjugated diene.
III. Hexa-1, 3-diene is a conjugated diene.
IV. Buta-1, 3-diene is an isolated diene.
V. Prop-I, 2-diene is a cummulative diene.
(a) I, II
(b) H, III
(c) IV, V
(d) II, V
(e) III, V
Answer
E
Question. What will be the compound if two valencies of carbonyl group are satisfied by two alkyl groups?
(a) Aldehyde
(b) Ketone
(c) Acid
(d) Acidic anhydride
Answer
B
Question. CH3—CH—CH2—CH3 the IUPAC name is
l
OC2H5
(a) 2-ethoxy pentane
(b) 4-ethoxy pentane
(c) pentylethyl ether
(d) 2-pentoxy ethane
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3COCH(CH3)2 is
(a) isopropylmethyl ketone
(b) 2-methyl-3-butanone
(c) 4-methylisopropyl ketone
(d) 3-methyl-2-butanone
Answer
D
Question. Hyperconjugation involves overlap which of the following orbitals ?
(a) σ – σ
(b) σ – p
(c) p – p
(d) n – n
Answer
B
Question. Mesometic effect involves delocalisation of
(a) pi-electrons
(b) sigma-electrons
(c) protons
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The number of sigma and pi-bonds in 1-butene-3-yne are
(a) 6 sigma and 4 pi
(b) 7 sigma and 3 pi
(c) 5 sigma and 5 pi
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following acid does not have acarboxylic group?
(a) Methanoic acid
(b) Ethanoic acid
(c) Propanoic acid
(d) Picric acid
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is s-butyl phenyl vinyl methane?
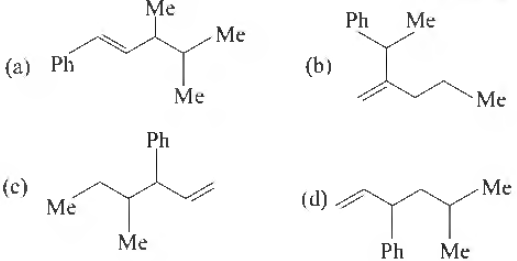
Answer
C
Question. The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system of nomenclature is
(a) —, COOH,— SO3H — CONH2 ,— CHO
(b) — SO3H,— COOH,— CONH2 ,— CHO
(c) — CHO,— COOH,— SO3H, — CONH2
(d) — CONH2 ,— CHO,—SO3H,— COOH
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of C2H5 — O — CH<CH3CH3 is
(a) ethoxy propane
(b) 1, 1-dimethyl ether
(c) 2-ethoxy-iso-propane
(d) 2-ethoxy propane
Answer
D
Question. Correct structural formula of compound 5-nitro- 3-methoxy-3-methylhexanoyl chlo1ide is
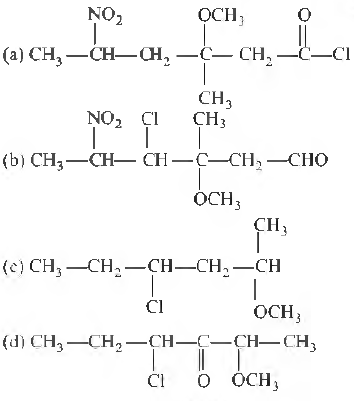
Answer
A
Question.
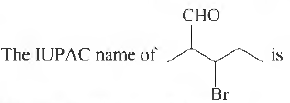
(a) 2-methyl-3-bromohexanal
(b) 3-bromo-2-methylbutanal
(c) 2-bromo-3-bromobutanal
(d) 3-bromo-2-methylpentanal
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is phenyl ethanoate?

Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name of H3C—CH—C3H7 is
l
OC3H7
(a) 4-propoxy pentane
(b) pentyl-propyl ether
(c) 2-propoxy pentane
(d) 2-pentoxy propane
Answer
C
Question. The IUPAC name for tertiary butyl iodide is
(a) 4-iodo butane
(b) 2-iodo butane
(c) 1-iodo-3-methyl propane
(d) 2-iodo-2-methyl propane
Answer
D
Question. The chemical name of anisole is
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) methoxy benzene
(c) propanone
(d) acetone
(e) propanol
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3—CH= CH—C = CH is
(a) pent-3-en-1-yne
(b) pent-3-en-4-yne
(c) pent-2-en-4-yne
(d) pent-2-en-3-yne
Answer
A
Question. The correct name fo~w;ng hydmrarl>on fa
(a) tricyclo (4. 1.0) heptane
(b) bicyclo (5.2.1) heptane
(c) bicyclo (4. 1.0) heptane
(d) bicyclo ( 4. 1.0) hexane
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following represents neo-pentyl alcohol?
(a) CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2OH
(b) (CH3)3 C—CH2OH
(c) CH3(CH2)3 OH
(d) CH3CH2CH(OH)C2H5
Answer
B
Question. In cyclopropane, cyclobutane and cyclohexane, the common group is
l
(a) —C—
l
l
(b) CH2
l
(c) —CH3
l
(d) —CH
l
Answer
B
Question. The IUP AC name for
Cl
l
CH3—C—CH2—CH=CH—CH3 is
l
H
(a) 5-chloro-hex-2-ene
(b) 2-chloro-hex-5-ene
(c) 1-chloro- 1 -methylpent-3-ene
(d) 5-chloro-5-methylpent-2-ene
Answer
A
Question. IUPAC name of CH3—CH—CH2—CHO is
l
Cl
(a) 3-chlorobutanol
(b) 3-chlorobutanaldehyde
(c) 3-chlorobutanal
(d) 2-chlorobutanol
Answer
C
Question. t-butyl alcohol is
(a) 2-methylpropan-2ol
(b) 2-methylpropan-1 ol
(c) 3-methylbutan-1-ol
(d) 3-methylbutan-2-ol
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound,
CH2—CH—COOH is
l l
OH NH2
(a) 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
(b) 1-hydroxy-2-aminopropan-3-oic acid
(c) 1-amino-2-hydroxypropanoic acid
(d) 3-hydroxy-2-aminopropanoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. This can be explained using
(a) – M-effect
(b) – I-effect
(c) + M effect
(d) + I-effect
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a primary halide?
(a) Isopropyl iodide
(b) Secondary butyl iodide
(c) Tertiary butyl bromide
(d) Neo hexyl chloride
Answer
D
Question. IUP AC name of HC—C=CH—CH—CH3 is Cl—CH3
l l
CI CH3
(a) 2-chloro-4-methyl-2-pentene
(b) 4-chloro-2-methyl-3-pentene
(c) 4-methyl-2-chloro-2-pentene
(d) 2-chloro-4, 4-dimethyl-2-butene
Answer
A
Question. Crown ethers are nan1ed as X-crown-Y. In the following crown ether, X and Y respectively, are
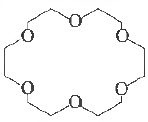
(a) 6 and 12
(b) 18 and 6
(c) 24 and 6
(d) 6 and 24
(e) 6 and 18
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of the following compound is
HOOC—CH2—CH—CH2—CH2—COOH
l
COOH
(a) 2(carboxymethyl)-pentane-1, 5-dioic acid
(b) 3-carboxyhexane-1, 6-dioic acid
(c) butane-1, 2, 4-tricarboxylic acid
(d) 4-carboxyhexane-1, 6-dioic acid
(e) 1, 2-dicarboxy pentanoic acid
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3 — CH2 — CHO is
(a) propanal-1
(b) 2-methylbutanal
(c) butanal-1
(d) pentanal-1
Answer
A
Question. The IUP AC name of the following compound is

(a) bicyclo [2, 2, O] octane
(b) bicyclo [O, 2, 2] hexane
(c) bicyclo [2, l, 1] hexane
(d) bicyclo [2, 2, O] hexane
Answer
D
Question. Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. This can be explained using
(a) – M-effect
(b) – I-effect
(c) + M effect
(d) + I-effect
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of (CH3 )3C—CH= CH2 is
(a) 1, 1, 1-trimethy 1-2-propene
(b) 3, 3, 3-trimethy 1-2-propene
(c) 2, 2-dimethyl-3-butene
(d) 3, 3-dimethyl-1-butene
Answer
D
Question. The IUPAC name of
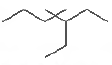
is
(a) l, l -diethyl-2, 2-dimethylpentane
(b) 4, 4-dimethyl-5, 5-diethylpentane
(c) 5, 5-diethyl-4, 4-dimethylpentane
(d) 3-ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
Answer
D
Question. Glycerol is an alcohol which can be classified as
(a) trihydric
(b) monohydric
(c) dihydric
(d) hexahydric
Answer
A
Question. In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is
H H
l l
H3 C1—C2—3 C+—4C—C5H3
l l l
OH H CH3
(a) CH3 at C-4
(b) H at C-4
(c) CH3 at C-2
(d) H at C-2
Answer
D
Question. The most contributing tautomeric Me COCH2CO2 Et is enol form of
(a) CH2 = (OH)CH2CO2 Et
(b) MeC(OH) = CHCO2 Et
(c) MeCOCH = C(OH)O Et
(d) CH2 = C(OH)CH = C(OH)O Et
Answer
B
Question. Give the IUPAC name of the following compound.
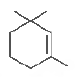
(a) I, l, 3-trimethylcyclohex-2-ene
(b) l , 3, 3-trimethylcyclohex-1-ene
(c) I, I, 5-trimethylcyclohex-5-ene
(d) 2, 6, 6-trimethylcyclohex-1-ene
Answer
B
Question. Ibuprofen contains
(a) only S-enantiomers
(b) only R-enantiomers
(c) racemic mixture of both Rand S enantiomers
(d) both Rand S-enantiomers are active pain colour
Answer
C
Question. Which of the followng shows optical isomerism?
(a) Butan-1-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) Butene
(d) But-2-enol
Answer
B
Question. C11H24 can contain maximum methyl group upto
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 6
(d) 11
Answer
B
⊕
Question. R3N — CH =CH2 →HBr product. Predominant product is
⊕
(a) R3N—CH—CH3
l
Br
(b) R3N—CH2 — CH2 — Br
⊕ Θ
(c) CH2 =CH — NR3 Br
(d) No reaction
Answer
C
Question. C — H bond energy is about 101 kcal/moI for methane, ethane and other alkanes but is only 77 kcal/mol for C — H bond of CH3 in toluene. This is because
(a) of inductive effect due to — CH3 in toluene
(b) of the presence of benzene ring in toluene
(c) of the resonance among the structures of benzyl radical in toluene
(d) aromaticity of toluene
Answer
B
Question. The correct IUP AC name of the following acid is
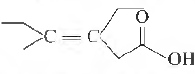
(a) Z-3-ethyl-4-methylhex-3-en-l-oic acid
(b) Z-3-ethyl-4-methylhexanoic acid
(c) Z-3,4-diethylpent-3-en-1-oic acid
(d) E-3-ethyl-4-methylhex-4-en-l-oic acid
(e) E-3-ethyl-4-methylhex-3-en-1-oic acid
Answer
E
Question. The correct name following hydmrarbon is

(a) tricyclo (4. 1.0) heptane
(b) bicyclo (5.2.1) heptane
(c) bicyclo (4. 1.0) heptane
(d) bicyclo ( 4. 1.0) hexane
Answer
C
Question. Among the following, the strongest nucleophilic is
(a) C2H5SH
(b) CH3COO–
(c) CH3NH2
(d) NCCH–2
Answer
A
Question. Bromination of arkanes involves
(a) carbanions
(b) carbocations
(c) carbenes
(d) free radicals
Answer
D
Question. The IUP AC name of the following compound, is
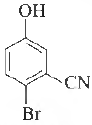
(a) 4-bromo-3-cyanophenol
(b) 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzonitrile
(c) 2-cyano-4-hydroxybromobenzene
(d) 6-bromo-3-hydroxybenzonitrile
Answer
D
Question. Reaction of phenol with chloroform/sodium hydroxide to give o-hydroxy benzaldehyde involves the formation of
(a) dichloro carbene
(c) chlorine atoms
(b) trichloro carbene
(d) chlorine molecules
Answer
A

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 Chemistry with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.

