Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry The p – Block Elements Chapter 7 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 7 The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
The p – Block Elements Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) S–S bond is present in H2S2O6.
(B) In peroxosulphuric acid (H2SO5) sulphur is in +6 oxidation state.
(C) Iron powder along with Al2O3 and K2O is used as a catalyst in the preparation of NH3 by Haber’s process.
(D) Change in enthalpy is positive for the preparation of SO3 by catalytic oxidation of SO2.
Answer
B
Question. Bond dissociation enthalpy of E-H (E = element) bond is given below. Which of the compounds will act as strongest reducing agent?
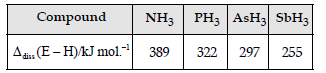
(A) NH3
(B) PH3
(C) AsH3
(D) SbH3
Answer
D
Question. On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
(A) It is highly poisonous and has smell like rotten fish.
(B) It’s solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(C) It is more basic than NH3.
(D) It is less basic than NH3.
Answer
C
Question. A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of:
(A) [Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+
(B) FeSO4.NO2.
(C) [Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
(D) FeSO4.HNO3.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are true?
(A) Only types of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(B) Ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(C) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is a redox reaction.
(D) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Answer
A
Question. Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and non-metals.Which of the following element is oxidised by conc.
H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
(A) Cu
(B) S
(C) C
(D) Zn
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following elements can be involved in pp–dp bonding?
(A) Carbon
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Phosphorus
(D) Boron
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are peroxoacids of sulphur?
(A) H2SO5 and H2S2O8
(B) H2SO5 and H2S2O7
(C) H2S2O7 and H2S2O8
(D) H2S2O6 and H2S2O7
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against each?
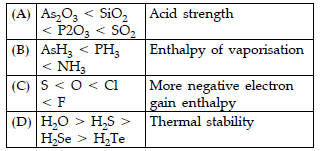
Answer
A,D
Question. Which of the following statements is wrong?
(A) Single N–N bond is stronger than the single P–P bond.
(B) PH3 can act as a ligand in the formation of coordination compound with transition elements.
(C) NO2 is paramagnetic in nature.
(D) Covalency of nitrogen in N2O5 is four.
Answer
A
Question. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O2+PtF6– as a base compound. This is because
(A) both O2 and Xe have same size.
(B) both O2 and Xe have same electron gain enthalpy.
(C) both O2 and Xe have same ionisation enthalpy.
(D) both Xe and O2 are gases.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following does not react with oxygen directly?
(A) Zn
(B) Ti
(C) Pt
(D) Fe
Answer
C
Question. Affinity for hydrogen decreases in the group from fluorine to iodine. Which of the halogen acids should have highest bond dissociation enthalpy?
(A) H-F
(B) HCl
(C) HBr
(D) HI U
Answer
A
Question. Reduction potentials of some ions are given below.Arrange them in decreasing order of oxidising power.

(A) ClO4– > IO4– > BrO4–
(B) IO4– > BrO4– > ClO4–
(C) BrO4–> IO4– > ClO4–
(D) BrO4– > ClO4– > IO4–
Answer
C
Question. Main source of helium is
(A) Air
(B) Radium
(C) Monazite
(D) Water
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements are correct for SO2 gas?
(A) It acts as bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(B) Its molecule has linear geometry.
(C) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute H2SO4 with metal sulphide.
(D) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is iso-electronic pair?
(A) ICl2, ClO2
(B) BrO2–, BrF2 +
(C) ClO2, BrF
(D) CN–, O3 A
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reactions is an example of redox reaction?
(A) XeF4 + O2F2 → XeF6 + O2
(B) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+[PF6]–
(C) XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
(D) XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2F2 + 2HF
Answer
A
Question. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish yellow gas. When excess of this gas reacts with NH3 an unstable tri-halide is formed. In this process the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from:
(A) – 3 to +3.
(B) – 3 to 0.
(C) – 3 to +5.
(D) 0 to – 3.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following does not exist?
(A) XeOF4
(B) NeF2
(C) XeF2
(D) XeF6
Answer
B
Question. In which of the following reactions conc. H2SO4 is used as an oxidising reagent?
(A) CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
(B) 2HI + H2SO4 → I2 +SO2 + 2H2O
(C) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2+ 2H2O
(D) NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
Answer
B,C
Question. Which of the following statements are true?
(A) Only types of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(B) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is a redox reaction.
(C) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
(D) None of the above.
Answer
A
Question. When XeF4 is partially hydrolysed, it yields
(A) XeSO3
(B) XeOF2
(C) XeOF4
(D) XeF2
Answer
B
Question. Complete the following reaction: Xe + PtF6 →
(A) Xe + PtF6 → XeF4 + PtF2
(B) Xe + PtF6 → XeF6 + Pt
(C) Xe + PtF6 → Xe+[PtF6]–
(D) Xe + PtF6 → XeO2F4 + Pt
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not tetrahedral in shape?
(A) NH4 +
(B) SiCl4
(C) SF4
(D) SO42−
Answer
C
Question. The shape of XeF4 is
(A) tetrahedral
(B) square planar
(C) pyramidal
(D) linear
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(B) Leaving F – F bond, all halogens have weaker X – X bond than X – X’ bond in inter-halogens.
(C) Among inter-halogen compounds maximum number of atoms ate present in iodine fluoride.
(D) Inter-halogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Answer
B
Question. On heating ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately we get
(A) N2 in both cases
(B) N2 with ammonium dichromate and NO with barium azide
(C) N2O with ammonium dichromate and N2 with barium azide
(D) N2O with ammonium dichromate and NO2 with barium azide
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following elements is most metallic ?
(A) P
(B) As
(C) Sb
(D) Bi
Answer
D
Question. The correct decreasing order of basic strength is:
(A) AsH3 > SbH3 > PH3 > NH3
(B) SbH3 > AsH3 > PH3 > NH3
(C) NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
(D) PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3 > NH3
Answer
C
Question. Maximum covalency of nitrogen is __________.
(A) 3
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 6
Answer
C
Question. The three important oxidation states of phosphorus are
(A) –3, +3 and +5
(B) –3, +3 and –5
(C) –3, +3 and +2
(D) –3, +3 and +4
Answer
A
Question. A deep brown gas is formed by mixing two colourless gases which are
(A) NO2 and O2
(B) N2O and NO
(C) NO and O2
(D) NH3 and HCl
Answer
C
Question. Nitrogen is relatively inactive element because
(A) its atom has a stable electronic configuration
(B) it has low atomic radius
(C) its electronegativity is fairly high
(D) dissociation energy of its molecule is fairly high
Answer
D
Question. Liquid ammonia bottles are opened after cooling them in ice for sometime. It is because liquid NH3
(A) Brings tears to the eyes
(B) Has a high vapour pressure
(C) Is a corrosive liquid
(D) Is a mild explosive
Answer
B
Question. Pick out the wrong statement.
(A) Nitrogen has the ability to form pπ-pπ bonds with itself.
(B) Bismuth forms metallic bonds in elemental state.
(C) Catenation tendency is higher in nitrogen when compared with other elements of the same group.
(D) Nitrogen has higher first ionisation enthalpy when compared with other elements of the same group.
Answer
C
Question. Pure nitrogen is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of
(A) NH4OH + NaCl
(B) NH4NO3 + NaCl
(C) NH4Cl + NaOH
(D) NH4Cl + NaNO2.
Answer
D
Question. Among the 15th group elements, as we move from nitrogen to bismuth, the pentavalency becomes less pronounced and trivalency becomes more pronounced due to
(A) Non metallic character
(B) Inert pair effect
(C) High electronegativity
(D) Large ionization energy
Answer
B
Question. NH3 gas is dried over :
(A) CaO
(B) HNO3
(C) P2O5
(D) CuSO4
Answer
A
Question. Pentavalence in phosphorus is more stable when compared to that of nitrogen even though they belong to same group.
This is due to
(A) dissimilar electronic configuration
(B) due to presence of vacant d-orbitals
(C) reactivity of phosphorus
(D) inert nature of nitrogen
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is not an use of ammonia ?
(A) To produce various nitrogenous fertilizers.
(B) In manufacture of nitric acid
(C) As a refrigerate
(D) In the pickling of stainless steel
Answer
D
Question. Most acidic oxide among the following is –
(A) N2O5
(B) P2O5
(C) N2O4
(D) As2O3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following species has the highest dipole moment?
(A) NH3
(B) PH3
(C) AsH3
(D) SbH3
Answer
A
Question. Which oxide of nitrogen is obtained on heating ammonium nitrate at 250ºC ?
(A) Nitric oxide
(B) Nitrous oxide
(C) Nitrogen dioxide
(D) Dinitrogen tetraoxide
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following fluorides does not exist?
(A) NF5
(B) PF5
(C) AsF5
(D) SbF5
Answer
A
Question. Ionic radii (in Å) of As3+, Sb3+ and Bi3+ follow the order
(A) As3+ > Sb3+ > Bi3+
(B) Sb3+ > Bi3+ >As3+
(C) Bi3+ > As3+ > Sb3+
(D) Bi3+ > Sb3+ > As3+
Answer
D
Question. With respect to protonic acids, which of the following statements is correct ?
(A) PH3 is more basic than NH3
(B) PH3 is less basic than NH3
(C) PH3 is equally basic as NH3
(D) PH3 is amphoteric while NH3 is basic
Answer
B
Question. Which of the follow group 15 element forms metallic bonds in elemental state ?
(A) As
(B) P
(C) Sb
(D) Bi
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following oxides is neutral ?
(A) N2O3
(B) N2O4
(C) N2O5
(D) N2O
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following has the highest pπ – pπ bonding tendency ?
(A) N
(B) P
(C) As
(D) Sb
Answer
A
Question. Elements of group-15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state.
However, bismuth forms only one well characterised compound in +5 oxidation state. The compound is
(A) Bi2O5
(B) BiF5
(C) BiCl5
(D) Bi2S5
Answer
B
Question. Zinc on reaction with dilute HNO3 gives x and zinc on reaction with concentrated HNO3 gives y. Identify x and y.
(A) x = NO2 , y = N2O
(B) x = N2O , y = NO
(C) x = NO , y = NO2
(D) x = N2O , y = NO2
Answer
D
Question. In Haber’s process for the manufacture of NH3 :
(A) finely divided nickel is used as a catalyst
(B) finely divided iron is used as a catalyst
(C) finely divided molybdenum is used as a catalyst
(D) no catalyst is necessary
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect for group 15 elements ?
(A) Order of ionization enthalpies is ΔiH1 < ΔiH2 < ΔiH3
(B) The boiling point and melting point increases from top to bottom in the group
(C) Dinitrogen is a gas while all others are solids
(D) All statements are correct
Answer
B
Question. Ammonia on reaction with hypochlorite anion can form :
(A) NO
(B) N2H4
(C) NH4Cl
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is incorrect for white and red phosphorus ?
(A) They are both soluble in CS2
(B) They can be oxidised by heating in air
(C) They consist of the same kind of atoms
(D) They can be converted into one another
Answer
A
Question. The shape of ammonia molecule is
(A) tetrahedral
(B) pyramidal
(C) planar triangle
(D) octahedral
Answer
B
Question. Nitrogen forms N2, but phosphorus is converted into P4 from P, the reason is
(A) Triple bond is present between phosphorus atom
(B) pπ – pπ bonding is strong
(C) pπ – pπ bonding is weak
(D) Multiple bond is formed easily
Answer
C
Question. In which the NH3 is not used ?
(A) Cold storage
(B) Anaesthetic
(C) Manufacture of rayon and plastic
(D) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which one has the lowest boiling point ?
(A) NH3
(B) PH3
(C) AsH3
(D) SbH3
Answer
B
Question. Ammonia is generally manufactured for fertilizers by the reaction
(A) 2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2NH3
(B) By passing an electric discharge in a mixture of N2 and H2
(C) By passing a mixture of N2 and H2 under high pressure and moderate temperature over a catalyst
(D) None of these
Answer
C
Question. PCl5 is possible but NCl5 does not exist :
(A) in N, d-sub-shell is absent
(B) ionization energy of N is very high
(C) it does not like Cl
(D) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Nitrogen dioxide cannot be obtained by heating :
(A) KNO3
(B) Pb(NO3)2
(C) Cu(NO3)2
(D) AgNO3
Answer
A
Question. The bonds present in N2O5 are :
(A) only ionic
(B) covalent and coordinate
(C) only covalent
(D) covalent and ionic
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following shows nitrogen with its increasing order of oxidation number?
(A) NO < N2O < NO2 < NO3– < NH4+
(B) NH4+ < N2O < NO2 < NO3– < NO
(C) NH4+ < N2O < NO < NO2 < NO3–
(D) NH4+ < NO < N2O < NO2 < NO3–
Answer
C
Question. In which one of the following oxides of nitrogen, one nitrogen atom is not directly linked to oxygen?
(A) NO
(B) N2O4
(C) N2O
(D) N2O3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following oxides of nitrogen reacts with FeSO4 to form a dark brown compound
(A) N2O
(B) NO
(C) NO2
(D) N2O3
Answer
B
Question. When ammonia is heated with cupric oxide, a molecule of ammonia will
(A) gain 3 electrons
(B) lose 3 electrons
(C) gain 2 electrons
(D) lose 2 electrons
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following can be used as an anaesthesia ?
(A) N2O
(B) NO
(C) NCl3
(D) NO2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct for nitrogen?
(A) Its electronegativity is very high
(B) d-orbitals are available for bonding
(C) It is a typical non-metal
(D) Its molecular size is small
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is a coloured gas?
(A) N2O
(B) NO
(C) N2O5
(D) NO2
Answer
D
Question. The catalyst used in the manufacture of HNO3 by Ostwald’s process is :
(A) platinum gauze
(B) vanadium pentoxide
(C) finely divided nickel
(D) platinum black .
Answer
A
Question. What causes nitrogen to be chemically inert ?
(A) Multiple bond formation in the molecule
(B) Absence of bond polarity
(C) Short internuclear distance
(D) High bond energy
Answer
D
Question. Concentrated nitric acid, upon long standing, turns yellow brown due to the formation of
(A) NO
(B) NO2
(C) N2O
(D) N2O4
Answer
B
Question. Collectively the elements of group 15 are called –
(A) pnicogens
(B) pnicopens
(C) nicopen
(D) None of these
Answer
A
Question. What will be the A and B in the following equations.
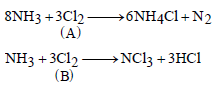
(A) A = Excess, B = Excess
(B) A = Limited, B = Excess
(C) A = Excess, B = Limited
(D) A = Limited, B = Limited
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent ?
(A) NH3
(B) PH3
(C) BiH3
(D) SbH3
Answer
C
Question. The p-block element of group 15 that forms predominantly basic oxide is
(A) N
(B) P
(C) As
(D) Bi
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following element will form acidic oxides of type E2O3?
(A) As
(B) Sb
(C) Bi
(D) P
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following elements does not form stable diatomic molecules ?
(A) Iodine
(B) Phosphorus
(C) Nitrogen
(D) Oxygen
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following trihalide is unstable?
(A) NF3`
(B) AsCl3
(C) SbBr3
(D) NCl3
Answer
D
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false and R is True
Question. Assertion (A): H2O a liquid and H2S a gas.
Reason (R): Water molecules are held by H-bonds while in H2S molecules no such interactions are present between molecules.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): NaCl reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to give colourless fumes with pungent smell. But on adding MnO2 the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason (R): MnO2 oxidises HCl to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): N2 is less reactive than P4.
Reason (R): Nitrogen has more electron gain enthalpy than phosphorus.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur exist as S8 but oxygen exists as O2.
Reason (R): Oxygen forms pp-pp multiple bond due to small size and small bond length but pp-pp bonding is not possible in sulphur.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): HNO3 makes iron passive.
Reason (R): HNO3 forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion(A): Helium diffuses through most commonly used laboratory materials.
Reason(R): This gas has a very low melting point.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): SF6 cannot be hydrolysed but SF4 can be.
Reason (R): Six atoms in SF6 prevent the attack of H2O on sulphur atom of SF6.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): HI cannot be prepared by the reaction of KI with concentrated H2SO4.
Reason (R): HI has lowest H–X bond strength among halogen acids.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Bismuth forms only one well characterised compound in +5 oxidation state.
Reason (R): Elements of group-15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): F2 has lower bond dissociation energy than Cl2.
Reason (R): Flourine is more electronegative than chlorine.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Helium used in diving apparatus.
Reason (R): Helium is very less soluble in blood.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion(A): Group 18 gases exhibit very high ionisation enthalpy.
Reason (R): They have a stable electronic configuration.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): F2 is a strong oxidizing agent.
Reason (R): Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): NaCl reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to give colourless fumes with pungent smell. But on adding MnO2 the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason (R): MnO2 oxidises HCl to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow
Answer
A
Question. Assertion(A): The noble gases are inactive.
Reason(R): These gases have a closed shell structure.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): F2 has lower reactivity.
Reason (R): F-F bond has low Δbond Ho.
Answer
D
CASE-BASED MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
In spite of the predictions of stable noble gas compounds since at least 1902, unsuccessful attempts at their synthesis gave rise to the widely held opinion that noble gases are not only noble but also inert. It was not until 1962 that this dogma was shattered when Bartlett in Canada published the first stable noble gas compound XePtF6. This discovery triggered a worldwide frenzy in this area, and within a short time span many new xenon, radon, and krypton compounds were prepared and characterized. The recent discoveries show the ability of xenon to act as a ligand . The discovery by Seppelt’s group that more than one xenon atom can attach itself to a metal center which in the case of gold leads to surprisingly stable Au- Xe bonds. The bonding in [AuXe4]2+ involves 4 Xe ligands attached by relatively strong bonds to a single Au(II) center in a square planar arrangement with a Xe-Au bond length of about 274 pm This discovery provides not only the first example of multiple xenon ligands but also represents the first strong metal – xenon bond.
Question. Xe is a ___________ ligand
(A) ambidentate
(B) bidantate
(C) unidentate
(D) hexadentate
Answer
C
Question. Hybridisation shown by Au in [AuXe4]2+ is:
(A) sp3
(B) sp3d
(C) sp3d2
(D) sp2
Answer
B
Question. Compounds of noble gases except _______ are known.
(A) Krypton
(B) Radon
(C) Helium
(D) Xenon
Answer
C
Question. In the complex ion [AuXe4]2+, Xe acts as:
(A) central atom
(B) ligand
(C) chelating agent
(D) electrophile
Answer
A
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
In the last 10 years much has been learned about the molecular structure of elemental sulfur. lt is now known that many different types of rings are sufficiently metastable to exist at room temperature for several days. It is known that at high temperature, the equilibrium composition allows for a variety of rings and chains to exist in comparable concentration, and it is known that at the boiling point and above, the vapor as well as the liquid contains small species with three, four, and five atoms. The sulfur atom has the same number of valence electrons as oxygen. Thus, sulfur atoms S2 and S3 have physical and chemical properties analogous to those of oxygen and ozone. S2 has a ground state of 38 σ3s2σ*3s2σ3pz2π3px 2 = p3py2π*3px1 = π*3py1. S3 , thiozone has a wellknown uv spectrum, and has a bent structure, analogous to its isovalent molecules 03, SO2, and S20. The chemistry of the two elements, sulphur and oxygen, differs because sulfur has a pronounced tendency for catenation. The most frequently quoted explanation is based on the electron structure of the atom. Sulfur has low-lying unoccupied 3d orbitals, and it is widely believed that the 4s and 3d orbitals of sulfur participate in bonding in a manner similar to the participation of 2s and 2p orbitals in carbon.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): Thiozone has bent structure like ozone.
Reason (R): Ozone has a lone pair which makes the molecule bent.
Ans. Option (B) is correct.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Sulphur has a greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.
Reason (R): 3d and 4s orbitals of Sulphur have same energy.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Sulphur belongs to same group in the periodic table as oxygen.
Reason (R): S2 has properties analogous to O2.
Answer
B
Ques tion. Assertion (A): S2 is paramagnetic in nature
Reason (R): The electrons in p*3px and p*3py orbitals in S2 are unpaired.
Answer
A
III. Read the given passage and answer the questions (i) to (iv) that follow:
The halogens have the smallest atomic radii in their respective periods. The atomic radius of fluorine is extremely small. All halogens exhibit –1 oxidation state. They are strong oxidising agents and have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy. Among halogens, fluorine shows anomalous behaviour in many properties. For example electronegativity and ionisation enthalpy are higher for fluorine than expected whereas bond dissociation enthalpy, m.p. and b.p. and electron gain enthalpy are quite lower than expected. Halogens react with hydrogen to give hydrogen halides (HX) and combine amongst themselves to form a number of compounds of the type XX’, XX’3, XX’5 and XX’7 called inter-halogens.
Question. Why fluorine shows anomalous behaviour as compared to other halogens?
Answer: (i) It has smallest in size.
(ii) Very high electronegativity.
(iii) Absence of d-orbitals.
(iv) dissociation enthalpy in molecular form is least.
Question. What are the sizes of X and X’ in the interhalogen compounds?
Answer: Size of X is greater than X’.
Question. Why halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy?
Answer: Halogens have only seven electrons in their valence shell. So they require only one electron to attain a noble gas configuration.Hence they have maximum electron gain
enthalpy.
Question. Arrange the hydrogen halides (HF to HI) in the decreasing order of their reducing character.
Answer: HI > HBr > HCl > HF
Question. Why fluorine is a stronger oxidizing agent than chlorine?
Answer: Because fluorine has greater E° value (2.87V) than chlorine (1.36V).

