Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
Frothing in Yamuna:
The primary reason behind the formation of the toxic foam is high phosphate content in the wastewater because of detergents used in dyeing industries, dhobi ghats and households. Yamuna’s pollution level is so bad that parts of it have been labelled ‘dead’ as there is no oxygen in it for aquatic life to survive.

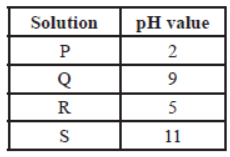
Question. Which of the following correctly represents the solutions in increasing order of their hydronium ion concentration?
(a) P > Q > R > S
(b) P > S > Q > R
(c) S < Q < R < P
(d) S < P < Q < R
Answer
C
Question. If a sample of water containing detergents is provided to you, which of the following methods will you adopt to neutralize it?
(a) Treating the water with baking soda
(b) Treating the water with vinegar
(c) Treating the water with caustic soda
(d) Treating the water with washing soda
Answer
B
Question. Predict the pH value of the water of river Yamuna if the reason for froth is high content of detergents dissolved in it.
(a) 10-11
(b) 5-7
(c) 2-5
(d) 7
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is correct for the water with detergents dissolved in it?
(a) low concentration of hydroxide ion (OH– )and high concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
(b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH–)and low concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
(c) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH–) as well as hydronium ion (H3O+)
(d) equal concentration of both hydroxide ion (OH–) and hydronium ion (H3O+).
The table provides the pH value of four solutions P, Q, R and S
Answer
B
Question. High content of phosphate ion in river Yamuna may lead to:
(a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae
(b) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and no effect of growth of algae
(c) increased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae
(d) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and decreased growth of algae
Answer
A
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.
Question. Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water. Identify the main reason.

(a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide
(b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
(c) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calciumcarbonate
(d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Answer
C
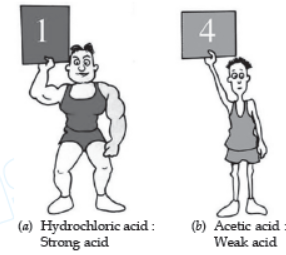
Whenever a solution has a pH of less than 7, it will be an acidic solution. For e.g, a solution having a pH of 4 will be acidic in nature (or it will be an acid). Please note that more acidic a solution is, the lower will be its pH. For example, a solution of pH 1 is much more acidic than another solution of pH 4. In other words, a solution of pH 1 will be a much more stronger acid than another acid having pH4 (see the figure). The solutions having pH of 0, 1, 2 and 3 are usually considered to be strong acids and the solutions having pH of 4, 5 and 6 are considered to be weak acid solutions. It is clear that the acidity of a substance is related to its pH. Strongly acidic substances have a very low pH in fact, lower the pH, the stronger the acid.
Question. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When milk changesinto curd, the pH value will:
(a) become 7
(b) become less than 6
(c) become more than 7
(d) remain unchanged
Answer
B
Question. The pH values of three acids A, B and C having equal molar concentrations are 5.0, 2.8 and 3.5 respectively. Arrange these acids in order of the increasing acid strengths.
(a) A, C, B
(b) B, C, A
(c) A, B, C
(d) C, B, A
Answer
A
Question. A solution turns red litmus blue. Its pH is likely to be:
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer
D
Question. A beaker of concentrated hydrochloric acid has a pH of 1. What colour will full range universal indicator turn if it is added to this beaker?
(a) red
(b) blue
(c) no change in colour
(d) pink
Answer
A
Question. The pH values of six solutions A to F are given as: A = 0, B = 11, C = 6, D = 3, E = 13, F = 8 Which of the above solutions are acids?
(a) A, C, D
(b) A, B, C
(c) A, C, D, F
(d) A, C, D, E
Answer
A
A girl met with an accident and his leg fractured. She went to orthopedics doctor for treatment. On examination, the doctor mixed the white powder in water and applied to her leg along with the cotton and gauze. After a while, it turned into white, solid, hard mass. He said that it would support her fractured bone in the right position.
Question. The graph shows the porosity and expansion of plaster with respect to water content.

At what temperature, the reaction would occur?
(a) 373K
(b) 673K
(c) 273K
(d) 573K
Answer
A
Question. Study the following reaction and choose the correct option:
CaSO4.1/2 H2O + 3/2 H2O → CaSO4.2H2O
(a) Reactant is calcium hemihydrate, product is Gypsum.
(b) Reactant is Gypsum, product is calcium hemihydrate.
(c) Reactant is Gypsum, product is calcium hemihydrate.
(d) Reactant is calcium sulfate hemihydrate, product is Gypsum.
Answer
D
Question. After treatment, the doctor repacked the white powder back into moisture proof, airtight container. Why?
(a) The fungus growth will occur in open.
(b) The powder would react to moisture and turn into solid mass.
(c) The powder with react to sunlight and turn into solid mass.
(d) To prevent the stealing of the powder as it is very expensive.
Answer
B
Question. The reaction involved in the formation of white mass is:
(a) Combustion
(b) Oxidation
(c) Mineralisation
(d) Crystallisation
Answer
D
Question. What is ‘white, solid hard mass’ called as?
(a) Talcum powder
(b) Paris of Plaster
(c) Plaster of Paris
(d) Copper sulphate
Answer
C
Ajay wanted his house to be white washed. He bought 10 kg of quicklime from the market. Before mixing all 10 kg, he took one beaker and took small quantity of quicklime in a beaker then he added some water, he observed that the water started boiling even when it was not being heated and he touch the beaker carefully. The beaker feels to be quite hot.

Question. The chemical reaction between quicklime and water is characterised by:
(a) evolution of hydrogen gas
(b) formation of slaked lime precipitate
(c) change in temperature of mixture
(d) change in colour of the product
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not an endothermic reaction?
(a) CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
(b) 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
(c) 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
(d) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Answer
D
Question. What is formed when water is added to quicklime?
(a) CaCO3
(b) CaO
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) NaOH
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is correct about the above reaction based on your observations?
I. It is an endothermic reaction.
II. It is an exothermic reaction
III. The pH of the resulting solution will be more than seven.
IV. The pH of the resulting solution will be less than seven.
(a) II and IV
(b) II and III
(c) I and IV
(d) III and IV
Answer
B
Question. The nature of the product formed is:
(a) Acidic
(b) Basic
(c) Neutral
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Oxidation has damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metal is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity. The phenomenon due to which metals are slowly eaten away by the reaction of air, water and chemicals present in atmosphere, is called corrosion. For example, iron articles are shiny when new, but get coated with a reddish brown powder when left for sometime. This process is known as rusting of iron. Rancidity is the process of slow oxidation of oil and fat (which are volatile in nature) present in the food materials resulting in the change of smell and taste in them.
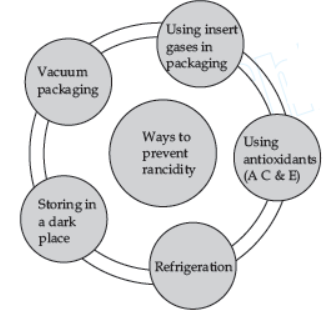
Question. Which of the following measures can be adopted to prevent or slow down rancidity?
I. Food materials should be packed in air tight container.
II. Food should be refrigerated.
III. Food materials and cooked food should be kept away from direct sunlight.
Select the correct option.
(a) Only II and III
(b) Only I and III
(c) Only I and II
(d) I, II and II
Answer
D
Question. A science teacher wrote the following statements about rancidity:
I. When fats and oils are reduced, they become rancid.
II. In chips packet, rancidity is prevented by oxygen.
III. Rancidity is prevented by adding antioxidants.
Select the correct option:
(a) I only
(b) II & III only
(c) III only
(d) I, II & III
Answer
C
Question. Rancidity can be prevented by
(a) adding antioxidants
(b) packaging oily food in nitrogen gas
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
Answer
C
Question. Two statements are given below regarding rusting of iron.
I. 4Fe + 3O2 → 4Fe3+ + 6O2–
II. The metallic iron is oxidised to Fe2+ and O2 is reduced to O2–.
Select the correct statement(s).
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Combination of phosphorus and oxygen is an example of
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) rancidity
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question. A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place?

(a) 15-20 min
(b) 10-15 min
(c) 5-10 min
(d) 0-5 min
Answer
D
Question. Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process?
(a) sodium
(b) sodium oxide
(c) calcium
(d) calcium oxide
Answer
D
Question. The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is
(a) Dolomite
(b) A marble statue
(c) Calcined gypsum
(d) Sea shells.
Answer
C
Question. Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process –
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Transpiration
(d) Photolysis
Answer
B

