Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
For an internal combustion engine to move a vehicle down the road, it must convert the energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. In your car, the distributor and battery provide this starting energy by creating an electrical “spark”, which helps in combustion of fuels like gasoline. Below is the reaction depicting complete combustion of gasoline in full supply of air: 2C8H18(I) + 25O2(g) → 16 ‘X’ + Y
Question. ‘A student while walking on the road observed that a cloud of black smoke belched out from the exhaust stack of moving trucks on the road.’ Choose the correct reason for the production of black smoke:
(a) Limited supply of air leads to incomplete combustion of fuel.
(b) Rich supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
(c) Rich supply of air leads to a combination reaction.
(d) Limited supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following are the products obtained from the reaction mentioned in the above case? Product ‘X’ Product ‘Y’
(a) CO2 H2O2
(b) H2O CO
(c) CH3OH H2O
(d) CO2 H2O
Answer
D
Question. On the basis of evolution/absorption of energy, which of the following processes are similar to combustion of fuel?
(i) Photosynthesis in plants
(ii) Respiration in the human body
(iii) Decomposition of vegetable matter
(iv) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate.
(a) (ii) & (iii)
(b) (i) & (ii)
(c) (iii) & (iv)
(d) (ii) & (i)
Answer
A
Question. ‘Although nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere, it does not take part in combustion’. Identify the correct reason for this statement.
(a) Nitrogen is a reactive gas
(b) Nitrogen is an inert gas
(c) Nitrogen is an explosive gas
(d) Only hydrocarbons can take part in combustion
Answer
B
Question. Identify the types of chemical reaction occurring during the combustion of fuel:
(a) Oxidation & Endothermic reaction
(b) Decomposition & Exothermic reaction
(c) Oxidation & Exothermic reaction
(d) Combination & Endothermic reaction
Answer
C
In the below experiment, when an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, a brown coating of copper is formed in the surface of iron and the colour of copper sulphate solution changes from blue to pale green. The reaction shows that iron is more reactive than copper because it displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution.
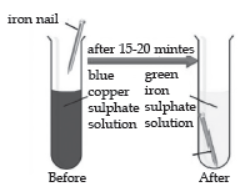
Question. A substance which oxidised itself and reduces other is known as:
(a) Oxidising agent
(b) Reducing agent
(c) Both (a) and (b) ‘
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. In the following equation:
Cu + xHNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + yNO2 + 2H2O.
The values of x and y are:
(a) 3 and 5
(b) 8 and 6
(c) 4 and 2
(d) 7 and 1
Answer
C
Question. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a:
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Double displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction
(d) Displacement reaction
Answer
D
Question. Name the products formed when iron filings are heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Fe (III) chloride and water
(b) Fe (II) chloride and water
(c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
(d) Fe (III) chloride and hydrogen gas
Answer
C
Question. When copper rod is dipped in iron sulphate solution:
(a) Copper displaces iron
(b) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is obtained
(c) No reaction takes place
(d) Reaction is exothermic
Answer
C
Rahul is a skilled painter. He mixed a white coloured powder, compound X with water. The compound X reacted vigorously with water to produce a compound Y and a large amount of heat. Then, Rahul used the compound Y for white washing the walls. Customer was not satisfied with the work of Rahul as walls were not shining. But Rahul guaranteed him that the walls would shine after 2-3 days. And after 3 days of white wash, the walls became shiny.

Question. What type of reaction is occurred here?
(a) Decomposition reaction
(b) Displacement reaction
(c) Double displacement reaction
(d) Combination reaction
Answer
D
Question. Compound X, that Ramesh mixed with water is
(a) Calcium
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Calcium carbonate
(d) Calcium hydroxide
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reactions is responsible for shiny finish of the walls?
(a) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(b) Ca + CO2 → CaCO3
(c) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(d) CaCO3 + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + CO2
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is responsible for shiny finish of the walls?
(a) CaCO3
(b) CaO
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) Ca
Answer
A
Question. Name the compound Y, that Ramesh got after mixing X with water.
(a) Calcium
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Calcium carbonate
(d) Calcium hydroxide
Answer
D
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products.
Study this table related to the different types of reactions/processes and answer the questions that follow:

Question. When a chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light and energy, then the reaction which takes place is known as
(a) photosynthesis
(b) combustion
(c) combination
(d) thermal decomposition.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reactions is an example of combustion reaction?
(a) C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
(b) Zn(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
(c) Zn(s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(d) 3Mg(s) + N2 (g) + Mg3N2 (s)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is essential for photosynthesis?
(a) Sunlight
(b) Combustion
(c) Glucose
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is an example of combination reaction?
(a) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) light → 2HCl (g)
(b) Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS (g)
(c) 2H2 (g) → O2 (g) 2H2O (l)
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. The reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance under suitable conditions is
(a) Combination
(b) Combustion
(c) Decomposition
(d) Photosynthesis
Answer
A
The reaction between MnO2 with HCl is depicted in the following diagram. It was observed that a gas with bleaching abilities was released .
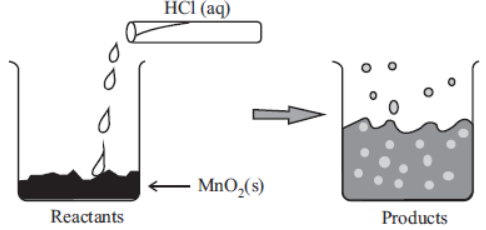
Question. Identify the correct statement from the following:
(a) MnO2 is getting reduced whereas HCl is getting oxidized
(b) MnO2 is getting oxidized whereas HCl is getting reduced.
(c) MnO2 and HCl both are getting reduced.
(d) MnO2 and HCl both are getting oxidized.
Answer
A
Question. In the above discussed reaction, what is the nature of MnO2?
(a) Acidic oxide
(b) Basic oxide
(c) Neutral oxide
(d) Amphoteric oxide
Answer
B
Question. What will happen if we take dry HCl gas instead of aqueous solution of HCl?
(a) Reaction will occur faster.
(b) Reaction will not occur.
(c) Reaction rate will be slow.
(d) Reaction rate will remain the same.
Answer
B
Question. The chemical reaction between MnO2 and HCl is an example of:
(a) displacement reaction
(b) combination reaction
(c) redox reaction
(d) decomposition reaction.
Answer
C
Question. Chlorine gas reacts with _____ to form bleaching powder.
(a) dry Ca(OH)2
(b) dil. solution of Ca(OH)2
(c) conc. solution of Ca(OH)2
(d) dry CaO
Answer
A


