Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce Chapter 8 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
How do the Organisms Reproduce Assignments Class 10 Science
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. What are all organisms called which bear both the sex organs in the same individual.
Give one example of such organism.
Answer: Organisms which bear both male and female sex organs in the same individual are called bisexual. For example, Hibiscus.
Question. Name the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.|
Answer: Reproduction is a life process that helps in multiplication of an organism and growth of its population.
Question. Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual.
Answer: The method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favorable conditions is fragmentation. This is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Question. When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA?
Answer: When a cell reproduces, DNA replication occurs which forms two similar copies of DNA.
Question. What happens when a mature Spirogyrafllament attains considerable length?
Answer: When a mature Spirogyra flament attains considerable length it simply breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment then grows into a new Spirogyra.
QuestionName the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Answer: Calyx and corolla are parts of a flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Question. Name the largest cell present in human body.
Answer: Ovum is the largest cell present in human body.
Question. What is DNA ?
Answer: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a polymer made up of large number of nucleotide units. It carries genetic information from generation to generation.
Question. List two functions of ovary of human female reproductive system.
Answer: Two functions of ovary of human female are:
(i) production of female gametes i.e., ova
(ii) secretion of female hormones i.e., estrogen and progesterone.
Question. What happens when a Planaria gets cut into two pieces?
Answer: When Planaria is cut into two pieces then each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
Question. Name the method by which Hydra reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual ?
Answer: Hydra generally reproduces through budding.
It is an asexual method of reproduction.
Question. Define multiple fission. Give its one example.
Answer: Multiple fission is an asexual mode of reproduction in which the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time.
Multiple fission occurs in Plasmodium.
Question. List two unisexual flowers.
Answer: Flowers of papaya and cucumber are unisexual.
Question. Name the part of Bryophyllum where the buds are produced for vegetative propagation.
Answer: Bryophyllum propagates vegetatively by the buds produced at the margins of leaves.
Question. Name the causative agent of the disease ‘‘Kalaazar’’ and its mode of asexual reproduction.
Answer: Causative agent of the disease Kala-azar is Leishmania. It reproduces asexually by binary fission.
Question. No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why?
Answer: No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population because sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings by providing genetic variation.
Question. Identify and write the male reproductive parts from the list of di erent parts of a Flower given below:
Stigma, Sepal, Anther, Petal, Ovule, Filament
Answer: The male reproductive parts that are present in a flower from given list are:
(i) anther and (ii) flament.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? Write two of its advantages.
Answer: Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual reproduction in plants in which the parts other than seeds are used as propagules.
Question. Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration.
Answer: Hydra and Planaria are two organisms that have the ability to regenerate.
Question. List four modes of asexual reproduction other than fission in the living organisms.
Answer: The four modes of asexual reproduction other than ¬ssion in living organisms are :
(i) budding
(ii) spore formation
(iii) regeneration and
(iv) fragmentation.
Short Answer Type Questions :
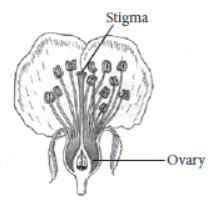
Question. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it (i) stigma and (ii) ovary.
Answer: The labelled diagram of L.S. of flower is as follows:
Question. What is AIDS? Which microbe is responsible for AIDS infection? State one mode of transmission of this disease. Explain in brief one measure for prevention of AIDS.
Answer: AIDS is an infectious viral disease which weakens the immune system of human body and generally leads to death. It is caused by a retrovirus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). AIDS can be transmitted by having sexual contact with an infected person.
Use of condoms which are physical barriers can reduce the risk of a sexual exposure to HIV.
Question. Draw longitudinal section of a bisexual flower and label the following parts on it.
(a) Anther (b) Ovary
(c) Stigma (d) Style
Answer: L.S. of a bisexual flower is as follows:

Question. (i) Implantation (ii) Placenta
(a) What is the average duration of human pregnancy?
Answer: (a) The average duration of human pregnancy is 280 days or 40 weeks from first day of the woman’s last menstrual period, i.e., approximately 9 months.
Question. (i) that produces egg
(ii) where fusion of egg and sperm takes place, and
(iii) where zygote gets implanted.
(a) Describe in brief what happens to the zygote after it gets implanted.
Answer: (a) After implantation of zygote or embryo in the thick lining of the uterus, a disc-like special tissue develops between the uterus wall and the embryo, which is called as placenta. Placenta meets all the requirements for developing the fetus like nutrition, respiration, excretion, etc.
When fetus (embryo) develops completely, the rhythmic contraction of uterus muscles gradually pushes the baby out of the mother’s baby through vagina a baby is born.
Question. (a) Name the part of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(b) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Answer:
(a) In human female the fertilisation occurs in the oviducts or Fallopian tube.
(b) The developing embryo gets nourishment from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. This is a disc like structure embedded in uterine wall. It contains villi that provides a large surface area to pass glucose and oxygen from mother to embryo. Placenta links the embryo to the mother through umbilical cord.
Question. What is placenta? Explain its function in humans.
Answer: Placenta is an intimate connection between fetus and uterine wall of the mother to exchange the materials. It is a disc shaped structure embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on embryo’s side and blood spaces towards mother’s side. Blood spaces surround villi.
Placenta performs the following functions :
(i) All nutritive elements from maternal blood pass into the fetus through it.
(ii) Placental helps in respiration i.e., supply of oxygen and removal of CO2 from fetus to maternal blood.
(iii) Fetal excretory products diffiuse out into maternal blood through placenta and are excreted by mother.
(iv) Placenta also secretes hormone.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually?
Answer: Difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction is as follows :
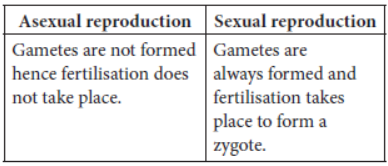
Species reproducing sexually have a better chance of survival as variation occurs only during the sexual reproduction. Variations are necessary for evolution and to increase chances of survival in changed environmental conditions.
Question. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction? What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer: DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction as it results in passing of nearly same genetic information from parents to the offisprings. DNA replication also ensures that same number of chromosomes are passed from parents to offispring.
Advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that sexual reproduction provides variations which is a major factor for evolution that helps in survival of species in changing environment.
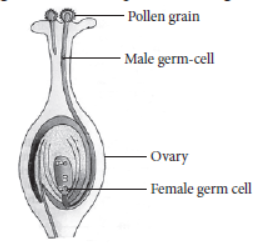
Question. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower exhibiting germination of pollen on stigma and label (i) ovary, (ii) male germ-cell, (iii) female germ-cell and (iv) ovule on it.
Answer: The diagram of the longitudinal section of flower is follows:

Question. Write names of those parts of a flower which serve the same function as the following do in the animals
(i) testis
(ii) sperm
(iii) ovary
(iv) egg.
Answer: The parts of a flower which serve the same function as following do in the animals are
(i) testis – anther of stamen
(ii) sperm – pollen
(iii) ovary – ovary of pistil
(iv) egg – female germ cell present in ovule.
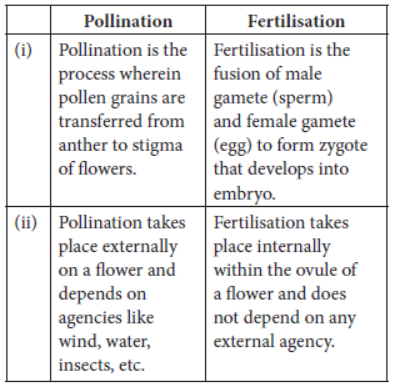
Question. List any two differences between pollination and fertilisation.
Answer: Differences between pollination and fertilisation are as follows:
Question. Name one sexually transmitted disease each caused due to bacterial infection and viral infection. How can these be prevented?
Answer: Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a sexually transmitted disease caused by HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus).
These sexually transmitted disease can be prevented by following monogamy and by using male or female condoms during sexual act.
Question. (a) List two functions performed by testes in human beings.
Answer: (a) The human male possesses two testes which are the primary reproductive organs lying outside the abdominal cavity. Testes are the sites where male gametes, i.e., sperms are produced. Testes also produce testosterone (male sex hormone).
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction. Write the importance of such reproductions in nature.
Answer: The basic requirement for sexual reproduction is involvement of both sexes, i.e., male and female, to produce an offispring. It takes place by the combination of gametes which come from two different parents.
The importance of sexual reproduction in nature are :
• Fusion of male and female gametes coming from two different and sexually distinct individuals, exhibit diversity of characters in offisprings.
• Meiosis during gametogenesis provides
opportunities for new combination of genes, which leads to variation required for evolution and plays a prominent role in the origin of new species. Variations lead to the appearance
of such characters, which fit to the changing environment, resulting in the survival of the species.
Question. What does HIV stands for? Is AIDS an infectious disease? List any four modes of spreading AIDS.
Answer: HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease. It is transmitted sexually or through exposure to contaminated blood.
Four modes of spreading AIDS are :
(i) unprotected sex with an infected partner
(ii) use of contaminated needle and syringes
(iii) use of contaminated razors for shaving
(iv) transfusion of infected blood or blood products.
Question. State the changes that take place in the uterus when :
(a) Implantation of embryo has occurred.
(b) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised.
Answer: (a) Implantation is the close attachment of the blastocyst (young multicellular embryo) to the uterine wall. It is followed by a number of developmental changes in the thickened wall of uterus. An intimate connection between the fetal membrane and the uterine wall called placenta is formed. This is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. The placenta serves as the nutritive, respiratory and excretory organ of the fetus.
(b) As the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself, every month to receive fertilised egg by making its lining thick and spongy to nourish the embryo if fertilisation had taken place. When the female gamete/egg is not fertilised, this lining is not needed any longer.
So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place every month and is known as menstrual cycle.
Question. List any two steps involved in sexual reproduction and write its two advantage.
Answer: The two main steps involved in sexual reproduction are:
(i) formation of male and female gametes.
(ii) fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete to form a new cell called zygote by the process of fertilisation.
The two important advantages of sexual reproduction are:
(i) It promotes diversity of characters in the offisprings through genetic variations.
(ii) It plays an important role in continuous evolution of better organisms that may lead to the origin of new species.
Question. List three techniques that have been developed to prevent pregnancy. Which one of these techniques is not meant for males?
How does the use of these techniques have a direct impact on the health and prosperity of a family?
Answer: Methods developed to prevent pregnancy are:
(i) barrier method, i.e., use of condoms, diaphragm, etc.
(ii) chemical method, i.e., use of oral pills or vaginal pills.
(iii) surgical method, i.e., vasectomy and tubectomy.
Out of these methods, chemical method is not meant for males.
Use of these techniques help to keep control over number of children in a family, which directly effects prosperity of a family. One of the most common reason for deterioration of women’s health is frequent conception and child bearing.
Controlled chilbirth will directly affect women health and this will indirectly affect the prosperity of family and nation.
Question. (b) What is menstruation? Why does it occur?
Answer: (b) Menstruation is the cyclic discharge of blood along with endometrial lining of the uterus and unfertilised egg in women. It last for 3-5 days.
After the release of egg in the females, the uterine lining becomes thickened for the implantation of fertilised egg or zygote. In the absence of fertilisation, the egg along with endometrial lining is expelled out of the body in the form of menstruation.
Question. How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Answer: In organisms reproducing asexually, only single parent is involved in reproduction. Therefore, amount of DNA remains same from parent to offispring. For example in Amoeba, whole organism divides into two daughter individuals by binary fission. Therefore, amount of DNA remain constant.
In organisms reproducing sexually. Reproduction take place with the help of formation of haploid gametes. Gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23 chromosomes. So, when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
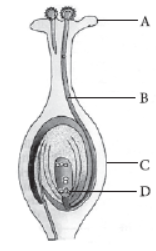
Question. Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.
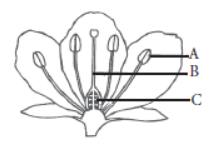
Answer: In the given figure part A is anther, part B is style and part C is ovule.
Anther (A) is a part of male reproductive organ of flower called stamen. Large number of pollen grains are formed inside anther. Style (B) and ovule (C) are parts of female reproductive organ of flower called carpel / pistil.
Style is a long conducting tube which gives the passage to pollen tube carrying male gametes so that it reaches ovary which contains one or more ovules. Ovules contain female gamete or egg. On fertilisation ovary converts into fruit and ovules give rise to seeds.
Question. What are sexually transmitted diseases? List two examples each of diseases caused due to (i) bacterial infection and (ii) viral infection.
Which device or devices may be used to prevent the spread of such diseases?
Answer: The diseases that are spread by sexual contact with an infected person are called sexually transmitted disease (STDs).
(i) Bacterial infection causes Gonorrhoea, Syphilis.
(ii) Viral infection causes AIDS, Genital herpes.
STDs can be prevented by using male and female condoms.
Question. Suggest three contraceptive methods to control the size of human population which is essential for the health and prosperity of a country. State the basic principle involved in each.
Answer: Three contraceptive methods which can help control human population are:
(i) Condoms : It is a mechanical barrier which does not allow sperms and ovum to meet hence prevents fertilisation. Condoms are made of thin rubber/latex sheath used to cover the penis in the male and vagina/cervix in female just before coitus (intercourse) so that the ejaculated semen is not released in the female reproductive tract.
(ii) Intrauterine devices (IUDs) : These are devices inserted by doctors or expert nurses in the uterus through vagina. These are presently available as non-medicated IUDs, copper releasing IUDs (CuT, etc.) and hormone releasing IUDs. They increase phagocytosis of sperms within uterus and suppress sperm motility and its fertilising capacity.
They also make uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to sperms.
(iii) Oral pills : Oral pills contain progesterone alone or a combination of progestogen and estrogen. They inhibit ovulation and make uterus unsuitable for implantation, hence prevent fertilisation.
Question. What are the functions of testis in the human male reproductive system? Why are these located outside the abdominal cavity? Who is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Answer: Testes, in human males, are the primary reproductive organs. They are the site of sperm formation. The testes also produce male sex hormone testosterone. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. The temperature of the testes in the scrotum is about 2–2.5°C lower than normal body temperature. This temperature is ideal for sperm formation and development. Hormone testosterone brings about the development of secondary sexual
character during puberty in boys like growth of facial hair, deepening of voice, growth of scrotum and penis, accumulation of muscle mass, etc., and also regulates formation of sperms.
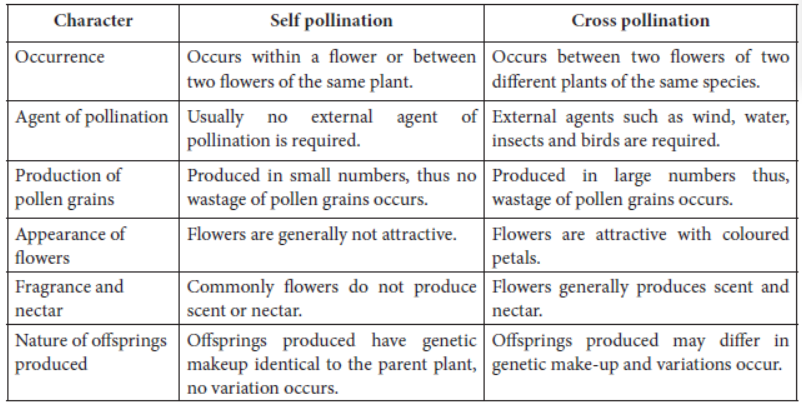
Question. What is meant by pollination? Name and differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants.
Answer: The process of transfer of pollen grains from anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same species is known as pollination. The two modes of pollination are self pollination and cross pollination.
Differences between self pollination and cross pollination are:
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly accurate, on the reproductionprocess? How does the amount of DNA remain constant through each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
Answer: In the process of reproduction, if DNA copying is not perfectly accurate, variation occurs. These in turn may allow few individuals of a population to survive in an altered niche and becomes the basis of evolution and over time. Such variations are useful for the survival of species.
The combination of DNA copies of two individuals (male and female) occurs during sexual reproduction. Reduction division (meiosis) during gamete formation halves the chromosome number in both male and female gametes. Since these two gametes fuse during fertilisation, the original number of chromosomes (as in the parent) is restored in the o spring. By this way the amount of DNA remains constant in each new generation.
Question. Reproduction is one of the most important characteristic of living beings. Give threereasons in support of the statement.
Answer: Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings because :
(i) it is essential for existence and continuity of a species.
(ii) it helps to pass genetic information to next generation.
(iii) it brings variations in next generation which is the basis for evolution.
Question. How does Plasmodium reproduce. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Answer: Plasmodium reproduces through multiple fission method. In this method, the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time. is is an asexual method of reproduction.
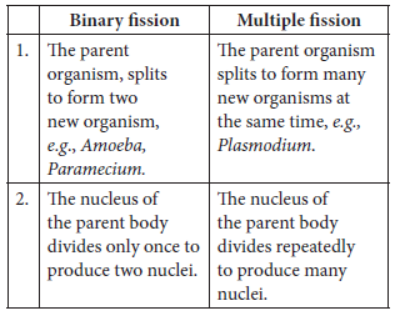
Question. Write two differences between binary fission and multiple fission in a tabular form.
Answer: Differences between binary fission and multiple fission are as follows:
Question. List four advantages of vegetative propagation.
Answer: The following are the advantages of vegetative propagation :
(i) The characters of the parent plants are preserved hence a good variety produced can be propagated by vegetative means.
(ii) The plants, which do not produce viable seeds or produce very few seeds, can be reproduced by this method, for example, banana, potato, grapes, sugarcane, rose, orange, etc.
(iii) It is an easier, quicker and cheaper method of propagation.
(iv) It is easier to get rid of pathogen from any part of plant by vegetative propagation.
Question. List four modes of asexual reproduction.
Answer: The four modes of asexual reproduction are :
(i) binary fission, (ii) budding
(iii) regeneration and
(iv) vegetative propagation.
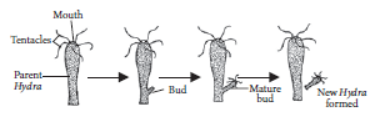
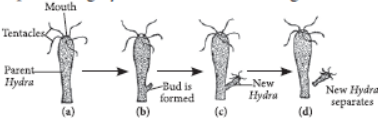
Question. Draw labelled diagrams to illustrate budding in Hydra.
Answer: The given diagram illustrates budding in Hydra:
Question. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer: The process of reproduction results in the production of offsprings which are similar (but not identical) to parents. The exact blue print of body design is inherited in the o springs due to DNA replication (copying) in parent cell during reproduction. Thus, DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction.
Question. Explain the terms:
(i) Implantation of zygote
Answer: (i) Implantation of zygote refers to the process of attachment of the blastocyst on the inner wall of the uterus. It occurs on 7th day after fertilisation and is controlled by estrogen and progesterone hormones.
Question. Write the full form of DNA. Name the part of the cell where it is located. Explain its role in the process of reproduction of the cell.
Answer: The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is located in the nucleus of a cell in the form of chromosomes. It contains information for the inheritance of characteristics from the parents to the next generation. Copying of DNA is an essential part of the process of reproduction because its makes possible the transmission of characteristics of the parents to its offsprings in the next generation. At the time of replication two copies of DNA are formed. DNA copying is accompanied by creation of additional cellular apparatus and then DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus. Thus, a cell divides to form two daughter cells.
Question. Describe the role of the following in human beings.
(i) Seminal vesicles
(ii) Prostate gland
Answer: (i) Seminal vesicles are one pair of sac like structures near the base of bladder. Seminal fluid is a watery alkaline fluid that contains nutrients (fructose) which serve as a source of energy for the sperm. Each seminal vesicle releases its contents into the ejaculatory duct during ejaculation.
(ii) Prostate gland is a single large gland that surrounds urethra. It secretes a slightly acidic, milky fluid that forms 25% of volume of semen.
Secretion of prostate gland nourishes the sperms and helps in its mobility.
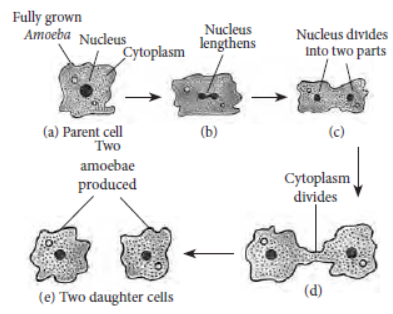
Question. With the help of diagrams show the different stages of binary fission in Amoeba.
Answer: Different stages of binary fission in Amoeba are as follows:
Question. What happens when (a) accidently, Planaria gets cut into manypieces
(b) Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil (c) on maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts?
Answer: (a) When Planaria accidently gets cut into many pieces then its each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
(b) When the Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil, the buds present in the notches along the leaf margin develop into new plants. This is known as vegetative propagation.
(c) The sporangia of Rhizopus contain cells or spores that can eventually develop into new Rhizopus individuals when it bursts on maturation.
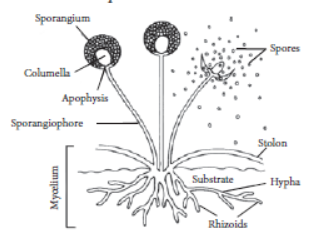
Question. Describe reproduction by spores in Rhizopus.
Answer: Fungus Rhizopus reproduces by spore formation. During the growth of Rhizopus, small rounded, bulb-like structures develop at the top of the erect hyphae. Such structures are called sporangia. Inside each sporangium, nucleus divides several times. Each nucleus gets surrounded by a little amount of cytoplasm to become spore.
Large number of spores are formed inside each sporangium. After sometime sporangium bursts and spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions, they germinate into new individuals.
Question. (a) What is fragmentation in organisms?
Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by this method.
(b) What is regeneration in organism?
Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer: (a) Fragmentation is the mode of reproduction in which parent body breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment develops into a new individual. It is a method of reproduction in many flamentous algae, mycelial fungi and thalloid bryophytes, e.g., Spirogyra.
The given figure shows the process of fragmentation in Spirogyra.

(b) Regeneration may be defined as the ability of an organism to regenerates lost part of the body which have been removed as by injury or autotomy.
Many fully differentiated organisms use this ability as a mode of reproduction and give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts. It is common in Hydra, Planaria, etc.
The process of regeneration in Planaria is described in the figure given below.

Question. Describe the role of Fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system.
Answer: Fallopian tubes are a pair of elongated, ciliated, muscular and tubular structures extending from close to ovaries to uterus. It is the site of fertilisation and helps in the conduction of ovum or zygote towards uterus by ciliary action and peristalsis.
Question. Define reproduction. How does it helps in providing stability to the population of species?
Answer: The production of new organisms by the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction. It is linked to the stability of population of a species. DNA replication during reproduction ensures transfer of specific characters or body design features that is essential for an individual of a population to live and use that particular niche. Some variations present in a few individuals of population caused due to reproduction also help in their survival at changing niches.
Question. How do Plasmodium and Leishmania reproduce? Write one difference in their mode of reproduction.
Answer: Plasmodium and Leishmania reproduce by the process of fission which is asexual mode of reproduction. Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission. About 1000 daughter cells are produced by the multiple fission of a Plasmodium. Leishmania reproduces by the process of binary fission. In Leishmania, the splitting of parent cell takes place in a definite plane (longitudinally) with respect to flagellum at its end to produce two daughter cells.
Question. What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Answer: Multiple fission refers to the process of asexual reproduction in which many individuals are formed from a single parent. This method of reproduction occurs in unfavourable conditions. The unicellular organism develops a protective covering called cyst, over the cell. The nucleus of the cell divides repeatedly producing many nuclei.
Later on, each nucleus is surrounded by small amount of cytoplasm and many daughter cells are produced within the cyst.
When conditions are favourable the cyst breaks and small offsprings are liberated. This type of reproduction is seen in some protozoans, e.g., malarial parasite (Plasmodium).
Question. What is the main difference between sperms and eggs of humans? Write the importance of this difference.
Answer: The main difference between sperms and eggs of humans is that a sperm has X or Y chromosome whereas egg has X chromosome. This helps in determination of the sex of a person and maintaining the genetic continuity in the organisms.
Question. In the context of reproduction of species state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each.
Answer: The main differences between fission and fragmentation are as follows:
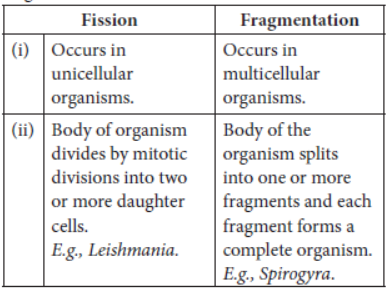
Question. Explain giving one example of each, the unisexual and the bisexual flowers.
Answer: (i) Unisexual flowers : These flowers contain either stamens (male reproductive part) or carpel (female reproductive part). Example: Papaya, watermelon.
(ii) Bisexual flower : The flower is said to be bisexual when both male and females parts i.e., stamens and carpels, are present on the same flower. Example : Hibiscus, mustard.
Question. What happens when (a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces
(b) a mature Spirogyra flament attains considerable length
(c) on maturation sporangia burst?
Answer: (a) When Planaria is cut into two pieces then each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration.
(b) When a mature Spirogyra flament attains a considerable length it breaks into small pieces called fragments. These fragments grow into new individuals and this mode of reproduction is called fragmentation.
(c) When a sporangium burst, large number of spores are released in the air. When these spores land on food or soil, under favourable conditions they germinate into new individuals.
Question. State the role of placenta in the development of embryo.
Answer: Placenta is a physiological connection between an embryo and uterine wall of the mother through which nutrients and other useful substances enter into fetus from mother’s blood and waste products like urea and carbon dioxide are expelled into mother’s blood from fetus.
Question. What is binary fission in organisms? With the help of suitable diagrams, describe the mode of reproduction in Amoeba.
Answer: Binary fission is the division of adult parental body into two nearly equal daughter cells. It is the simplest and most common method of asexual reproduction found in protistan protozoans i.e. Amoeba, Paramecium, etc.
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts. When the Amoeba cell has reached its maximum size of growth, then first the nucleus of Amoeba lengthens and divides into two parts. After that the cytoplasm of Amoeba divides to form two smaller Amoeba (called daughter amoebae).
Diagrammatic representation of binary fission in Amoeba is as follows :

Question. What is vegetative propagation? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing some types of plants.
Select two plants from the following which are grown by this process :
Banana, Wheat, Mustard, Jasmine, Gram
Answer: Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of reproduction in plants. In this method, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves), without the help of any reproductive organs.
Advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows:
(i) Vegetative propagation is usually used for the propagation of those plants which produce either very few seeds or do not produce viable seeds.
(ii) Seedless plants can be obtained by artificial vegetative propagation.
(iii) Grafing is a propagation method which is very useful for fruit trees and flowering bushes. It enables to combine the most desirable characteristics of two plants.
(iv) Plants like rose, sugarcane, cactus, etc., can be rapidly propagated through stem cuttings as this method produces new plants from just one plant quickly without waiting for flowers and seeds.
Banana and jasmine are generally grown through vegetative propagation method.
Question. What is DNA copying? State its importance.
Answer: DNA copying is the production of similar copies of DNA present in a cell using various chemical reactions. DNA copying is essential for reproduction through which the organisms pass on their body features to their offsprings. Moreover, minor alternations during the process of DNA copying result in the production of variations. Such variations are useful for the survival of species over time.
Question. List two advantages of vegetative reproduction practised in case of an orange plant.
Answer: The two advantages of vegetative propagation practised in case of an orange plant are :
(i) The new plants produced by vegetative propagation will be exactly like the parent plant.
Therefore, any desirable features of the parent plant will be replicated in the new plants.
(ii) The orange plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds, can also be propagated.
Question. Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria. How is this process different from reproduction?
Answer: Planaria possesses great power of regeneration.
If the body of Planaria somehow gets cut into a number of pieces, then each body piece can regenerate into a complete Planaria by growing all the missing parts. This is shown in following figure.

During the process of reproduction new organism is formed from the complete parent organism however, during fragmentation, a fragment of original parent body grows into new individual.
Question. List two advantages of practising vegetative propagation in plants. Select two plants raised by this method from the list given below :
Banana, Gram, Pea, Rose, Tomato, Wheat
Answer: Two advantages of the vegetative propagation of plants are :
(i) Any desirable features of the parent plant can be replicated in the new plants.
(ii) Flowers and fruits can be grown in a shorter time as compared to the plants grown from seeds.
The two plants raised by this method are banana and rose.
Question. Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give one reason.
Answer: When a cell reproduces, DNA replication occurs which results in formation of two similar copies of DNA. The process of copying the DNA have some variations each time. As a result, the DNA copies produced are similar to each other but may not identical sometimes.
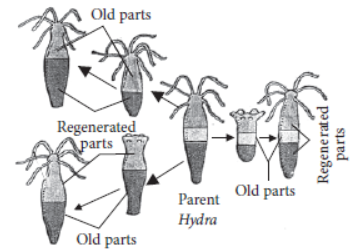
Question. On cutting the body of an organism into many pieces, it was observed that many of these pieces developed as new individuals.
Name the process and list two organisms in which this process may be observed. Draw a schematic diagram to illustrate the changes that are likely to be observed during the development of new individuals in any one of the organisms named.
Answer: On cutting the body of an organism into many pieces, each of these pieces develop as new individuals. This process is known as regeneration.
Hydra and Planaria are the organism in which this process may be observed. Following is the diagram show development of new individuals by regeneration of body parts of a parent Hydra.
Question. With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the various steps of budding in Hydra.
Answer: In multicellular organisms, such as Hydra, a small protuberance arises from one side of the body. The protuberance grows, and develops adult like structure. In Hydra it develops a hypostome and tentacles at its free end. It develops a basal disc at the point of attachment with the parent organism and finally gets detached to lead an independent life.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method.
Answer: Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which the plant parts other than seeds are used as a propagule.
Advantages of vegetative propagation :
(i) Desirable character of the plant can be preserved through generation.
(ii) Seedless plants can be grown through this method.
Disadvantages of vegetative propagation :
(i) Plants produced by this method posses less vigour and are more prone to diseases.
(ii) Plants produced by this method show no genetic variation.
Question. List any two modes of asexual reproduction in animals. Under which mode of reproduction is vegetative propagation placed and why? List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Answer: The two modes of asexual reproduction in animals are : (i) fission (ii) fragmentation.
Vegetative propagation is placed under asexual mode of reproduction because in this mode new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves), without the help of any reproductive organs.
Question. Name an organism which reproduces by spore formation. List three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow.
Answer: Rhizopus reproduce by the method of spore formation.
The three conditions favourable for spores to germinate and grow are moisture, suitable temperature and food (nutrition).
Question. (a) Name the following:
(i) Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus.
(ii) ‘Blobs’ that develop at the tips of the nonreproductive threads in Rhizopus.
(b) Explain how these structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus.
Answer: (a) (i)Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus are called hyphae.
(ii) Blobs developing at the tip of hyphae are called sporangia which contain spores.
(b) The structures called spores are present in sporangia which can develop into new Rhizopus individuals. These spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with another moist surface and can begin to grow.
Question. Why is ferilisation not possible without pollination?
Answer: The process of pollination (in plants) ensures that male gametes bearing structure called pollen comes in contact with the female reproductive structure of the plant. Once the male and female gametes are in close vicinity, they fuse and fertilisation is accomplished. Hence, fertilisation cannot take place without pollination.
Question. List two preparations shown every month by the uterus in anticipation of pregnancy in humans.
Answer: The two preparation shown every month by the uterus in anticipation of pregnancy in human are:
(i) the wall of uterus becomes thick to receive the fertilised egg and
(ii) the uterine wall is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
Question. State one genetically different feature between sperms and eggs of humans. What is its consequence?
Answer: A sperm may have X or Y chromosomes whereas egg have X chromosomes. The consequence of this is that sperm decides the sex of the child because eggs contribute only X
chromosome while sperms contribute either X or Y chromosomes to the offspring. Therefore, if a child inherits X chromosome from her father, will be a girl and the one that inherit Y chromosome will be a boy.
Question. “The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same”. Justify this statement.
Answer: In sexual reproduction, two gametes, male and female, combines together to form a new cell ‘zygote’. The reproductive cells or gametes contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the non-reproductive cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosome and the human egg has also 23 chromosomes. So when a sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes in humans.
Question. Explain the term “regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms.
Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Answer: The process of formation of entire organism from the body parts of a fully differentiated organism is called regeneration. It occurs by process of growth and development.
Simple animal like Hydra shows regeneration.
When a small piece of Hydra breaks of it grows into complete new Hydra.
During regeneration, the cells of cut body part of the organism divide rapidly to make a mass of cells. The cells here move to their proper places within the mass where they have to form different types of tissues. In this way complete organism is regenerated.
Question. (a) What is spore formation?
(b) Draw a diagram showing spore formation in Rhizopus.
(c) List two advantages for organisms to reproduce themselves through spores.
Answer: (a) Spore formation is the process of formation of microscopic reproductive structures called spores. These spores when detaches from the parent gives rise to a new individual. Reproduction by the formation of spores is a common method of asexual reproduction in some bacteria and most of the fungi.
(b) Following figure shows the process of spore formation in Rhizopus.
(c) Two advantages to spore producing organism are as follows:
(i) Spores help organism to survive harsh environmental conditions as spores are covered by thick walls which protect them until they come in contact with moist surface and germinate.
(ii) Spores are generally very small and light.
Therefore, it ensures easy dispersal by wind, water and animal.
Question. List the parts of human male reproductive system which contribute fluid to the semen.
State two advantages semen ofers to the sperms.
Answer: The secretion of male accessory reproductive glands i.e., seminal vesicles, prostate gland and Cowper’s glands contribute fluid to the semen.
The two advantages that semen offers to the sperms are :
(i) it provides nutrition to the sperm and (ii) it also activates the sperms and make their transport easier into the vagina of female during sexual act.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located?
Explain in brief the structure of its female reproductive parts.
Answer: The reproductive organs of an angiosperm are stamen (male reproductive part) and carpel/pistil (female reproductive part). These are located in the flowers of an angiospermic plant. The given diagram shows the structure of female reproductive part of a flower.

A carpel is made of three parts : stigma, style and ovary. The top part of carpel is called stigma.
Stigma is for receiving the pollen grains during pollination. Stigma is sticky so that pollen can stick to it. The middle part of carpel is called style.
Style is a tube which connects stigma to the ovary.
The swollen part at the bottom of a carpel is called ovary. The ovary contains ovules. Ovules contain the female gametes or female sex cells (egg) of the plant.
There are usually many ovules in the ovary. Each ovule contains only one female gamete of the plant.
Question. (a) Mention the role of the following organs of human male reproductive system.
(i) Testis (ii) Scrotum (iii) Vas deferens
(iv) Prostate gland
(b) What are the two roles of testosterone?
Answer: (a) (i) Testis : The two testes in male are the sites where male gametes, i.e., sperms are formed.
Testes also produce the male sex hormone called testosterone.
(ii) Scrotum : The scrotum is a pouch of skin that lie outside abdominal cavity. The two testes lie in respective scrotal sacs. The scrotum acts as a thermoregulator and provides an optimal temperature for the formation of sperms.
(iii) Vas deferens : This is a straight tube, about 40 cm long, which carries the sperms to the seminal vesicles, where mucus and a watery alkaline fluid containing fructose, mix with the sperms.
(iv) Prostate gland : It is a single large gland that surrounds the urethra and produces a milky, slightly acidic secretion. Secretion of prostate gland nourishes and activates the sperm to swim.
(b) Two roles of testosterone are :
(i) It plays a key role in development of male secondary sex organs such as prostate, etc.
(ii) It promotes the secondary sexual characteristics in males such as increased muscle and bone mass, growth of body hair, etc.
Question. List any four methods of contraception used by humans. How does their use have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of a family.
Answer: The four methods of birth control which deliberately prevent fertilisation in humans are:
(i) Barrier method- These are physical devices to prevent the entry of sperm in the female e.g., condoms.
(ii) Chemical method – It involves the use of oral pills that check ovulation. These are mainly hormonal preparations and contain estrogen and progesterone.
(iii) Intrauterine contraception device- These devices are implemented into uterus, e.g., copper – T, to prevent fertilisation.
(iv) Surgical methods : These methods involves removal of a small portion of vas deferens in males or Fallopian tube in females to prevent fertilisation.
Contraception prevents frequent pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases thus supports good health and prosperity of a family.
Question. Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts :
(i) Female germ cell (ii) Male germ cell
(iii) Ovary
Answer: The flowers which contain only one sex organ, either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flowers. E.g., flowers of papaya and watermelon whereas the flowers which
contain both the sex organs, stamens as well as carpel, are called bisexual flowers, e.g., flowers of Hibiscus and mustard. The given diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma.
Question. List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
Answer: Six specific characteristic of sexual reproduction are as follows:
(i) Two different sexes, i.e., male and female are involved in this process.
(ii) Sexual reproduction involves formation of special sex cells called gametes.
(iii) Fusion of gametes or fertilisation takes place in the body of female (internal fertilisation) or outside (external fertilisation).
(iv) Offisprings inherit traits from both parents (heredity) and also show some new traits of their own (variation), hence they are not clones of the parents.
(v) Variations in sexually reproducing organisms arises on account of crossing over during meiotic division during gamete formation.
(vi) It plays a prominent role in origin of new species as it leads to variations which accumulate over a period of time and get carried to successive generations.
Question. On the notice board of ultrasound clinics it is generally stated. “Here prenatal sex determination and disclosure of sex (boy or girl before birth) of fetus is not done. It is prohibited and punishable under law.”
(a) List two advantages of imposing ban on prenatal sex determination.
(b) What can students do to educate the society about the following?
(i) The ill-effects of indiscriminate female feticide.
(ii) Adopting small family norms
Answer: (a) The two advantages of imposing ban on prenatal sex determination are
(i) check on female feticide
(ii) improving sex ratio in the country.
(b) Students should educate the society as that (i) female feticide is reducing the number of girls drastically in some societies. For a healthy society, the male-female sex ratio must be maintained at almost the same level. Due to reckless female feticide, the male-female child sex ratio is declining at an alarming rate in some sections of our society.
(ii) Children in a small family can be provided with all the resources from education, good amenities like food, clothing and healthy life style.
As the family grows larger, the resources should be shared with increased number of member. Having fewer children also keeps the mother in good health.
Question. Name the two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower which contain the germ cells.
State the location and function of its female reproductive part.
Answer: The two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower which contain the germ cells are carpel (female reproductive part) and stamen (male reproductive part). Carpel is situated in the centre of the flower as a fask-shaped structure. A carpel is made up of three parts–stigma, style and ovary. The distal part of a carpel is called stigma. Stigma is responsible
for receiving pollen during pollination. Style is an elongated tubular structure which connects stigma with ovary. The basal swollen part of carpel is ovary.
Ovary bears several ovules. After fertilisation ovules form seeds and ovary forms the fruit.
Question. (a) List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
(b)

(i) Name the part marked A in the diagram.
(ii) How does A reaches part B?
(iii) State the importance of the part C.
(iv) What happens to the part marked D after fertilisation is over?
Answer: (a) Variations arise in sexually reproducing organisms on account of the following :
(i) Genetic variations occur of because DNA copying mechanism is not absolutely accurate.
(ii) Creation of new combinations of genetic variations because variations from two individuals combine during fusion of gametes.
(b) (i) A is pollen grain.
(ii) Part B is stigma. It is the part of pistil (female reproductive organ) that receives pollen grains.
Pollen grain reach stigma through various agencies like wind, water, insect, etc.
(iii) Pollen tube (C) carries male gametes to the ovule present in ovary. Male gametes fuse with egg and secondary nucleus to give rise to zygote and endosperm.
(iv) Female gamete (D) fuses with male gamete and converts to embryo after fertilisation.
Question. What is sexual reproduction? List its four significances.
Answer: Sexual reproduction is the process of production of offispring by the fusion of male and female gametes.
Here haploid gametes fuse to form diploid zygote which develop into a mature organism.
Significances of sexual reproduction are as follows:
(i) Sexual reproduction gives rise to genetic variations because of genetic recombination that takes place during fusion of gametes.
(ii) Progenies arising through sexual reproduction sometimes show better combination of traits and get better adapted to their surroundings.
(iii) Genetic recombination, interaction, etc.
during sexual reproduction provide vigour and vitality to the offispring.
(iv) Variations in genes play an important role in evolution.
Question. State in brief the changes that take place in a fertilised egg(zygote) till birth of the child in the human female reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilised?
Answer: When the ovum (or egg) is fertilised in the oviduct, then a zygote is formed. The zygote divides rapidly by mitosis as it moves down slowly in the oviduct and forms a ball of cells. This hollow ball of cells, called an embryo sinks into the soft and thick lining of the uterus and gets embedded in it. The embedding of embryo in the thick lining of the uterus is called implantation.
After implantation, a disc-like special tissue developsbetween the uterus wall (called uterine wall) and the embryo (or fetus), which is called placenta. The fetus is connected to placenta in mother’s body through umbilical cord. It is through the placenta that all the requirements of the developing fetus like nutrition, respiration and excretion, etc., are met from the mother’s body.
The time period from the fertilisation upto the birth of the baby is called gestation. The average gestation period in humans (or the average during of human pregnancy) is about nine months.
During the gestation period, the fetus grows to become a baby. Birth begins when the strong muscles in the walls of the uterus start to contract rhythmically. The rhythmic contraction of uterus muscles gradually pushes the baby out of the mother’s baby through vagina and a baby is born.
If, a sperm is not available at the time of ovulation, then fertilisation of ovum (or egg) does not take place. Since the ovum (or egg) is not fertilised, so the thick and soft uterus lining having lot of blood capillaries in it is not required. The unfertilised ovum dies within a day and the uterus lining also breaks down. The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick and soft lining of the uterus alongwith its blood vessels is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
Question. Expand AIDS. List any four methods of prevention (control) of AIDS.
Answer: AIDS is expanded as Acquired Immunode deficiency Syndrome. Four methods of prevention or control of AIDS are :
(i) use of sterilised needles and syrings for injecting drugs or vaccine
(ii) to avoid sex with multiple partners
(iii) use of condoms during intercourse
(iv) avoid use of contaminated razor in barber shop.
Question. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country.
Answer: The general awareness regarding reproductive health in a society is significant as :
(i) maintenance of personal hygiene among youngsters and proper knowledge of their reproductive parts helps them adjust with the physical changes and cope with emotional disturbance .
(ii) reproductively healthy society must be free from the curse of child marriage which begets many complications at the level of individual and society both.
(iii) proper care of expecting mothers, monitoring their health after child birth and care of new born help in building a healthy society.
(iv) married couples aware of contraceptive methods lead a better married life as they are capable of avoiding unwanted pregnancies and have negligible chances of contracting sexually
transmitted diseases.
In past 50 years various areas related to reproductive health have been launched which have improved the reproductive health of our society in following ways : Two of them are :
(i) reduced mortality rate of mother and infant
(ii) birth control due to easily available contraceptive and reduced STDs cases.
Question. (a) Write the functions of each of the following parts in a human female reproductive system.
(i) Ovary
(ii) Uterus
(iii) Fallopian tube
(b) Write the structure and functions of placenta in a human female
Answer: (a) (i) The ovaries in female are primary sex organs (or female gonads) which perform the dual function – production of female gametes (eggs or ova) and secretion of female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
(ii) Uterus is a single, pear-shaped, highly muscular, hollow structure present in the pelvic cavity, lying between urinary bladder and rectum.
If fertilisation takes place, the embryo gets implanted to the wall of uterus and grows there until birth. Development of foetus occurs inside uterus, hence it is also called womb.
(iii) Oviducts or Fallopian tube are paired tubes originating near to the ovaries of their respective sides and extend upto uterus. The terminal part of Fallopian tube is funnel-shaped with fingerlike projections called fimbriae lying near ovary.
Fimbriae pick up the ovum released from ovary and push it into Fallopian tube. Fertilisation also takes place in the oviduct.
Question. (a) Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.
(b) What is pollination? Explain its signi- ficance.
(c) Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develop after fertilisation into (i) seed, (ii) fruit.
Answer: (a) In the given diagram A is stigma, B is pollen tube, C is ovary and D is female germ cell.
(b) The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower is known as pollination.
Pollination is important because it brings pollen grains to the female reproductive part (carpel) of the plant that leads to fertilisation.
(c) Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary.
Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg.
After fertilisation,
(i) ovule develops into seed
(ii) ovary develops into fruit.
Question. Write two examples each of sexually transmitted diseases causes by (i) virus, (ii) bacteria. Explain how the transmission of such diseases be prevented?
Answer: The infectious (communicable) diseases, which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person by sexual contact, are called sexually transmitted diseases.
Sexually transmitted diseases caused by virus are :
AIDS (Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome) and genital warts while caused by bacteria are gonorrhoea and syphilis.
Preventive measures for the diseases are:
(i) educating people in high risk groups.
(ii) mutually faithful monogamous relationship.
(iii) avoiding prostitution, multipartner sex and homosexuality.
(iv) using condoms, etc.
Question. (a) Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label that part where
(i) eggs develop
(ii) fertilisation take place
(iii) fertilised egg gets implanted
(b) Describe, in brief, the changes that uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote
(ii) if zygote is not formed.
Answer: (a) The sectional view of human female reproductive system is as follows:

(i) Ovary is the part where eggs develop.
(ii) Fallopian tube is the part where fertilisation takes place.
(iii) Uterus is the part where fertilised egg gets implanted.
(b) (i) When the ovum (or egg) is fertilised in the oviduct, then a zygote is formed. The uterus prepares itself every month to receive a zygote.
The inner lining of uterus becomes thick and spongy with lot of blood capillaries in it. This would be required for nourishment and further development of embryo.
(ii) If a sperm is not available at the time of ovulation, then fertilisation of ovum does not take place. Since the ovum (or egg) is not fertilised, so the thick and soft uterus lining having lot of blood capillaries in it is not required. The unfertilised ovum dies within a day and the uterus lining also breaks down. The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick and soft lining of the uterus alongwith its blood vessels in the form of vaginal bleeding is called menstrual flow or menstruation.
Question. List in tabular form the two differences between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Name and explain with the help of labelled diagram the process by which Hydra reproduces asexually.
Answer: Differences between asexual and sexual forms of reproduction are following.

Hydra is simple multicellular animal. It reproduces asexually by the process of budding. In Hydra first a small outgrowth called ‘bud’ is formed on the side of its body by the repeated mitotic divisions of its cells. This bud then grows gradually to form a small Hydra by developing a mouth a tentacles.
Finally, the tiny new Hydra detaches itself from the body of parent and lives as a separate organism. In this way, the parent Hydra produce a new Hydra. The following figure shows Hydra reproducing by the method of budding.
Question. (a) Explain why variations are observed in the offisprings of sexually reproducing organisms?
Answer: (a) Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes coming from male and female parents. Variations occur due to (i) fusion of gametes which come from two different and sexually distinct individuals and (ii) meiosis which occurs during gametogenesis and create a new combination of genes. It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species and leads to variations required for evolution. Therefore, offisprings of sexually reproducing organisms show variation.
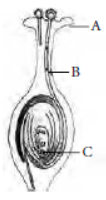
Question. (a) Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
(b) Mention the role of gamete and zygote in sexually reproducing organisms.
Answer: (a) A represents stigma. It receives the pollen grains from the anther of stamen. Stigma is sticky so that pollen can stick to it so that fertilisation can occur. B represents pollen tube. Pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells from the pollen grain at stigma to the ovules at the base of the carpel for the process of fertilisation. C represent female germ cell. Female germ cell fertilise with male germ cells to forms zygote which develops into an embryo within the ovule. Ovule converts into a seed that gives rise a new individual.
(b) Role of Gamete : Gametes are the reproductive cells involved in sexual reproduction having half of the chromosome. Gametes carry variations generated during its formation (meiosis). A male gamete and a female gamete fuses to form zygote.
Role of Zygote : The fusion of male gamete with female gamete forms a zygote during sexual reproduction. Zygote has normal number of chromosomes and new combinations of variation that express in new generation. The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions to form the embryo which has the potential to form a complete individual.
Question. (a) Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flower.
(b) Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
(c) How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals.
Answer: (a) Unisexual flowers bear organs of only one sex, i.e., either stamen or pistil, e.g., papaya.
Bisexual flowers contain both stamen and pistil, e.g., Hibiscus.
(b) After fertilisation, the fertilised egg (or zygote) divides several times to from an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat around it and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary of flower develops and becomes a fruit (with seeds inside it). The other parts of flower like sepals, petals, stamens ,stigma and style dry up and fall of. Only the ovary is left behind. So, at the place on plant where we had a flower originally, we now have a fruit (which is the ovary of the flower containing seeds). A fruit protects the seeds.
(c) The amount of DNA remain constant in each new generation because of formation of haploid gametes. Gametes are special type of cells called reproductive cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have the normal amount of DNA. For example, the human sperm has 23 chromosomes and the human egg (or ovum) has also 23 chromosomes. So, when a
sperm and an egg fuse together during fertilisation, then the zygote formed will have 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes, which is the normal number of chromosomes.
Question. (a) Give an example of a bisexual flower.
(b) Draw a longitudinal section of a pistil showing the germination of pollen grains. Label the following parts:
(i) Stigma (ii) Male germ cell
(iii) Female germ cell (iv) Ovary
(v) Style (vi) Pollen tube
Answer: (a) Hibiscus is an example of a bisexual flower.
(b) Diagrammatic representation of pistil showing germination is as follows:

Question. Define the terms pollination and fertilisation.
Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following: pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary.
Answer: The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower is known as pollination.
Fertilisation is the fusion of male gamete with the female gamete (or egg).
Diagrammatic representation of pistil showing germination is as follows:



