Please refer to Improvement in Food Resources Chapter 15 Class 9 Science Assignments below. We have provided important questions and answers for Improvement in Food Resources which is an important chapter in Class 9 Science. Students should go through the notes and also learn the solved assignment with solved questions provided below. All examination and class tests questions are as per the latest syllabus and books issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have also provided Class 9 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Science Assignments
Question. What type of shelter is provided to broiler and layers?
Answer
Broilers do not require much space and lighting.
Question. Why should weeds be constantly removed from cultivated fields?
Answer
Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of the crop.
Question. Write four methods of weed control.
Answer
Spraying weedicide, mechanical removal, sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation also help in weed-control.
Question. State one demerit with composite fish culture system.
Answer
Fish breed only during monsoon and lack of availability of good quality seeds.
Question. State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
Answer
Photoperiod in agriculture provide adequate light for flowering.
Question. What is Pisciculture?
Answer
The production and management of fish is called Pisciculture.
Question. What are the harmful effects of fertilizer?
Answer
Continuous use of fertilizer can cause of soil and water pollution and also destroy soil fertility.
Question. How does Bombay duck differ from common carp?
Answer
Bombay duck is a marine fish, while common carp is a freshwater fish.
Question. Mention any two advantages of using Italian bee variety in honey production.
Answer
The Italian bees have high honey collection capacity.They sting somewhat less. They stay in a given beehive for long periods and breed very well.
Question. Name the two vitamins which are added in the poultry feed.
Answer
Vitamins A and K.
Question. From where do plants acquire the following nutrients?
(a) Nitrogen, (b) Hydrogen.
Answer
(a) Nitrogen from soil,
(b) Hydrogen from waste.
Question. State the reason of introducing Italian bee variety in bee farms.
Answer
An Italian bee variety, A mellifera, has also been brought in to increase yield of honey.
Question. Which nutrients are supplied by cereals and pulses?
Answer
Carbohydrate is supplied by cereals and protein is supplied by pulses.
Question. Name two rabi crops.
Answer
Wheat and gram.
Question. Define animal husbandry.
Answer
Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals by humans for profit.
Question. Mention the components of food present in vegetable and fruits.
Answer
Vegetables, spices and fruits provide a range of vitamins and minerals in addition to small amounts of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Question. Name any two fodder crops.
Answer
Berseem and sudan grass are raised as food for the livestock, called fodder crops.
Question. What do you understand by photoperiod of sunlight?
Answer
Photoperiod are related to the duration of sunlight required for plant growth.
Question. Name the cereals which provide us carbohydrate for energy requirement.
Answer
Cereals such as wheat, rice, maize, millets and sorghum provide us carbohydrate for energy requirement.
Question. Name any two weeds.
Answer
Parthenium and Xanthium.
Question. Mention two examples of mixed cropping.
Answer
Some combinations of mixed cropping are : wheat and mustard, groundnut and sunflower.
Question. (i) Name an exotic variety of honey bee grown in India.
(ii) What is called the rearing of fish on a large scale?
Answer
(i) Apis cerana indica
(ii) Pisciculture
Question. Name one micronutrient and one macronutrient which plants take from the soil.
Answer
Macronutrients are : Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg) and Micronutrients are : Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl).
Question. Is breeding and rearing of Bombay duck part of poultry farming or a part of pisciculture?
Answer
It is a part of pisciculture as Bombay duck is fish not a duck.
Question. Name four marine fish varieties.
Answer
Pomphret, mackerel, tuna and sardines.
Question. What is apiculture?
Answer
Keeping bee for obtaining honey commercially is called apiculture.
Question. Name the products obtained from apiculture.
Answer
Honey and wax both are obtained from apiculture.
Question. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Answer. During the storage of grains, various biotic factors such as insects, rodents, mites, fungi, bacteria, etc. and various abiotic factors such as inappropriate moisture, temperature, lack of sunlight, etc. are responsible for losses of grains. These factors act on stored grains and result in degradation, poor germ inability, discolouration, etc.
Question. Why there is necessity of animal husbandry?
Answer. To fulfil growing demand for milk, eggs and meat and providing self employment livestock production is needed.
Question. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage? Also mention any two preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Answer. Factors responsible for losses are :
Biotic : Insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria.
Abiotic : Inappropriate moisture and temperatures in the place of storage. Cleaning of the produce before storage, proper drying of the produce first in sunlight and then in shade, and fumigation are preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Question. What are the major group of activities involved for improving of crop yields?
Answer.
(i) Crop variety improvement
(ii) Crop production improvement
(iii) Crop protection improvement
Question.What are the types of food requirements of dairy animals? Why external and internal parasites live on and in the cattle can be fatal.
Answer. Roughage and concentrates are the types of food requirements of dairy animals. The external parasites live on the skin and mainly cause skin diseases. The internal parasites like worms, affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage the liver.
Question. What is composite fish culture system? Mention one merit and one demerit of this system.
Answer. The composite fish culture system is a technology to grow both local and imported fish species in the water in the paddy field. One problem with such composite fish culture is that many of these fish breed only during monsoon mixed with other species, one of the advantages is that fish do not compete for food.
Question. What are the different ways/methods of hybridisation?
Answer.
Hybridisation can be :
(i) Intervarietal – between different varieties of crops
(ii) Interspecific – between two species of same genus
(iii) Intergeneric – between two different genera
Question. List any six factors for which variety improvement in crops is done.
Answer.
(i) Higher yield,
(ii) Improved quality,
(iii) Biotic and abiotic resistance,
(iv) Change in maturity duration,
(v) Wider adaptability,
(vi) Desirable characteristics.
Question. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer. Fertilisers are synthesized in factories from inorganic materials. On the other hand, manure is made from organic materials; through the process of decomposition. Excessive use of fertilisers is not good for soil and may lead to soil pollution. Use of manure is beneficial for soil.
Question. Name any three methods of irrigation and briefly describe them.
Answer.
(a) Drip irrigation : In this kind of irrigation, water is supplied drop by drop near the roots of the crops or plants. They is generally used in the areas where there is a scarcity of water. However, it is very expensive.
(b) Sprinkler system : In this system, the water escapes from the revolving nozzles and is sprinkled like rain on the crops. This system is used for sandy soils and uneven land.
(c) Surface irrigation : Method to supply water to agricultural lands from well, river, dam, etc.
Question. Define manures. What are its three different kinds?State two limitations of manures.
Answer.Manure is an organic matter prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste.
They are : Compost, vermi-composting and green manure.
Two limitations of manures are :
(i) Supplies small quantities of nutrients to the soil
(ii) Losses about half the available nitrogen
(iii) Releases greenhouse gases
Question. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer. Cross breeding between a two good variety crops is called hybridization that also results in a new improved variety. Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic. This results in genetically modified crops.
Question. Name two fresh initiatives taken to increase the water availability for agriculture.
Answer. Two new irrigation systems have been developed to save water and increase the availability of water to the crops. These are :
(1) Drip irrigation system : Here, water is supplied to the roots of the plants directly in a drop wise manner. This prevents unnecessary wastage of water.
(2) Sprinkler system : Here water is sprinkled over the crops like it happens in rain. So, water is absorbed by the soil in a better way.
Question. How do plants get nutrients?
Answer. Nutrients are supplied to plants by air, water and soil. Air supplies carbon and oxygen, hydrogen comes from water and soil supplies the other thirteen nutrients to plants.
Question. What is meant by bee-keeping? Name : (a) the variety commonly used for commercial honey production. (b) the variety having high honey collection capacity.State how pasturage is related to honey production.
Answer. Beekeeping is the practice of rearing bee for making honey (a) Indian bee (Apis ceranaindica), (b) The Italian (Apis mellifera) bees have high honey collection
capacity. Pasturage is the availability of flowers to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. Pasturage is related to honey production because it determines the taste of honey and the quantity of honey.
Question. State the difference between manure and fertilizer.
Answer.
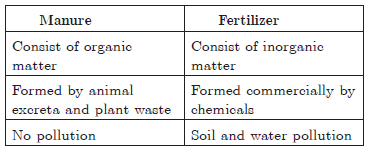
Question. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer. Continuous plantation of crops in a field affects soil fertility. Plants utilize all the nutrients from soil which leads to depletion of nutrients in the soil. As a result,soil fertility reduces drastically.
Question. A group of gardening club students prepared a kitchen garden in the school campus and did organic farming to grow the vegetables. Then the students presented their group work in the assembly to spread the awareness and make students understand the importance of organic products.
(a) What is horticulture?
(b) What is green manure?
Answer.
(a) Hotriculture is the commercial production of vegetables and fruits.
(b) The green plants like sun hemp are turned into the soil which enriches the soil with nitrogen and phosphorus and is called green manure.
Question. Distinguish between a mullet and a prawn.
Answer. Mullet is a type of fish while prawn is a crustacean.Both live in water and serve as a food supplement worldwide. Prawn belongs to group arthropoda whereas mullet belongs to group Pisces.
Question. Large amount of food grains get spoiled every year in India due to improper storage of food grains. How can this be avoided?
Answer. Food grains get spoiled by insects, fungi, rodents,bacteria, moisture at the place of storage. Storage losses can be reduced by taking some preventive and control measures.
(i) The seeds that are to be stored should be dry
(ii) The grains should be cleaned
(iii) The grains should be fumigated using chemicals that kills pest.
(iv) The storage houses should be waterproof.
(v) The grains should be stored in sealed gunny bags.
(vi) The bags should be kept few centimetres away from the wall.
(vii) The walls and the floor should be water-proof with no holes in it, to avoid rodents, pests.
Question. What are manures? Give its classification.
Answer. Substance rich in organic matter and also supplies small quantities of nutrients to soil is called manure.
Manure is classified based on the kind of biological material used to make it as :
(i) Compost, (ii) Vermi-compost, (iii) Green manure.
(i) Compost : The manure prepared by decomposing farm waste, livestock excreta, plant waste, etc. in a pit is known as compost.
(ii) Vermi-compost : When the above given matter is allowed to decompose in the pit along with some earthworms to fasten the process of decomposition is called vermi-composting.
(iii) Green manure : Some plants like sun-hemp are used to prepare manure by mulching them into soil by plough is known as green manure.
Question. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil,
(b) Sowing,
(c) Weeding,
(d) Threshing
Answer.
(a) Preparation of soil : Preparation of soil is the first step of farming. Soil is loosened and turned over.
This helps in making the soil more airy so that roots can breathe in air. Moreover, loosening of soil also facilitates better penetration of roots into the soil. Seeds can be easily sown in loosened soil.
(b) Sowing : The method of putting the seeds into soil is called sowing. Traditionally, seed is sown manually by spreading the seeds by hands. This process is called broadcasting. Seed drills are used when sowing needs to be done on a large scale.
(c) Weeding : Removal of weeds is called weeding. Unwanted plants which grow along with the crop are called weeds. They compete for resources; like sunlight, water and air; with the main crop. So, it is necessary to remove weeds for proper growth of crops. Weeding is usually done manually by using hands and sickles. Sometimes weedicides are also sprayed.
(d) Threshing : Separation of grains from harvested stems is called threshing. For smaller quantity, threshing is done by hands. For somewhat bigger quantity, threshing is done using animal;especially bullocks. Animals are made to trample over the harvested stock which helps in separation of grains. Threshing machines are used for bigger quantities.
Question. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer. The crop of wheat needs mild to moderate temperature and frost free days; along with irrigation but no water logging. Winters are suitable for growing wheat. In the kharif season; which coincides with the peak summer months in India, temperature is at its peak which is not suitable for wheat. Moreover, during rainy season lot of water accumulates in fields which would be harmful for wheat crop. Hence, if wheat is sown in the kharif season; the productivity would be minuscule and would not be profitable for the farmers.
Question. What are weeds? How can we control them? Give different methods of weed control.
Answer. Unwanted plants which grow along with crops are called weeds. Weeds compete with crops for natural resources; like sunlight, water and nutrients. Thus, weeds hamper the growth of crops. Weeds are usually removed manually by hands and by sickles. This process is called weeding. Sometimes, weedicides are also sprayed to kills weeds. Weeds can be controlled by different methods :
(a) Weedicides : These are the chemicals sprayed on the weeds to kill them. Excessive use is poisonous and causes environmental pollution.
(b) Mechanical removal : In this method weeds are uprooted by removing manually or by machines.
(c) Preventive methods : Proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation helps in weed control.
Question. How are fish obtained?
Answer. Fish are obtained by two ways:
(i) Capture fisheries from natural resources
(ii) Fish farming by culture for commercial purposes.
Question. What is the advantage of composite fish culture?
Answer. Combination of five or six fish species in a single fish pond is known as composite fish culture. Basis of selection of species is food habits so that they do not compete for food among themselves. As a result, the food available in all parts of the pond is utilized without competing with each other. This increases the fish yield from the pond.
Question. What are the desirable characters of the varieties suitable for honey production?
Answer. Desirable characters in varieties for honey production are:
(a) Capacity to collect a large amount of honey.
(b) Should stay in beehive for a longer time.
(c) Should have good breeding capacity.
Question. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Answer. Flowers available for nectar and pollen collection is known as pasturage . The quality and taste of honey depends on adequate quantity of pasturage and flowers available. Exercises
Question. Explain anyone method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Answer. Inter cropping is a method used for a high yielding crop production. In this method, two or more crops are grown simultaneously on the same field in definite pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of second crop.
Example: soybean, maize or finger millet (bajara) and caw pea (labia). The selected crops should have different nutrient requirements. This ensures maximum utilisatian of the nutrients supplied. It also prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field. This method gives a better crop yield.
Question. Why are manure and fertilizers used in fields?
Answer.The essential nutrients of the soil are full filled by manures and fertilizers supply. Therefore, they help in good vegetative growth, giving rise to healthy plants that rise in high crap production.
Question. What are the advantages of inter-cropping and crop rotation?
Answer. Advantages of inter-cropping
Maintain soil fertility.
Save time and labour.
Increases productivity per unit area.
Both crops can be easily harvested and threshed separately.
Advantages of crop rotation
Improves soil fertilitiy.
Reduces pest infestation and diseases. Helps in weed control.
Avoids depletion of a particular nutrient from soil.
Question. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful In agricultural practices?
Answer. Transferring desirable genes from one plant to another plant far the production of varieties with desirable characters is known as genetic manipulation.
Example: Profuse branching in fodder craps, high yielding varieties in maize wheat, etc.
Uses in agricultural practices:
Better adaptability to adverse environmental conditions.
Contain desirable features.
Helps in increasing yield and quality.
Maturation period is shorter.
Question. How do storage grain losses occur?
Answer. The main reason for the losses of storage grain is abiotic and biotic factors.
The abiotic factors: Moisture and temperature
The biotic factors: Insects, rodents, birds, mites and bacteria.
Question. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Answer. Benefits of good farming practices:
(i) It provides improved breeds of domestic animals.
(ii) It increase the production of products like milk, egg and meat.
(iii) Proper shelter, feeding, care and protection against disesase help the farmers to improve their economic conditions.
Question. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Answer. Benefits of cattle farming
(i) Milk production is increased.
(ii) Good quality meat, fibre and skin is obtained.
(iii) Goad breed of draught animals can be obtained.
Question. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee keeping?
Answer. Cross breeding is a common practice between poultry, fisheries and bee keeping for increasing production.
Question. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture?
Answer. Differences between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture Fishing
1. Fish are obtained from natural resources, like ponds, canals, rivers,
2. I Locating fish is easy and can be captured by using fishing nets.
Mariculture
1. A method of marine fish culture in the open sea.
2. Fish can be located with the help of satellites and echosounders. These can be caught by many kinds of fishing nets using fishing boats.
Aquaculture
1. Production of fish from freshwater and brackish water resources.
2. Can be located easily and caught using fishing nets.

