Please refer to Human Health and Diseases Class 12 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Biology Important Questions Human Health and Diseases
Objective Questions
Question. In pneumonia the infected organs are
(a) Small intestine
(b) Alveoli of lungs
(c) Brain cells
(d) Lymphatic vessels of lower limbs
Answer
B
Question. Pneumonia is spread by
(a) Mosquito bite
(b) Consuming contaminated food
(c) Inhaling droplets released by infected person
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Common cold is caused by
(a) Haemophilus influenza
(b) Rhinovirus
(c) Wuchereria bancrofti
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Which statement is not true for common cold ?
(a) Common cold is spread by droplet resulting from cough and sneezes of infected person
(b) Transmission of droplets resulting from cough and sneeze of infected person through contaminated object
(c) Symptoms of common cold last for 3-7 days
(d) Nasal congestion and discharged mucus blood in stool cough hoarseness are the important symptoms of common cold
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following does not cause malaria?
(a) P. vivax
(b) P.malaria
(c) P. malayi
(d) P.falciparum
Answer
C
Question. The infectious stage of plasmodium is
(a) male gametophytes
(b) sporozoites
(c) female gametophytes
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. The infectious stage of malarial parasites infects which body organ after entering the body
(a) Respiratory
(b) Brain
(c) Liver
(d) Salivary gland
Answer
C
Question. Malarial parasite attacks which body part after liver
(a) WBC
(b) RBC
(c) Lungs
(d) Brain
Answer
B
Question. Sporozoites are stored in
(a) Human stomach
(b) Mosquito’s salivary gland
(c) Mosquito’s blood
(d) Human intestine
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a vector for malaria?
(a) Human
(b) Female anopheles mosquito
(c) House fly
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Hippocrates belonged to
(a) Africa
(b) Greece
(c) Britain
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Biology states that mind influences the immune system through
(a) Neural system
(b) Endocrine system
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Respiratory system
Answer
C
Question. Health is affected by
(a) Genetic disorders
(b) Mental disorders
(c) Speech disorders
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is important for good health?
(a) Balanced diet
(b) Personal hygiene
(c) Regular exercise
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is necessary for good health?
(a) Awareness about disease
(b) Vaccination
(c) Control of vectors of disease
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. AIDS and cancer are example of
(a) Infectious disease
(b) Non-infectious disease
(c) AIDS infectious and cancer non – infectious
(d) AIDS infectious and cancer infectious
Answer
C
Question. Pathogens are
(a) Disease causing bacteria
(b) Disease causing protozoan
(c) Disease causing virus
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Pathogens that enter through gut have to save itself from
(a) Alkaline pH of stomach
(b) Various digestive enzymes
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Pathogen will make the host enviroment according to its survival needs
Answer
B
Question. Pathogens of typhoid enter the body through
(a) Mosquito bite
(b) Inhaling the aerosols released by the infected person
(c) Contaminated water and food
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Widal test is a confirmation test of
(a) Malaria
(b) Pneumonia
(c) Common cold
(d) None of these
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name two diseases whose spread can be controlled by the eradication of Aedes mosquitoes.
Ans. Dengue/Chikungunya/yellow fever/Eastern equine encephalitis/West Nile fever/Zika virus disease. (Any two)
Question. Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Ans. Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus. Secondary lymphoid organs are spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix.
Question. “Pranay suffered from measles at the age of 10 years. There are rare chances of his getting infected with the same disease for the rest of his life.” Give reason for the statement.
Ans. First exposure to the infection works as vaccination, the immune system of the body gets familiar with the nature of microorganisms and specific antibodies can be produced against infection.
Question. In what way are monocytes a cellular barrier in immunity?
Ans. Monocytes can phagocytose (by the process called phagocytosis) and thereby destroy the pathogens.
Question. How does colostrum provide initial protection against diseases to new born infants? Give one reason.
Ans. Colostrum contains several antibodies which are absolutely essential for developing resistance in the new-born babies.
Question. High fever, loss of appetite, stomach pain and constipation are some of the symptoms seen in a patient. How would the doctor confirm that the patient is suffering from typhoid and not amoebiasis?
Ans. By performing Widal test.
Question. Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Ans. Yes, friends can influence a person to take alcohol or drugs. It can be avoided by (i) avoiding addicted friends.
(ii) avoiding experimental use of alcohol/drug just for curiosity and pressure.
Question. What is it that prevents a child to suffer from a disease he/she is vaccinated against? Give one reason.
Ans. The immunological memory induced by the vaccine in a child prevents the recurrence of a disease.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the two types of immune systems in a human body. Why are cell-mediated and humoral immunities so called?
Ans. The two types of immune systems in a human body are innate and adaptive immunity.
Humoral immunity is called so because it consists of antibodies that are present in humors or body fluids, whereas cell-mediated immunity is provided by T-cells and defends body against viruses, fungi and some bacteria which enter host cells. T-cells recognise non-self cells and kill them.
Question. Describe the role of lymph nodes in providing immunity.
Ans. Lymph nodes trap microorganisms or other antigens. These trapped antigens activate lymphocytes present in the lymph and cause an immune response.
Question. What are the various routes by which transmission of human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
Ans. Various routes by which transmission of HIV takes place:
(i) Transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
(ii) By sharing infected needles in case of intravenous drug abusers.
(iii) Sexual contact with an infected person.
(iv) From mother to child through placenta.
Question. Name the plant source of cocaine. How does it affect the human body?
OR
Name the drug obtained from Erythroxylum coca and write its effects on the human body.
Ans. Plant source of cocaine is Erythroxylum coca. It has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. State the functions of primary and secondary lymphoid organs in humans.
Ans. Primary lymphoid organs are the sites where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes.
Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where the lymphocytes interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells.
Question. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Ans.
| S.No. | Benign tumour | Malignant tumour |
| (i) | It is a non-cancerous tumour. | It is a cancerous tumour. |
| (ii) | Benign tumour does not show metastasis and is non-invasive. | It shows metastasis and thus invades other body parts. |
| (iii) | It stops growth after reaching a certain size. | Malignant tumour shows indefinite growth as proliferating cells, called Neoplastic or tumor cells, grow rapidly, invade and damage other tissues. |
| (iv) | Limited adherence occurs amongst cells of benign tumour. | There is no adherence amongst cells. They tend to slip past one another. |
| (v) | It is less fatal to the body. | It is more fatal to the body. |
Question. Write the biological (binomial) names of causal organisms of the following diseases:
(a) Typhoid (b) Pneumonia
Ans. (a) Salmonella typhi
(b) Streptococcus pneumoniae
Question. (a) Name one primary and one secondary lymphoid organ in the human body.
(b) How do they differ in their functions?
Ans. (a) Primary lymphoid organ: Bone marrow/thymus. (Any one)
Secondary lymphoid organ: Spleen/Lymph nodes/Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). (Any one)
(b) Primary lymphoid organs are the sites where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes.
Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where the lymphocytes interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells.
Question. (a) Name the lymphoid organ in humans where all the blood cells are produced.
(b) Where do the lymphocytes produced by the lymphoid organ mentioned above migrate and how do they affect immunity?
Ans. (a) Bone marrow.
(b) The lymphocytes produced migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like spleen, lymph nodes,etc. They trap the microorganisms thereby activating the lymphocytes present in the lymph nodes and produce an immune response.
Question. Write the scientific names of the causal organisms of elephantiasis and ringworm in humans.
Mention the body parts affected by them.
Ans.
| Disease | Causal Organism | Body parts affected |
| Elephantiasis | Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. | Lymph vessels of lower limbs and genital organs |
| Ringworm | Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton | Skin, nails and scalp. |
Question. A young boy when brought a pet dog home started to complain of watery eyes and running nose. The symptoms disappeared when the boy was kept away from the pet.
(a) Name the type of antibody and the chemicals responsible for such a response in the boy.
(b) Mention the name of any one drug that could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Ans. (a) Antibody: IgE; chemicals: Histamine and serotonin
(b) Drugs: Antihistamine, adrenalin, steroids. (Any one)
Question. (a) Highlight the role of thymus as a lymphoid organ.
(b) Name the cells that are released from the above mentioned gland. Mention how they help in immunity.
Ans. (a) Immature lymphocytes differentiate into mature T-lymphocytes and become antigensensitive in thymus.
(b) T-lymphocytes are released from thymus. T-cells help B-cells to produce antibodies and provide cell-mediated immunity.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Under polio prevention programme, infants in India were given polio vaccines on a large scale at regular intervals to eradicate polio from the country.
(a) What is a vaccine? Explain how does it impart immunity to the child against the disease.
(b) With the help of an example each, differentiate between active and passive immunity.
Ans. (a) Vaccination is the process of introduction of weakened or inactivated pathogens or proteins (vaccine) into a person to provide protection against a disease.
• Vaccines are weakened or inactivated pathogens or proteins introduced into a person to provide protection against a disease.
• Immunisation is the process by which the body produces antibodies against the vaccine (primary response) and develops the ability to neutralise pathogens during actual infection (secondary response).
• Vaccination provides immunisation after a time gap.
• Vaccination and immunisation are based on the property called ‘Memory’ of the immune system.
(b) • It is the ability of an organism to resist or defend itself from the development of a disease.
(i) Innate immunity
• It is present from the birth and is inherited from parents.
• It is non-specific type of defence.
• It is accomplished by providing different types of barriers to entry of foreign agents 4 types of barriers are:
Question. (a) What precaution(s) would you recommend to a patient requiring repeated blood transfusion?
(b) If the advise is not followed by the patient, there is an apprehension that the patient might contract a disease that would destroy the immune system of his/her body. Explain
with the help of schematic diagram only how the immune system would get affected and destroyed.
Ans. (a) A patient requiring repeated blood transfusion must ensure that the donor’s blood has been screened for HIV and other pathogens before transfusion.
Question. During a school trip to ‘Rohtang Pass’, one of your classmate suddenly developed ‘altitude sickness’. But, she recovered after sometime.
(a) Mention one symptom to diagnose the sickness.
(b) What caused the sickness?
(c) How could she recover by herself after sometime?
Ans. (a) Nausea/fatigue/heart palpitation
(b) The sickness was caused due to low atmospheric pressure at high altitude because of which the body was deprived of oxygen.
(c) The body compensates low oxygen availability by increasing RBC production decreasing the binding capacity of haemoglobin and by increasing breathing rate.
Question. A heavily bleeding bruised road accident victim was brought to a nursing home. The doctor immediately gave him an injection to protect him against a deadly disease.
(a) Write what did the doctor inject into the patient’s body.
(b) How do you think this injection would protect the patient against the disease?
(c) Name the disease against which this injection was given and the kind of immunity it provides.
Ans. (a) Tetanus antitoxins/Tetanus toxoid.
(b) The preformed antibody injected act on the pathogen immediately to provide protection.
(c) This injection was given against tetanus and it provides passive immunity.
Question. Write the source and the effect on the human body of the following drugs:
(i) Morphine (ii) Cocaine (iii) Marijuana
Ans. (i) Morphine: It is obtained from poppy plant Papaver somniferum. It binds to specific opioid receptors present in central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
(ii) Cocaine: It is obtained from coca plant Erythroxylum coca. It interferes with the transport of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
(iii) Marijuana: It is obtained from Cannabis sativa. It affects the cardiovascular system of the body.
Question. On a visit to a Hill station, one of your friend suddenly become unwell and felt uneasy.
(a) List two symptoms you would look for the term it to be due to allergy.
(b) Explain the response of the body to an allergen.
(c) Name two drugs that can be recommended for immediate relief.
Ans. (a) Sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing are symptoms of allergy.(Any two)
(b) In response to an allergen, the body releases antibodies of IgE type.
(c) Antihistamine, adrenalin, steroids. (Any two)
Question. (a) All human beings have cellular oncogenes but only a few suffer from cancer disease. Give reasons.
(b) How is a malignant tumour different from a benign tumour?
Ans. (a) All humans have cellular oncogenes or proto-oncogenes, but only a few suffer from cancer because cancer only occurs on activation of oncogenes. This activation is induced by
carcinogens which can be physical, chemical or biological. The chemical carcinogens present in tobacco and smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer.
Question. Prior to a sports event, blood and urine samples of sports persons are collected for drug tests.
(a) Why is there a need to conduct such tests?
(b) Name the drugs the authorities usually look for.
(c) Write the genetic names of two plants from which these drugs are obtained.
Ans. (a) Such tests are conducted to detect drug abuse to ensure fair game.
(b) The authorities look for cannabinoids, cocaine, coca alkaloid, coke, crack, hashish, charas, ganja and hemp plant extract.
(c) These drugs are obtained from Cannabis, Atropa, Erythroxylum, Datura. (Any two)
Question. (a) Name a drug used (i) as an effective sedative and pain killer (ii) for helping patients to cope with mental illnesses like depression, but often misused.
(b) How does the moderate and high dosage of cocaine affect the human body?
Ans. (a) (i) Morphine
(ii) Lysergic acid diethyl amides (LSD).
(b) Cocaine has a potent simulating action on central nervous system producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
Question. A farmer while working on his farm was bitten by a poisonous snake. The workers in the farm immediately rushed him to the nearby health centre. The doctor right away gave him an injection to save his life. What did the doctor inject and why? Explain.
Ans. The doctor injected an antivenom. The antivenom contains preformed antibodies which when injected act on the pathogen immediately provide protection by providing passive immunity.
Question. Explain the role of the following in providing defence against infection in human body:
(i) Histamines
(ii) Interferons
(iii) B-cells
Ans. (i) Histamines: These are chemicals which cause inflammatory responses.
(ii) Interferons: These are glycoproteins which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
(iii) B-cells: These produce proteins called antibodies in response to pathogens into the blood to fight with them.
Question. A group of youth were having a ‘rave party’ in an isolated area and was raided by police. Packets of ‘smack’ and syringes with needles were found littered around.
(a) Why is taking ‘smack’ considered an abuse?
(b) Write the chemical name of ‘smack’ and the name of its source plant.
(c) Syringes and needles used by the youth for taking the drug could prove to be very fatal.Why?
Ans. (a) Taking smack is considered as abuse because it is highly addictive. It is a depressant and slows down body functions. It causes psychological and physical dependance.
(b) Its chemical name is diacetylmorphine and is obtained from poppy plant, Papaver Somniferum.
(c) Drugs taken intravenously (direct injection into the vein using a needle and syringe) are much likely to acquire serious infections like AIDS and hepatitis B. The viruses, which are responsible for these diseases are transferred from one person to another by sharing infected needles and syringes.
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the replication of HIV (retrovirus).
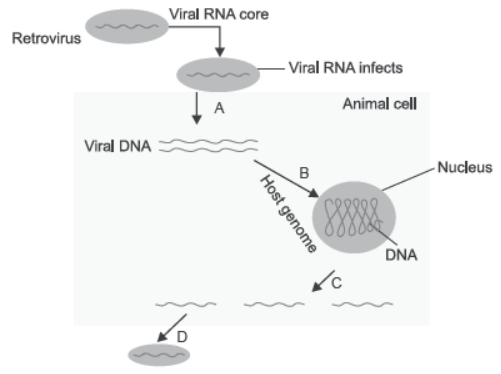
Ans. (A) Reverse transcription.
(B) Viral DNA incorporates into host genome.
(C) New viral RNA produced by infected cell.
(D) New viruses can infect other cells.
Question. Many microbial pathogens enter the gut of humans along with food. What are the preventive barriers to protect the body from such pathogens? What type of immunity do you observe in this case?
Ans. Preventive barrier to protect body are:
(i) The mucus coating of the epithelium lining of the gut helps in trapping microbes entering the body.
(ii) Saliva in the mouth and hydrochloric acid in gastric juice secreted by stomach prevent microbial growth.
This type of immunity is innate immunity.
Question. When someone buys packets of cigarettes, cannot miss the statutory warning that is present on the packing which warns against smoking and says how it is injurious to health. Yet, smoking is very prevalent in our society, both among young and old. Advise the adolescents about the importance of avoiding smoking. (Mention any six points.)
Ans. (i) Tobacco in cigarettes contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation, both of which raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
(ii) Smoking is associated with increased incidence of cancers of lung, urinary bladder, throat and oral cavity.
(iii) It is responsible for bronchitis and emphysema.
(iv) It is associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease, gastric ulcer, etc.
(v) Smoking increases carbon monoxide (CO) content in blood and reduces the concentration of haem-bound oxygen. This causes oxygen deficiency in the body.

