Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Science Periodic Classification of Elements Chapter 5 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Periodic Classification of Elements Assignments Class 10 Science
Question. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic Table.
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Answer
C
Question. Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is a solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si B
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Chlorine, bromine and iodine form a Dobereiner’s triad. The atomic masses of chlorine and iodine are 35.5 and 126.9 respectively. Predict the atomic mass of bromine.
Answer:

Question. Why was the system of classification of elements into triads not found suitable?
Answer: It is because all the elements discovered at that time could not be classified into triads.
Question. How does the metallic character of elements change along a period of the periodic table from the left to the right and why?
Answer: The metallic character goes on decreasing along a period from left to right because atomic size goes on decreasing therefore, tendency to lose electrons decreases.
Question. On the basis of electronic configuration, how will you identify the first and the last element of a period?
Answer: First element has 1 valence electron and last element has 8 valence electrons. Number of shells remain the same in the same period.
Question. Lithium, sodium and potassium form a Dobereiner’s triad. The atomic masses of lithium and potassium are 7 and 39 respectively. Predict the atomic mass of sodium.
Answer:

Question. By considering their position in the Periodic Table, which one of the following elements would you expect to have maximum metallic characteristic?
Answer. Since Be lies to the extreme left hand side of the periodic table, Be is the most metallic among the given elements.
Question. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table?
Answer. Scandium and germanium
Question. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group?
Answer. Noble gases are inert elements. Their properties are different from the all other elements. Therefore, the noble gases are placed in a separate group.
Question. How does the electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table?
Answer. In the modern periodic table, atoms with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. In a group, the number of valence electrons remains the same . Elements across a period show an increase in the number of valence electrons.
Question. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table?
Answer. Mendeleev’s periodic table was based on the observation that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses. This means that if elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses, then their properties get repeated after regular intervals.
Question. Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium . What is the basis for your choice?
Answer. Calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr) are expected to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium (Mg). This is because the number of valence electrons (2) is same in all these three elements. And since chemical properties are due to valence electrons, they show same chemical reactions.
Question. In the Modern Periodic Table, which are the metals among the first ten elements?
Answer. Among the first ten elements, lithium (Li) and beryllium (Be) are metals.
Question. What were the limitations of Dobereiner’s classification?
Answer. Limitation of Dobereiner’s classification:
All known elements could not be classified into groups of triads on the basis of their properties.
Question. In the Modern Periodic Table, calcium (atomic number 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21, and 38. Which of these have physical and chemical properties resembling calcium?
Answer. The element with atomic number 12 has same chemical properties as that of calcium. This is because both of them have same number of valence electrons (2).
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. State Mendeleev’s periodic law. Write two achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table
Answer: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: ‘Properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses.
Achievements:
1. It could classify all the elements discovered at that time.
2. It helped in discovery of new elements.
3. It helped in correction of atomic mass of somd of the elements.
Question. An element ‘M’ has atomic number 11.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) State the group to which ‘M’ belongs.
(c) Is ‘M’ a metal or a non-metal?
(d) Write the formula of its chloride.
Answer:

Question. the formula of its oxide An element ‘M’ has atomic number 12.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) State the group to which ‘M’ belongs.
(c) Is ‘M’ a metal or a non-metal?
(d) Write.
Answer:

Question. Choose from the following:
6C, 8O, 10Ne, 11Na,14Si
(a) Elements that should be in the same period.
(b) Elements that should be in the same group.
State reason for your selection in each case.
Answer:
(a) 6C, 8O, 10Ne are in same period, Le.
2nd period as they have two shells. nNa and 14Si are in same period, i.e. 3rd period as they have three shells.
(b) 6C,14Si are in same group because they have same number of valence electrons, i.e. four.
Question. The atomic numbers of three elements, X, Y and Z are 9,11 and 17 respectively.
Which two of these elements will show similar chemical properties? Why?
Answer: Electronic configuration of X, Y and Z will be:
X(9) : 2, 7
Y(11) : 2, 8, 1
Z(17) : 2, 8, 7
X and Z will show similar chemical properties due to same number of valence electrons.
Question. In the modern periodic table, the element Calcium (atomic number = 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21 and 38. Which of these elements has physical and chemical properties resembling those of Calcium and why?
Answer: Elements with atomic number 12, 38 resemble calcium in physical and chemical properties because they have same number of valence electrons and belong to same group 2.
Mg(12) : 2, 8, 2
Ca(20) : 2, 8, 8, 2
Sr(38) : 2, 8, 18, 8, 2
Question. How does the valency of elements vary
(a) in going down a group, and (b) in going from left to right in a period of the periodic table?
Answer: (a) Valency remains the same in a group.
(b) Valency first goes on increasing from left to right in a period till middle of period, then decreases.
Question. The elements of the second period of the Periodic Table are given below:
Li Be B C N O F
(a) Give reason to explain why atomic radii decrease from Li to F.
(b) Identify the most
(i) metallic and
(ii) non-metallic element.
Answer:
(a) It is because nuclear charge increases due to increase in atomic number, therefore, force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons increases, i.e. effective nuclear charge increases, hence atomic radii decrease from Li to F.
(b) (i) Most metallic element is ‘Li’ as it can lose electrons easily due to larger atomic size.
(ii) Most non-metallic element is ‘F’ because it can gain electrons easily due to smallest atomic size.
Question. The elements of the third period of the Periodic Table are given below:

(a) Which atom is bigger, Na or Mg? Why?
(6) Identify the most (i) metallic and (ii) non-metallic element in Period 3.
Answer: (a) Sodium is bigger than magnesium as it has lesser nuclear charge so there is less force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons and less effective nuclear charge. It is, therefore, bigger in size.
(b) (i) Sodium is the most metallic as it can lose electrons easily due to its larger atomic size,
(ii) Chlorine is the most non-metallic element because it can gain electrons easily due to its smallest atomic size.
Question. How can the valency of an element be determined if its electronic configuration is known? What will be ‘ the valency of an element of atomic number 9 (nine)?
Answer: If the element has 1, 2, 3, 4 valence electrons, its valency will be 1, 2, 3, 4 respectively. If the element has 5, 6, 7, 8 valence electrons, its valency will be 3, 2, 1, 0. Element
with atomic number 9 has electronic configuration 2, 7. So, its valency will be 1.
Question. How does the electronic configuration of an atom of an element relate to its position in the modern periodic table? Explain with one example.
Answer: The position of element depends upon number of valence electrons which depend upon electronic configuration. Those elements which have same valence electrons, occupy same group.
Those elements which have one valence electron belong to group 1.
Elements with two valence electrons belong to group 2.
Period number is equal to number of shells.
If valence electrons are equal to 1, it belongs to group 1. If it has 2 shells, it belongs to second period, e.g. if element ‘X’ has atomic number 11, its electronic configuration is 2, 8,1. It has one valence electron, it belongs to group 1 and it has three shells therefore, it is in third period.
Question. State the Modern Periodic Law for classification of elements. How many (a) groups and (b) periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table?
Answer: ‘Properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic number.’
(a) There are 18 groups and
(b) 7 periods in the Modern Periodic Table.
Question. An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 17 of the periodic table. State its
(a) electronic configuration, (b) valency. Justify your answer with reasoning.
Answer: (a) X(17) : 2, 8, 7
(b) Valency : 1
It has atomic number 17 and therefore, electronic configuration will be 2, 8, 7. It can gain one electron to become stable therefore, its valency is equal to 1. It belongs to third period, as it has three shells. It belongs to group 17 because it has 7 valence electrons.
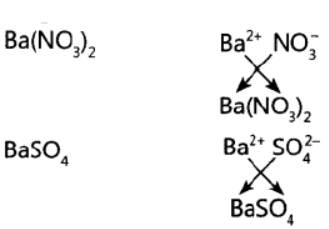
Question. The formula of magnesium oxide is MgO. State the formula of barium nitrate and barium sulphate, if barium belongs to the same group as magnesium.
Answer:
Question. Choose from the following:
20Ca,3Li,11Na,10Ne
(a) An element having two shells completely filled with electrons.
(b) Two elements belonging to the same group of the periodic table.
Answer:
(a) 10Ne has electronic configuration 2, 8. Its both shells are completely filled.
(b) 3Liand nNa belong to same group of periodic table, ie. 1st group.
Question. Why do all the elements of the (a) same group have similar properties, (b) same period have different properties?
Answer:
(a) Elements of same group have similar properties due to same number of valence electrons, therefore, they have same valency.
(b) Elements of same period have different properties as they differ in number of valence electrons.
Question. An element ‘E’ has following electronic configuration:
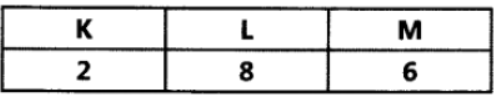
(a) To which group of the periodic table does element ‘E’ belong?
(b) To which period of the periodic table does element ‘E’ belong?
(c) State the number of valence electrons present in element ‘E’.
(d) State the valency of the element ‘E’.
Answer:
(a) ‘E’ belongs to group 16.
(b) It belongs to 3rd period.
(c) It has 6 valence electrons.
(d) Its valency is equal to 2.
Question. In the periodic table, how does the tendency of atoms to lose electrons change on going from
1. left to right across a period?
2. top to bottom in a group?
Answer:
1. Tendency to lose electrons decreases from left to right across a period.
2. Tendency to lose electrons increases from top to bottom in a group.
Question. An element has atomic number 13.
(a) What is the group and period number to which this element belongs?
(b) Is this element a metal or a non- metal? Justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) It belongs to group 13 and 3rd period.
(b) It is a metal because it can lose 3 electrons to become stable.
Question. The electronic configuration of two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2, 8, 3 and 2, 8, 7 respectively. Find the atomic number of these elements. State the nature and formula of the compound formed by the union of these two elements.
Answer:

Question. The atomic number of three elements are given below:
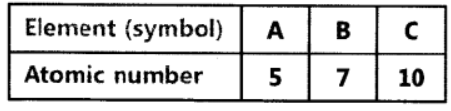
Write the symbol of the element which belongs to (o) group 13, (b) group 15, of the periodic table. State the period of the periodic table to which these elements belong. Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
(a) A belongs to group 13 because its electronic configuration is 2, 3, ie. it has 3 valence electrons.
(b) ‘B’ belongs to group 15 because its electronic configuration is 2, 5, ie. it has 5 valence electrons.
They belong to 2nd period as they ‘ both have two shells.
Question. Write the atomic number of these elements. What will be formula of the compound formed and the nature of bond between them when these two elements
chemically combine together?
Answer:
‘A’ has atomic number 17. Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. Its valency is equal to 1. number 20.
Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 8, 2. Its ‘B’ has atomic valency is 2.

Ionic bond will be formed.
Question. The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic Table is shown below:
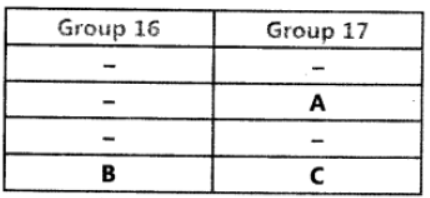
Giving reasons, explain the following:
(a) Element A is non-metal.
(b) Atom of element C has a larger size ‘ than atom of element A.
(c) Element B has a valency of 1.
Answer: (a) It is because it has 7 valence electrons.
It can gain one electron to form negative ion. So, it is a non-metal.
(b)’C’ has more number of shells than A. So, it is larger in size.
(c)’B’ has one valence electron. It can lose one electron to become stable. So, its valency is equal to 1.
Question. What physical and chemical properties of elements were used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table? List two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
Answer: Atomic mass as a physical property and nature and formulae of oxide and hydride formed, and chemical property was used by Mendeleev.
Following are the two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
(i) Increasing order of atomic weights could not be maintained while matching chemical properties.
Chemical properties do not depend upon atomic mass.
(ii) Isotopes have different atomic mass but same chemical properties.
Question. Give reasons:
1. Elements in a group have similar chemical properties.
2. Elements of Group I form ions with a charge of +1.
Answer:
1. Elements in a group have same number of valence electrons and same valency therefore have similar chemical properties.
2. It is because elements of group 1 lose one electron to acquire +1 charge and become stable.
Question. Table given below shows a part of the Periodic Table.
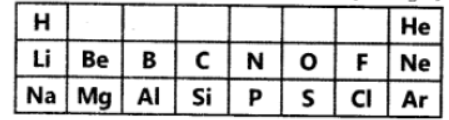
(b) Atomic size of Mg is less than that of Na.
(c) Fluorine is more reactive than Chlorine.
Answer:
(a) They can lose electrons easily due to bigger size; energy required to remove electron is less.
(b) It is because of greater effective nuclear charge on Mg, i.e. more number of protons attract more number of electrons than Na.
(c) ‘F’ can form F– more easily than Cl due to smaller atomic size. F– is more stable than Cl–.
Therefore, fluorine is more reactive than chlorine.
Question. (a) Why do we classify elements?
(b) What were the two criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table?
(c) Why did Mendeleev leave some gaps in his Periodic Table?
(d) In Mendeleev’s Periodic Table, why was there no mention of Noble gases like Helium, Neon and Argon?
(e) Would you place the two isotopes ‘ of chlorine, CI-35 and CI-37 in different slots because of their different atomic masses or in the same slot because their chemical properties are the same? Justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) It is done so as to study the properties of elements conveniently.
(b) Increasing order of atomic mass and similarities in chemical properties (especially nature and formulae of oxide and hydride formed).
(c) These gaps were left for undiscovered elements.
(d) Noble gases were not invented at that time.
(e) They will be kept at same slot as they have same chemical properties.
Question. (a) What is meant by periodicity in properties of elements with reference to the periodic table?
(b) Why do all the elements of the same group have similar properties?
(c) How will the tendency to gain electrons change as we go from left to right across a period? Why?
Answer:
(a) The repetition of same properties after definite interval is called periodicity in properties.
(b) It is because they have same valence electrons therefore, have similar properties.
(c) Tendency to gain electrons increases from left to right in a period because atomic size goes on decreasing and effective nuclear charge increases.
Question. (a) What are ‘groups’ and ‘periods’ in the ‘periodic table’?
(b) Two elements M and N belong to group I and II respectively and are in the same period of the periodic table. How do the following properties of M and N vary?
1. Sizes of their atoms
2. Their metallic characters
3. Their valencies in forming oxides
4. Molecular formulae of their chlorides
Answer:
(a) The vertical columns in the periodic table are called ‘groups’. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called ‘periods’.
(b) 1. ‘M’ and ‘N’ belong to same
period but group I and II. Therefore, ‘N’ will be smaller than ‘M’ as atomic size goes on decreasing from left to right.
2. ‘M’ is more metallic than ‘N’. Metallic character goes on decreasing from left to right as tendency to lose electrons decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
3. Their valencies are 1 and 2 respectively in forming oxides.
Valency goes on increasing first and then decreases.
4. MCI, NCI2 are molecular formulae of their chlorides.
Question. An element ‘X’ has atomic number 13.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) State the group to which ‘X’ belongs.
(c) Is ‘X’ a metal or a non-metal?
(d) Write the formula of its bromide.
Answer:

Question. (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements?
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
Answer. (a) Yes. The atoms of all the three elements lithium, sodium, and potassium have one electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Both helium (He) and neon (Ne) have filled outermost shells. Helium has a duplet in its K shell, while neon has an octet in its L shell.
Question. Use Mendeleev’s Periodic Table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements:
K, C, Al, Si, Ba.
Answer. K is in group 1. Therefore, the oxide will be K2O.
C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2.
Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3.
Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2.
Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO.
Question. Did Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands’ Octaves? Compare and find out.
Answer. Only one triad of Dobereiner’s triads exists in the columns of Newlands’ octaves. The triad formed by the elements Li, Na, and K of Dobereiner’s triads also occurred in the columns of Newlands’ octaves.
Dobereiner’s triads
Li Ca Cl
Na Sr Br
K Ba I
Newlands’ octaves
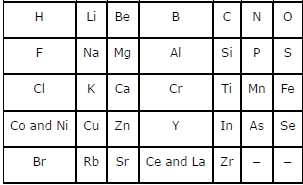
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of D is almost neutral.
Based on the above information answer the following questions:
1. To which group or period of the Periodic Table do the listed elements belong?
2. What would be the nature of compound formed by a combination of elements B and F?
3. Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
4. Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature?
5. If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G be 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer:
1. A and B belong to group 1 and 2 because they form basic oxides. C belongs to group 13 as it has 3 valence electrons. D belongs to group 14 as it forms almost neutral oxide. E and F belong to group 15 and 16 as they form acidic oxides, G belongs to group 17 as it has 7 valence electrons and H belongs to group 18. They belong to 3rd period of the Periodic Table because AG is NaCI, added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking and Na and Cl belong to 3rd period.
2. Ionic compounds will be formed because ‘B’ is metal and ‘F’ is non-metal. ‘B’ can lose two
electrons and ‘F’ can gain two electrons.
3. A and B are definitely metals as they form basic oxides.
4. G and H are gaseous at room temperature.
5. CG3 is the formula of the compound formed by combination of C and G.
Question.15 (a) did Mendeleev have gaps in his periodic table?
(b) any three limitations of Mendeleev’s classification.
(c) does electronic configurations of atoms change in a period with increase in atomic number?
Answer: (a)Gaps were left for undiscovered elements in the Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
(b)(i) Position of hydrogen was not justified.
(ii) Increasing order of atomic mass could not be maintained.
(iii) Isotopes have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses, they cannot be given separate places.
(c) Number of shells remains the same, number of valence electrons goes on increasing from left to right in a period till octet is comilete,e.g.

Question. Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of element D is almost neutral. Answer the following questions based on the information given herein:
1. To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belong?
2. Which one of the eight elements is likely to be a noble gas?
3. Which one of the eight elements would have the largest atomic radius?
4. Which two elements amongst these are likely to be non¬metals?
5. Which one of these eight elements is likely to be a semi-metal or metalloid?
Answer:
1. A and B belong to group 1 and 2 because they form basic oxides. C belongs to group 13 as it has 3 valence electrons. D belongs to group 14 as it forms almost neutral oxide. E and F belong to group 15 – and 16 as they form acidic oxides, G belongs to group 17 as it has 7 valence electrons and H belongs to group 18. They belong to 3rd period of Periodic Table because sodium belongs to 3rd period and AG is NaCI, ionic compound of sodium which can be obtained from sea water and A(Na) and G(CI) belong to 3rd period.
2. H belongs to noble gas.
3. A has the largest atomic radius.
4. E and F are likely to be non¬metals.
5. D is likely to be metalloid or semi-metal.
Question. (a) Which two criteria did Mendeleev use to classify the elements in his Periodic Table?
(b) State Mendeleev’s periodic law.
(c) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
(i) Sizes of their atoms
(ii) Their metallic characters
(iii) Their valencies in forming oxides
(iv) Molecular formulae of their chlorides
(a) The vertical columns in the periodic table are called ‘groups’. The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called ‘periods’.
(b) (i) ‘M’ and ‘N’ belong to same period but group I and II. Therefore, ‘N’ will be smaller than ‘M’ as atomic size goes on decreasing from left to right.
(ii) ‘M’ is more metallic than ‘N’. Metallic character goes on decreasing from left to right as tendency to lose electrons decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
(iii) Their valencies are 1 and 2 respectively in forming oxides. Valency goes on increasing first and then decreases.
(iv) MCI, NCI2 are molecular formulae of their chlorides.
(d) How and why does the atomic size vary as you go
(i) from left to right along a period?
(ii) down a group?
Answer:
(a) (i) Increasing order of atomic mass as physical property and similarities in chemical properties of elements.
(ii) The formulae and nature of hydrides and oxides formed by elements was treated as basic chemical property for its classification.
(b) Properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses.
(c) It is because it resembles both alkali metals as well as halogens.
(d) (i) Atomic size goes on decreasing
from left to right because one proton and one electron is being added successively therefore, force of attraction between . valence electrons and nucleus increases hence, the atomic size decreases.
(ii) The atomic size goes on increasing from top to bottom in a group because number of shells keep on increasing therefore, distance between nucleus and valence electrons increases.
Question. How could the Modern Periodic Table remove various anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
Answer. Mendeleev was unable to give fixed position to hydrogen and isotopes in the periodic table. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, the increasing manner of atomic mass of the elements is not always regular from one to its next. It was believed that a more fundamental property than atomic mass could explain periodic properties in a better manner.
It was Henry Moseley who demonstrated that atomic number of an element could explain periodic properties in a better way than atomic mass of an element and arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers. Then it was found that the various anomalies of Mendeleev’s periodic table were removed by the modern periodic table.
Question. (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as fluorine have in common?
Answer. (a) All the elements in the same column as boron have the same number of valence electrons (3). Hence, they all have valency equal to 3.
(b) All the elements in the same column as fluorine have the same number of valence electrons (7). Hence, they all have valency equal to 1.
Question. What were the limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves?
Answer. Limitations of Newlands’ law of octaves:
(i) It was not applicable throughout the arrangements. It was applicable up to calcium only. The properties of the elements listed after calcium showed no resemblance to the properties of the elements above them.
(ii) Those elements that were discovered after Newlands’ octaves did not follow the law of octaves.
(iii) The position of cobalt and nickel in the group of the elements (F, Cl) of different properties could not be explained.
(iv) Placing of iron far away from cobalt and nickel, which have similar properties as iron, could also not be explained.
Question. (a) Name three elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Name two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Name three elements with filled outermost shells.
Answer. (a) Lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K) have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Neon (Ne), argon (Ar), and xenon (Xe) have filled outermost shells.
Question. An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
(b) To which of the following elements would it be chemically similar? (Atomic numbers are given in parentheses.) N(7) F(9) P(15) Ar(18)
Answer. (a) The atomic number of this element is 17.
(b) It would be chemically similar to F(9) with configuration as 2, 7.
Question. Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic Table and the Modern Periodic Table.
Answer.

Question. The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic Table are shown below −

(a) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A?
Answer.
(a) A is a non-metal.
(b) C is less reactive than A, as reactivity decreases down the group in halogens.
(c) C will be smaller in size than B as moving across a period, the nuclear charge increases and therefore, electrons come closer to the nucleus.
(d) A will form an anion as it accepts an electron to complete its octet.
Question. Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
Answer.

Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorus. On moving down a group, the number of shell increases. Therefore, the valence electrons move away from the nucleus and the effective nuclear charge decreases. This causes the decrease in the tendency to attract electron and hence electronegativity decreases.
Question. Which element has
(a) two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons?
(b) the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2?
(c) a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell?
(d) a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell?
(e) twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell?
Answer. (a) Neon has two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons (2 electrons in K shell and 8 electrons in L shell).
(b) Magnesium has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2.
(c) Silicon has a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell, 8 electrons in L shell and 4 electrons in M shell).
(d) Boron has a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell and 3 electrons in L shell).
(e) Carbon has twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell (2 electrons in K shell and 4 electrons in L shell).
