Please refer to Assignments Class 11 Chemistry The s-Block Elements Chapter 10 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 11 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements Class 11 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
The s-Block Elements Assignments Class 11 Chemistry
Question. The composition of Sorels cement is
(a) KCl × MgCl2 × 6H2O
(b) MgCl2 × 5MgO × (xH2O)
(c) MgCO3 × CaCO3
(d) CaSO4 × 2H2O
Answer
B
Question. NaOH is prepared by the method
(a) Downs cell
(b) Castner cell
(c) Solvay process
(d) Castner – Kellner cell.
Answer
D
Question. Solubilities of carbonates decrease down the magnesium group due to decrease in
(a) Entropy of solution formation
(b) Lattice energies of solids
(c) Hydration energy of cations
(d) Inter – ionic attraction.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following alkali metals emit light of longest wavelength in the flame test ?
(a) Na
(b) K
(c) Cs
(d) Li
Answer
B
Question. Which one of these are main components of kidney stones?
(a) Sodium Oxalate
(b) Potassium Oxalate
(c) Calcium Oxalate
(d) Copper Oxalate
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following metals is most commonly used in photo – chemical cells?
(a) Lithium
(b) Calcium
(c) Caesium
(d) Francium
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following metal has stable carbonates?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following alkaline earth metals do not impart any color to the flame?
(a) Ca,Sr
(b) Mg,Ca
(c) Be,Mg
(d) Sr,Ba
Answer
B
Question. What will be final weight of 286 gm Na2CO3.10H2O by Heating at 373 K?
(a) 206 gm
(b) 162 gm
(c) 186 gm
(d) 124 gm
Answer
D
Question. Milk of lime reacts with chlorine to form ________, a constituent of bleaching powder.
(a) Ca(OCI)2
(b) Ca(CIO2)2
(c) Ca(CIO3)2
(d) Ca(CIO4)2
Answer
A
Question. Fill up the blanks with appropriate choices.

Answer
B
Question. Amphoteric hydroxides react with both alkalies and acids. Which of the following group 2 metal hydroxides is soluble in sodium hydroxide?
(a) Be(OH)2
(b) Mg(OH)2
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) Ba(OH)2
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of solubility of the sulphates of alkaline earth metals in water is Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba. This is due to
(a) decreasing lattice energy
(b) high heat of solvation for smaller ions like Be2+
(c) increase in melting points
(d) increasing molecular weight.
Answer
B
Question.
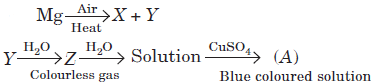
Substances X, Y, Z and A are respectively
(a) Mg3N2, MgO, NH3, CuSO4⋅5H2O
(b) Mg(NO3)2, MgO, H2, CuSO4⋅5H2O
(c) MgO, Mg3N2, NH3, [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
(d) Mg(NO3)2, MgO, H2O2, CuSO4⋅5H2O
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following has correct increasing basic strength?
(a) MgO < BeO < CaO < BaO
(b) BeO < MgO < CaO < BaO
(c) BaO < CaO < MgO < BeO
(d) CaO < BaO < BeO < MgO
Answer
B
Question. Halides of alkaline earth metals form hydrates such as MgCl2⋅6H2O, CaCCl2⋅6H2O, BaCl2 ⋅2H2O and SrCl2⋅2H2O. This shows that halides of group 2 elements
(a) are hygroscopic in nature
(b) act as dehydrating agents
(c) can absorb moisture from air
(d) all of the above.
Answer
D
Question. The charge/size ratio of a cation determines its polarizing power. Which one of the following sequence represents the increasing order of the polarizing power of the cationic species, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Be2+ ?
(a) Mg2+, Be2+, K+, Ca2+
(b) Be2+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+
(c) K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Be2+
(d) Ca2+, Mg2+, Be2+, K+
Answer
C
Question. For alkali metals, which one of the following trends is incorrect?
(a) Hydration energy : Li > Na > K > Rb
(b) Ionization energy : Li > Na > K > Rb
(c) Density : Li < Na < K < Rb
(d) Atomic size : Li < Na < K < Rb
Answer
C
Question. The first ionization energies of alkaline earth metals are higher than those of the alkali metals. This is because
(a) there is an increase in the nuclear charge of the alkaline earth metals
(b) there is a decrease in the nuclear charge of the alkaline earth metals
(c) there is no change in the nuclear charge
(d) none of the above.
Answer
A
Question. Match the elements given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.

(a) (i) → (C, D), (ii) → (B), (iii) → (D), (iv) → (A, E)
(b) (i) → (C), (ii) → (A), (iii) → (B), (iv) → (D, E)
(c) (i) → (A), (ii) → (D), (iii) → (E), (iv) → (B, C)
(d) (i) → (B, C), (ii) → (A), (iii) → (E), (iv) → (D)
Answer
A
Question. Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is 1s2 2s2 2p3, the simplest formula for this compound is
(a) Mg2X3
(b) MgX2
(c) Mg2X
(d) Mg3X2
Answer
D
Question. Metals form basic hydroxides. Which of the following metal hydroxide is the least basic?
(a) Mg(OH)2
(b) Ca(OH)2
(c) Sr(OH)2
(d) Ba(OH)2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following order is correct for the thermal stability of alkali metal carbonates?
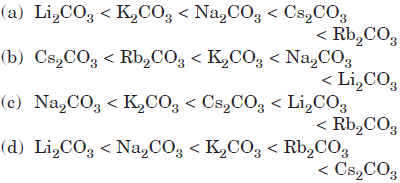
Answer
D
Question. Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
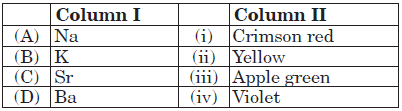
(a) (A) → (i), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
(b) (A) → (ii), (B) → (iv), (C) → (i), (D) → (iii)
(c) (A) → (iv), (B) → (iii), (C) → (ii), (D) → (i)
(d) (A) → (iii), (B) → (iv), (C) → (i), (D) → (ii)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are wrong?
1. Barium is more reducing than magnesium.
2. Ba(OH)2 is more basic than Be(OH)2.
3. Mg2+ is precipitated as MgCO3 by ammonium carbonate in presence of ammonium chloride.
4. MgCl2 gives colouration in flame test.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
B
Question. Choose the incorrect statement in the following.
(a) BeO is almost insoluble but BeSO4 is soluble in water.
(b) BaO is soluble but BaSO4 is insoluble in water.
(c) LiI is more soluble than KI in ethanol.
(d) Both Li and Mg form solid hydrogen carbonates.
Answer
D
Question. Group 2 elements form compounds in +2 oxidation state though total energy required to produce M2+ ions of these elements is quite high. This is because
(a) these elements predominantly form ionic compounds
(b) lattice enthalpy of bivalent compounds of group 2 elements more than compensates the energy requirement for the formation of +2 ions
(c) their hydration energy is quite high
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is false regarding alkali metals?
(a) Alkali metals are soft and can be cut with the help of knife.
(b) Alkali metals do not occur in free state in nature.
(c) Alkali metals are highly electropositive elements.
(d) Alkali metal hydrides are covalent in character.
Answer
D
Question. Some of the group 2 metal halides are covalent and soluble in organic solvents. Among the following metal halides, the one which is soluble in ethanol is
(a) BeCl2
(b) MgCl2
(c) CaCl2
(d) SrCl2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is true for magnesium?
(a) It is more electropositive than sodium.
(b) It is manufactured by electrolysis of aqueous magnesium chloride.
(c) It is a strong reducing agent.
(d) It resembles, in chemical properties, with its diagonally placed element boron in group 13 of the periodic table.
Answer
C
Assertion & Reason Based MCQs :
A statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Electrode potential is a measure of the tendency of an element to lose electrons in the aqueous solution. So, the reducing property can be correlated in terms of electrode potentials (E°) of alkali metals.
Reason : More negative is the electrode potential, higher is the tendency of the element to loose electrons and hence, stronger is the reducing agent.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : BeSO4 is soluble in water while BaSO4 is not.
Reason : Hydration energy decreases down the group from Be to Ba and lattice energy remains almost constant.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The ionization enthalpies of alkali metals increase progressively as we move down the group form Li to Cs.
Reason : The ionic radii increase as we move down the group from Li to Cs.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : The carbonate of lithium decomposes easily on heating to form lithium oxide and CO2.
Reason : Lithium being very small in size polarises large carbonate ion leading to the formation of more stable Li2O and CO2.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The first element (Li) of group I differs considerably from the rest of the elements of the same group.
Reason : Lithium has small ionic and atomic radii, high electronegativity and ionization enthalpy, high polarising power of its cation and absence of d-electrons in its valence shell compared to rest of the elements of the same group.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Lithium salts are hydrated.
Reason : Lithium has higher polarising power than other alkali metal group members.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The solubility of the alkaline earth metal hydroxides in water increases with increase in atomic number down the group.
Reason : The alkaline earth metal hydroxides are basic in character. The only exception is Be(OH)2 which is amphoteric.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Beryllium carbonate is kept in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide.
Reason : Beryllium carbonate is unstable and decomposes to give beryllium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Generally alkali and alkaline earth metals form superoxides.
Reason : There is a single bond between O and O in superoxides.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : s-block elements are highly electropositive.
Reason : The valence electrons present in s-orbital are loosely held.
Answer
A


