Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 11 Conic Sections Class 11 Mathematics with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 11 Mathematics issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Mathematics for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 11 Conic Sections in Class 11 Mathematics provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 11 Conic Sections MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 11 Conic Sections MCQ Questions Class 11 Mathematics with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 11 Conic Sections Class 11 Mathematics
Question. A (1/√2 .1/√2) is a point on the circle x2 + y2 = 1 and B is another point on the circle such that arc length AB = π/2 units. Then, coordinates of B can be
(a) (1/√2 .- 1/√2)
(b) (-1/√2 .1/√2)
(c) (-1/√2 .-1/√2)
(d) None of these
Answer
(a,b)
Question. If L = 2x + y = 6, then the locus of circumcentre of ΔPQR is
(a) 2x – y = 4
(b) 2x + y = 3
(c) x – 2y = 4
(d) x + 2y = 3
Answer
B
Question. If a circle passes through the point (1, 2) and cuts the circle x2 + y2 = 4 orthogonally, then the equation of the locus of its centre is
(a) x2 + y2 – 3x – 8y + 1 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y – 7 = 0
(c) 2x + 4y – 9 = 0
(d) 2x + 4y – 1= 0
Answer
C
Question. The locus of the centre of a circle which touches externally the circle x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y+ 14 = 0 and also touches the y-axis is given by the equation
(a) x2 – 6x – 10y + 14 = 0
(b) x2 – 10x – 6y + 14 = 0
(c) y2 – 6x – 10y + 14 = 0
(d) y2 – 10x – 6y + 14 = 0
Answer
D
QuestionRadius of circle in which a chord of length 2 makes an angle π/2 at the centre, is
(a) 1
(b) √3
(c) √3/2
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The condition that the chord x cos α + y sin α – p = 0 of x2 + y2 – a2 = 0 may subtend a right angle at the centre of circle, is
(a) a2 = 2p2
(b) p2 = 2a2
(c) a = 2p
(d) p = 2a
Answer
A
Question. The smallest circle with centre on y-axis and passing through the point (7, 3) has radius
(a) 58
(b) 7
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. If the lines 2x + 3 y + 1 = 0 and 3x – y – 4 = 0 lie along diameters of a circle of circumference 10p, then the equation of the circle is
(a) x2 + y2 – 2x + 2y – 23 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 23 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 2x + 2y – 23 = 0
(d) x2 + y2 + 2x – 2y – 23 = 0
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a point on the common chord of the circles x2 + y2 + 2x – 3y + 6 = 0 and x2 + y2 + x – 8y – 13 = 0 ?
(a) (1, – 2)
(b) (1, 4)
(c) (1, 2)
(d) (1, – 4)
Answer
D
Question. If the chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point on the circle x2 + y2 = a2 = 2 to the circle x2 + y2 = b2 touches the circle x2 + y2= C2, then a, b and c are in
(a) AP
(b) GP
(c) HP
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Find the equation of the circle which touches the both axes in first quadrant and whose radius is a.
(a) x2 + y2 – 2ax – 2by + a2 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 2ax – 2ay – a2 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 + 2ax – 2ay + a2 = 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The equation of the circle on the common chord of the circles (x – a)2 + y2 = a2 and x2 + (y+b)2 = 2 as diameter, is
(a) x2 + y2 + 2ab (bx + ay)
(b) x2 + y2 = bx + ay
(c) (a2 + b2)(x2 + y2 )=2ab (bx – ay)
(d) (a2 + b2)(x2 + y2 )=2ab (bx + ay)
Answer
C
Question. The circle x2 + y2 = 4x + 8y + 5 intersects the line 3x – 4 y = m at two distinct points, if
(a) -85 < m < -35
(b) -35 < m < 15
(c) 15 < m < 65
(d) 35 < m < 85
Answer
B
Question. If P andQare the points of intersection of the circles
x2 + y2 +3x + 7y + 2p – 5 = 0 and x2 + y2 +2x + 2y – p2 – 5 = 0, then there is a circle passing through P, Q and (1, 1) and
(a) all values of p
(b) all except one value of p
(c) all except two values of p
(d) exactly one value of p
Answer
C
Question. The equation of the circle and its chord are respectively x2 + y2 = a2 and x cos a + y sin a = p.
The equation of the circle of which this chord is a diameter is
(a) x2 + y2 – 2px cosα – 2py sinα + 2p2 – a2 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 2px cosα – 2py sinα + p2 – a2 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 2px cosα + 2py sinα + 2p2 – a2 = 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. Consider the circle x2 + (y – 1) = 9, (x – 1)2 + y2 = 25.
They are such that
(a) these circles touch each other
(b) one of these circles lies entirely inside the other
(c) each of these circles lies outside the other
(d) they intersect in two points
Answer
B
Question. If the circle x2 + y2 + 4x + 22y + C = 0 bisects the circumference of the circle x2 + y2 – 2x + 8y – d = 0 then c + d is equal to
(a) 60
(b) 50
(c) 40
(d) 30
Answer
B
Question. Let AB be a chord of the circle x2 + y2 = r2 subtending a right angle at the centre. Then, the locus of the centroid of the D PABas P moves on the circle is
(a) a parabola
(b) a circle
(c) an ellipse
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The circle x2 + y2 – 8x + 4y +4 = 0 touches
(a) x-axis
(b) y-axis
(c) both axis
(d) neither x-axis nor y-axis
Answer
B
Question. Equation of a circle which passes through (3, 6) and touches the axes is
(a) x2 + y2 + 6x + 6y + 3 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y – 9 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 6x – 6y + 9 = 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. The radical axis of the co axial system of circles with limiting point (1,2) and (–2, 1) is
(a) x + 3y = 0
(b) 3x + y = 0
(c) 2x + 3y = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The locus of a point which moves so that the ratio of the length of the tangents to the circles x2 + y2 + 4x + 3 = 0 and x2 + y2 – 6x + 5 = 0 is 2 : 3, is
(a) 5x2 + 5y2 + 60x – 7 = 0
(b) 5x2 + 5y2 – 60x – 7 = 0
(c) 5x2 + 5y2 + 60x + 7 = 0
(d) 5x2 + 5y2 + 60x + 12 = 0
Answer
C
Question. If (- 3, 2) lies on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y – 5 = 0 then c is equal to
(a) 11
(b) – 11
(c) 24
(d) 100
Answer
B
Question. Find the equation of a circle concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 12y + 15 = 0 and has double of its area.
(a) x2 + y2 – 6x + 12y – 15 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 6x – 12y + 15 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 6x + 12y + 15 = 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The locus of the middle point of the chords of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 such that the chords pass through a given point (x1 , y1) is
(a) x2 + y2 + xx1 – yy1 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 + x12 – y12 = 0
(c) x + y = x1 + y1
(d) x + y = x12 + y12
Answer
A
Question. If two distinct chords drawn from the point ( p, q) on the circle x2 + y2 = px + qy (where, pq ¹ 0) are bisected by the x-axis, then
(a) p2 = q2
(b) p2 = 8q2
(c) p2 < 8q2
(d) p2 > 8q2
Answer
D
Question. Two circles with centres (2, 3) and (5, 6) cut orthogonally. If radius of both circles are equal, then radius is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
C
Question. Tangents drawn from the point P(1, 8) to the circle x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y – 19 = 0 touch the circle at the points A and B. The equation of the circumcircle of the ΔPAB is
(a) x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y + 19 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 4x – 10y + 19 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 2x + 6y – 29 = 0
(d) x2 + y2 – 6x – 4y + 19 = 0
Answer
B
Question. If two circles, each of radius 5 units, touch each other at (1, 2) and the equation of their common tangent is 4x + 3 y = 10, then equation of the circle a portion of which lies in all the quadrants, is
(a) x2 + y2 – 10x – 10y + 25 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y – 15 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 + 2x + 6y – 15 = 0
(d) x2 + y2 + 10x + 10y + 25 = 0
Answer
B
Question. C1C2 and are circles of unit radius with centres at (0, 0) and (1, 0) respectively. C3 is a circle of unit radius, passes through the centres of the circles C1C2 and and have its centre above x-axis. Equation of the common tangent to C1C2 and which does not pass through C2, is
(a) x – √3y + 2 = 0
(b) √3x – y + 2 = 0
(c) √3x – y – 2 = 0
(d) x + √3y + 2 = 0
Answer
B
Question. The locus of centre of a circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y + 1 = 0, which rolls outside the circle x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y = 0, is
(a) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 34 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 6x – 8y + 11 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y – 11 = 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. The locus of the centre of a circle which cuts orthogonally the circle x2 + y2 – 20 + 4 = 0 and which touches x = 2 , is
(a) y2 = 16x + 4
(b) x2 = 16y
(c) x2 = 16y + 4
(d) y2 = 16x
Answer
D
Question. The centre of the circle, which cuts orthogonally each of the three circles x2 + y2 – 2x + 17y + 4 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 7x + 6y + 11 = 0, x2 + y2 – x + 22y + 3= 0, is
(a) (3, 2)
(b) (1, 2)
(c) (2, 3)
(d) (0, 2)
Answer
A
Question. The locus of centres of family of circle passing through the origin and cutting the circle x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y – 13 = 0 orthogonally, is
(a) 4x + 6 y + 13 = 0
(b) 4x – 6 y + 13 = 0
(c) 4x + 6 y – 13 = 0
(d) 4x – 6 y – 13 = 0
Answer
D
Question. The locus of the centre of circle which cuts the circles x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y + 9 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y + 4 = 0 orthogonally, is
(a) 12x + 8y + 5 = 0
(b) 8x + 12y + 5 = 0
(c) 8x – 12y + 5 = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If the circles x2 + y2 + 2x + 2ky + 6 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2ky + k = 0 intersect orthogonally, then k is
(a) 2 or -3/2
(b) -2 or 3/2
(c) 2 or 3/2
(d) – 2 or 3/2
Answer
A
Question. The circles x2 + y2 + 2g1x – a2 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2g2x – a2 = 0 cut each other orthogonally.
If p1 and p2 are perpendiculars from(0, a) and(0, – a) on a common tangent of these circles, then p1 p2 is equal to
(a) a2/2
(b) a2
(c) 2a2
(d) a2+ 2
Answer
B
Question. Two circles with radii a and b touch each other externally such that q is the angle between the direct common tangents (a > b ³ 2), then
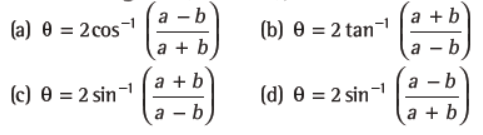
Answer
D
Question. If the circle S1 : x2 + y2= 16 intersects another circle S1 of radius 5 in such a manner that the common chord is of maximum length and has a slope equal to 3/4, the coordinates of the centre of S2 are
(a) (-9/12 . 12/5) (9/5 . -12/5)
(b) (-9/5 . -12/5) (9/5 . 12/5)
(c) (12/5 . 9/5) (-12/5 . 9/5)
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The locus of the mid-point of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 2 = 0, which makes an angle of 120° at the centre, is
(a) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y + 1= 0
(b) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 1= 0
(c) x2 + y2 – 2x – 2y – 1= 0
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The lengths of the tangents from any point on the circle 15x2 + 15y2 – 48x + 64y + 1= 0 to the two circles
5x2 + 5y2 – 24x + 32y + 75= 0 ,
5x2 + 5y2 – 48x + 64y + 300= 0 are in the ratio
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 3
(c) 3 : 4
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. If the radical axis of the circle x2 + y2 – 2gx + 2fy + C= 0 and x2 + y2 – 2x + 2y + 1= 0, then
(a) g = 3/4 and f ≠ 2
(b) g ≠ 3/4 and f = 2
(c) g = 3/4 or f = 2
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. P(a, b) be any point such that the length of tangents from P to both the circles x2 + y2 – 6x – 8y = 0 and x2 + y2 – 12x + 16y + 12 = 0 are equal, then
(a) 3a + 4b – 6 = 0
(b) 3a – 4b + 6 = 0
(c) 6a – 8b + 12 = 0
(d) 4a – 3b + 7 = 0
Answer
A
Question. If the area of the circle 4x2 + 4y2 – 8x + 16y k =0 is 9π sq units, then the value of k is
(a) 4
(b) 16
(c) – 16
(d) ± 16
Answer
C
Question. The area of the circle centred at (1, 2) and passing through (4, 6) is
(a) 5π
(b) 10π
(c) 25π
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If a circle passes through the point (0, 0), (a, 0) and (0, b), then find the coordinates of its centre.
(a) (-a/2 . -b/2)
(b) (a/2 . -b/2)
(c) (-a/2 . b/2)
(d) None of these
Answer
D
Question. The area of square inscribed in a circle x2 + y2 – 6x – 8y = 0 is
(a) 100 sq units
(b) 50 sq units
(c) 25 sq units
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The distinct points A(0, 0), B(0, 1), C(1, 0) and D(2a, 3a) are concyclic, then
(a) ‘a’ can attain only rational values
(b) a is irrational
(c) cannot be concyclic for any a
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The equation of a circle with origin as centre and passing through the vertices of an equilateral triangle whose median is of length 3a is
(a) x2 + y2 = 9a2
(b) x2 + y2 = 16a2
(c) x2 + y2 = 4a2
(d) x2 + y2 = a2
Answer
C
Question. If (mi , 1/mi) i = 1, 2, 3, 4 are concyclic points, then the value of m1 m2 m3 m4 is
(a) 1
(b) – 1
(c) 0
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. If the two circles (x −1)2 + ( y − 3)2 = r2 and x2 + y2 − 8x + 2 y + 8 = 0 intersect in two distinct point, then
(a) r > 2
(b) 2 < r < 8
(c) r < 2
(d) r = 2
Answer
B
Question. If y = 2x is a chord of the circle x2 + y2 – 10x = 0, then the equation of a circle with this chord as diameter, is x2 + y2 – ax – by = 0. Sum of a and b is
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 0
Answer
C
Question. The eccentric angles of the extremities of the latus rectum of the ellipse x2/a2 + y2/b2= 1 are given by
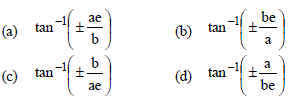
Answer
C
Question. The equation of the directrix of the parabola y2 + 4y + 4x + 2 = 0 is :
(a) x = –1
(b) x = 1
(c) x = –3/2
(d) x = 3/2
Answer
D
Question. The focal distance of a point on the parabola y2 – 12x is 4. The abscissa of this point is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. If a ≠ 0 and the line 2bx + 3cy + 4d = 0 passes through the points of intersection of the parabolas y2 = 4ax and x2 = 4ay, then
(a) d2 + (3b − 2c)2 = 0
(b) d2 + (3b + 2c)2 = 0
(c) d2 + (2b − 3c)2 = 0
(d) d2 + (2b + 3c)2 = 0
Answer
D
Question. The equation of the hyperbola with vertices at (0, ± 6) and e = 5/3 is
(a) x2/36 − y2/64 = 1
(b) y2/36 − x2/64 = 1
(c) x2/64 − y2/36 = 1
(d) y2/64 − x2/36 = 1
Answer
B
Question. What is the length of the smallest focal chord of the parabola y2 = 4ax ?
(a) a
(b) 2a
(c) 4a
(d) 8a
Answer
C
Question. If the lines 2x + 3y +1 = 0 and 3x − y − 4 = 0 lie along diameter of a circle of circumference 10π , then the equation of the circle is
(a) x2 + y2 + 2x − 2y − 23 = 0
(b) x2 + y2 − 2x − 2y − 23 = 0
(c) x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y − 23 = 0
(d) x2 + y2 − 2x + 2y − 23 = 0
Answer
D
Question. If x + y = k is normal to y2 = 12 x, then the value of k is
(a) 3
(b) 9
(c) –9
(d) –3
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns for the parabola given in the graph.
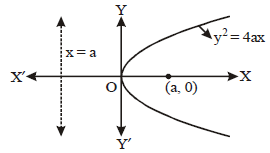

Codes
A B C D E F
(a) 5 4 1 2 3 6
(b) 5 4 2 1 6 3
(c) 6 1 4 2 3 5
(d) 6 1 2 3 4 5
Answer
A
Question. The equation of the circle which passes through the point (4, 5) and has its centre at (2, 2) is
(a) (x – 2) + (y – 2) = 13
(b) (x – 2)2 + (y – 2)2 = 13
(c) (x)2 + (y)2 = 13
(d) (x – 4)2 + (y – 5)2 = 13
Answer
B
Question. If the equation of hyperbola is x2/9 − y2/16 = , then
(a) transverse axis is along x-axis of length 6
(b) transverse axis is along y-axis of length 8
(c) conjugate axis is along y-axis of length 6
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The eccentricity of the hyperbola x2 − 3y2 = 2x + 8 is
(a) 2/3
(b) 1/3
(c) 2/√3
(d) 3/2
Answer
C
ASSERTION- REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : A hyperbola in which a = b is called a rectangular hyperbola.
Reason : The eccentricity of a hyperbola is the ratio of the distances from the centre of the hyperbola to one of the foci and to one of the vertices of the hyperbola.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : If P (3√3/2,1) is a point on the ellipse 4x2 + 9y2 = 36. Circle drawn AP as diameter touches another circle x2 + y2 = 9, where A ≡ (− √5,0)
Reason : Circle drawn with focal radius as diameter touches the auxiliary circle.
Answer
A
Question. Let the centre of an ellipse is at (0, 0)
Assertion: If major axis is on the y-axis and ellipse passes through the points (3, 2) and (1, 6), then the equation of ellipse is x2/10 + y2/40= 1
Reason: x2/b2 + y2/a2= 1 is an equation of ellipse if major axis is along y-axis.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: The area of the ellipse 2x2 + 3y2 = 6 is more than the area of the circle x2 + y2 – 2x + 4y + 4 = 0.
Reason: The length of semi-major axis of an ellipse is more than the radius of the circle.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Radius of the circle 2x2 + 2y2 + 3x + 4y + 9/8 = 0 is 1.
Reason : Radius of the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is

Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Length of focal chord of a parabola y2 = 8x making an angle of 60° with x-axis is 32.
Reason : Length of focal chord of a parabola y2 = 4ax making an angle α with x-axis is 4a cosec2 α.
Answer
D

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 11 Conic Sections Class 11 Mathematics with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.

