Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Social Science Sectors of Indian Economy Chapter 2 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Sectors of Indian Economy Assignments Class 10 Social Science
ONE MARK QUESTIONS
Question. Where is the disguised employment found mostly?
Ans : The disguised employment is mostly found in the agriculture sector.
Question. Name the sector in which the natural products are changed into other forms.
Ans : Primary sector is the sector in which the natural products are changed into other forms.
Question. Mention any one feature of the unorganised sector.
Ans : Unorganised sector is not registered with the government.
Question. When we produce goods by exploiting the natural resources, in which category of economic sector such activities come?
Ans : When goods are produced by exploiting the natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector.
Question. In which sector are a large number of workers losing their jobs since 1990 ?
Ans : In the organised sector, a large number of workers losing their jobs since 1990.
Question. Who has the ownership of the assets in the public sector?
Ans : The ownership of the assets in the public sector is with the government.
Question. What was the most important sector of economic activities at the earliest stages of development?
Ans : Primary sector was the most important sector of economic activities at the earliest stages of development.
Question. Give four reasons for the rising of the tertiary sector in India.
Ans : The four reasons for the rising of the tertiary sector in India are – provision of basic services, rise in income, development of primary and secondary sectors and development of ICT.
Question. Name the sector which forms the base for all other products.
Ans : Primary sector forms the base for all other products.
Question. Name the sector which helps in the development of primary and secondary sectors.
Ans : Tertiary sector helps in the development of primary and secondary sectors.
Question. What does GDP stands for ?
Ans : GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product.
THREE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Explain the working condition of the workers in unorganised sector.
Ans : The working condition of the workers in unorganised sector:
a. They do not follow the rules and regulations followed by the government.
b. There are no formal processes and procedures in this sector. Therefore, it is called unorganised.
c. There is no security of employment.
d. There are no fixed working hours and workers are not paid for overtime.
e. There are no benefits like paid holidays, medical facilities, safe working environment, provident fund etc.
Question. Why does disguised employment not help in the productivity of the country? Explain with the help of an example.
Ans : In the disguised unemployment, extra people are working on the fields. They are not required for work.
All seems working. No one sits idle. They share the labour effort. They work less than their potential. There is hidden unemployment. Underemployment is not just a feature of the primary sector. It can also be seen in the service sector such as people doing odd jobs like painters, plumbers etc.
The extra people working in these sectors does not help in increasing the production. Their presence or absence will not affect the total production.
For example: if a piece of land require only 8 people for completing the production but 10 people are engaged. The two people working are extra as they do not have any job opportunities outside. The land has a limit to produce. Engaging more people will not help in increasing the production from the land.
Question. Name the sector that is the largest employer in India. Why does this sector produce only a quarter of the national GDP?
or
Explain the meaning of disguised employment with the help of an example.
Ans : Primary sector is the largest employer sector in India. This sector produce only a quarter of the national GDP because there is a problem of disguised unemployment in this sector. Though almost 60% people of India are engaged in this sector but all are not required there. Many of them are extra people. They are forced to be in this sector as there is less job opportunities in the other sectors.
Question. How does service sector help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors? Explain with examples.
Ans : Tertiary sector does not produce any good but it helps in the production of goods in the primary and the secondary sectors. For example:
a. In the primary sector we need the service of transportation, cold storage, banking etc., which comes under the service sector.
b. In the secondary sector, we need the help of transportation for bringing the raw materials and taking the final products to the market. Banking, trade, technology etc., are the other requirements.
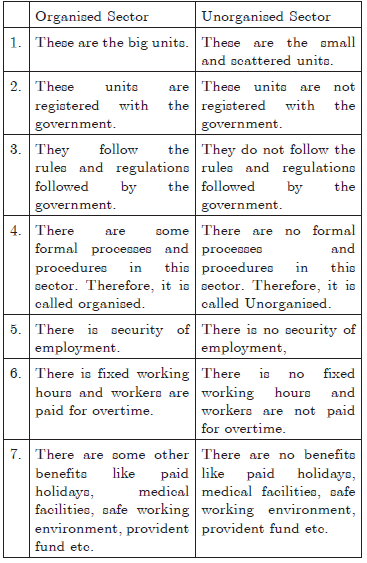
Question. Distinguish the service conditions of organised sector with that of unorganised sector.
or
Explain with suitable examples which part of the service sector is not growing in importance.
Ans : The service conditions of the organised and the unorganised sector are:
a. Service conditions of Organised sector:
1. These are the big units.
2. These units are registered with the government.
3. There are some formal processes and procedures in this sector. Therefore, it is called organised.
4. There is security of employment.
b. Service conditions of unorganised sector:
1. These are the small and scattered units,
2. These units are not registered with the government.
3. There are no formal processes and procedures in this sector. Therefore, it is called Unorganised.
4. There is no security of employment.
Question. With the example of sugarcane, explain the interdependence of all the three sectors of the economy.
Ans : All the three sectors primary, secondary and tertiary are highly interdependent. They need the help of each other, without which none of the sectors would be able to complete its production or service.
For example: Cultivation of sugarcane comes under the primary sector. This cultivated sugarcane, is the raw material for sugar-making industries (comes pnder secondary sector). Sugarcane is transported to the sugar mills with the help of vehicles which comes under the tertiary sector. Sugar made by sugar mills are further transported to various markets and sold by retailers and wholesalers using tertiary sector.
Question. Explain the objectives of implementing the NREGA 2005.
Ans : Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act:
a. This Act was passed in the year 2005.
b. According to this Act, 100 days of guaranteed employment is provided to all those who are able to work and are in need of work in the rural areas.
c. Unemployment allowance is provided to the workers if the government is riot able to provide them work within 15 days.
d. This Act helps in providing income and livelihood to the people in the rural areas.
Question. Explain disguised unemployment with two examples, one from urban areas and other from rural areas.
Ans : When more than the required people are working in a field, is called disguised unemployment. In several areas, all the members of a family work in the same agricultural land (which is small and does not require so much members).
In urban areas, people like plumber, carpenter, painter are not able to find work on a daily basis and hence do the odd job.
Question. Highlight the three factors responsible for the growth of service sector in the Indian economy.
Ans : Due to the following reasons, the tertiary sector is rising in importance in India:
a. Rise in the basic services provided by the government.
b. The development in the primary and secondary sectors has led to the development of the tertiary sector.
c. Due to the rise in income, people have started spending on the various kinds of services.
Question. How did NREGA 2005 bring upliftment of the rural people? Explain.
Ans : Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act:
a. This act was passed in the year 2005.
b. According to this Act, 100 days of guaranteed employment is provided to all those who are able to work and are in need of work in the rural areas.
c. Unemployment allowance is provided to the workers if the government is not able to provide them work within 15 days.
d. This Act helps in providing income and livelihood to the people in the rural areas.
Question. What constitutes the unorganised sector in the urban areas? Why do workers in this area need protection?
Ans : Workers in small scale industry, casual workers in construction, trade and transport constitutes the unorganised sector in the urban areas.
Workers in unorganised sector of the urban areas need protection because
a. They are paid very low.
b. Their work is erratic and so the income.
Question. Explain the interdependence of all three sectors giving examples from transportation system.
Ans : Tertiary sector does not produce any good but it helps in the production of goods in the primary and the secondary sectors. For example:
a. In the primary sector, we need the service of transportation for getting the supply of the agricultural inputs and also for selling the food grains in the market or supplying the agricultural raw materials to the agro- based industries.
b. In the secondary sector, we need the help of transportation for bringing the raw materials and taking the final products to the market.
c. Transportation is required in the service sector as well such as for providing medical facilities to the people and other services like fire services etc.
Question. What is unorganised sector? Describe the working procedure of this sector.
Ans : Unorganised sector are the small and scattered units. These units are not registered with the government.
The working procedure of this sector are:
a. They do not follow the rules and regulations followed by the government.
b. There are no formal processes and procedures in this sector. Therefore, it is called Unorganised.
c. There is no security of employment.
d. There is no fixed working hours and workers are not paid for overtime.
e. There are no benefits like paid holidays, medical facilities, safe working environment, provident fund etc.
Question. Why has the entire tertiary sector not grown in importance? Explain.
Ans : The service sector includes two different kinds of people. One who is highly educated, skilled and earning very high such as doctors, engineers, software professionals etc., and on the other hand those who are not educated and unskilled such as street vendors, repair persons etc. Though the service sector has grown over the past few decades but not all of the service sector has grown equally. The educated and highly skilled workers have grown very high whereas the uneducated and the unskilled are still struggling.
Question. “Consequences of the environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries.” Explain.
Ans : Yes, it is true to say that the consequences of the environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries.
For example: If any country or state causes air pollution then it will affect not only to that state or country but to all throughout the world.
If there is water pollution caused by any state/ country then it will affect all states/ countries through which the river is flowing.
FIVE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. What is GDP? Explain the process to calculate GDP.
Ans : GDP can be defined as the total value of all the final goods and services produced by the three different sectors in a country in a financial year.
GDP is a complex task. It is undertaken by the Central Government ministry after collecting all the data from the different states and the union territories.
Question. Give five reasons for the rising importance of the tertiary sector in production.
Ans : Five reasons for the rising importance of the tertiary sector in production are:
a. Rise in the basic services provided by the government.
b. The development in the primary and secondary sectors has led to the development of the tertiary sector.
c. Due to the rise in income people have started spending on the various kinds of services.
d. Due to the development of new kinds of services like IT sector services.
e. Due to the introduction of the new economic policy liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation, the trade expanded all over the world and the role of service sector became significant.
Question. In what ways can employment be increased in urban areas ?
Ans : Job opportunities can be increased in the urban areas through the following ways:
a. Government should invest in transportation and storage.
b. Government should provide loan to the people for starting their own business at reasonable rate of interest.
c. Opportunities for new industries should be identified, located and promoted in the small towns.
d. Opening of the services like the cold storages.
e. Jobs can be created in the field of education, health and tourism sector.
f. Jobs can be created by launching the various government schemes.
Question. Describe the provisions of National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005.
Ans : Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act:
a. This act was passed in the year 2005.
b. According to this Act, 100 days of guaranteed employment is provided to all those who are able to work and are in need of work in the rural areas.
c. Unemployment allowance is provided to the workers if the government is not able to provide them work within 15 days.
d. This act helps in providing income and livelihood to the people in the rural areas.
Question. Compare the employment conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sector?
Ans : The comparison between the employment conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sector is as follows :