VBQs Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science with solutions has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 10 Science with solutions. The following Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 10 examinations.
Carbon and Its Compound VBQs Class 10 Science
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group —Cl.
Answer.
(1) CH3Cl Chloromethane
(2) CH3CH2Cl Chloroethane
Question. Write the formula of first two members of homologous series whose functional group is —CHO.
Answer.
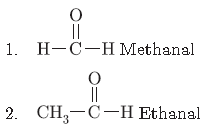
Question. Write the formula of first two members of homologous series whose functional group is

Answer.
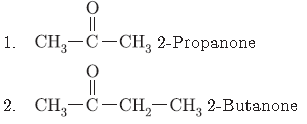
Question. Write the molecular formula of the first two members of the homologous series having functional group — COOH.
Answer.
(1) HCOOH Methanoic acid
(2) CH3COOH Ethanoic acid
Question. Select the saturated hydrocarbons from the following:
C3H6, C5H10, C4H10, C6H14, C2H4
Answer.
C4H10, C6H14 are saturated hydrocarbons
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecules.
Answer.
CH3CH2CH2OH, 1-Propanol
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer.
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, 1-Butanol
Question. Draw the structural formula of methanoic acid.
Answer.
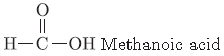
Question. A molecule of ammonia has the formula NH3. Predict the total number of bonds present around nitrogen atom.
Answer.
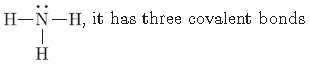
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer.
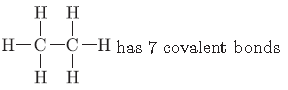
Question. Write the next homologue of propanol CH3CH2CH2OH and butanal CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Answer.
a. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, Butanol
b. CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO, Pentanal
Question. Unsaturated hydrocarbon gives a yellow flame with lot of black smoke when burnt in oxygen. Give reason.
Answer.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons have more amount of carbon, therefore burns with smoky flame due to incomplete combustion.
Question. Write molecular formula of alcohol which can be derived from butane.
Answer. .
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, 1-Butanol
Question. Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. How does carbon attain stable electronic configuration?
Answer.
Carbon can share four electrons to acquire stable electronic configuration.
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n.
Answer.
CH2 = CH—CH3 is second member of alkene.
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n+2 .
Answer.
CH3—CH3, Ethane
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n-2 .
Answer.
HC / C—CH3, Propyne
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of propane, C3H6.
Answer.
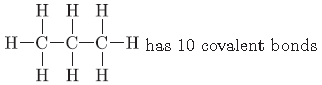
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecular formula of butane, C4H10.
Answer.
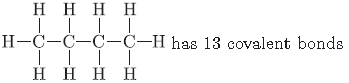
Question. Name the process by which unsaturated fats are changed into saturated fats.
Answer.
Hydrogenation
Question. Write the name of each of the following functional groups:

Answer.
a. Alcohol
b. Ketone
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of the first member of homologous series of alkynes.
Answer.
HC=CH, Ethyne
Question. Mention the functional group which always occurs at the terminal position of a carbon chain of an organic compound.
Answer.
a. Aldehyde
b. Carboxylic acid
Question. The formula of citric acid is shown below

State the name of —COOH functional group in citricacid.
Answer.
Carboxylic acid
Question. Name the functional group in the following compounds:
a. CH3—CH2—CH2—COOH
b. CH3—CO—CH2—CH3
Answer.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Ketone
Question. Will micelle formation take place when soap is dissolved in organic solvent?
Answer.
No, micelles will not be formed in organic solvent.
Question. Explain why washing clothes with hard water i not effective.
Answer.
Soap reacts with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in hard water to form scum.
Question. Draw the structure of simplest ketone.
Answer.
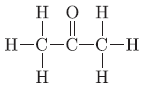
Question. Why do alkanes burn with blue flame?
Answer.
It is because they have less carbon and more hydrogen, therefore, undergo complete combustion and produce blue flame.
Question. What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol?
Answer.
Sodium ethoxide and H2 gas is formed 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question. What will you observe on adding a 5% alkaline KMnO4 solution drop by drop to some warm ethanol taken in a test tube? Write the name of the compound formed during the above chemical reaction.
Answer.
The purple colour of KMnO4 decolourises and ethanoic acid will be formed
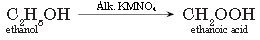
Question. How is scum formed?
Answer.
Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions react with soap (sodium stearate) to form calcium and magnesium stearate which is insoluble in water and called scum.
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds:
a. C2H5—Cl
b. C2H5OH
Answer.
a. Halogen
b. Alcohol
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following compounds:
a. HCOOH
b. C2H5CHO
Answer.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Aldehyde
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following compounds:
a. CH3COCH3
b. C2H5COOH
Answer.
a. Ketone
b. Carboxylic acid
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of the series of carbon compounds whose general formula is CnH2n.
Answer.
CH2=CH—CH3, Propene
Question. State the difference between oils and fats.
Answer.
Oils are unsaturated whereas fats are saturated compounds.
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethene molecule (C2H4).
Answer.
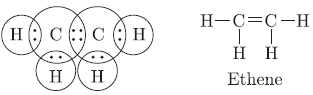
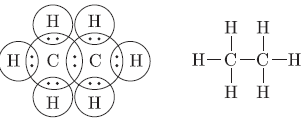
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethane molecule C2H6.
Answer.
Question. Draw the structure of butanone molecule, CH3COC2H5.
Answer.
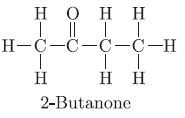
Question. Name the following compound:

Answer.
1-Hexyne
Question. Write the structural formula of chloroe thane.
Answer.

Question. Name the carbon compound which on heating with excess of cone. H2SO4 at 443 K gives ethene.
Answer.
Ethanol,

Question. What is meant by saturated hydrocarbon?
Answer.
Those hydrocarbons in which valency of carbon is satisfied by single bonds only are called saturated hydrocarbons.
Question. Name the compound formed when ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of few drops of cone. H2SO4.
Answer.
Ethyl ethanoate
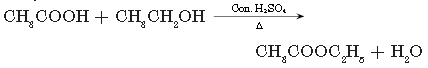
Question. What is the difference in the molecular formula of any two consecutive members of homologous series of organic compounds?
Answer.
The difference between successive members of homologous series is of —CH2 unit.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Draw the structural formulae of the possible isomers for the compound with molecular formula C3H6O.
Answer.
Question. Explain why cannot we have isomers of first three members of alkane family.
Answer.
It is because branching is not possible with carbon
atoms, that is why, there are no isomers till propane.
Question. What is homologous series? Write the name and draw the structure of the second member of alkene series.
Answer.
a. The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
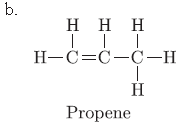
Question. With the help of a suitable example explain in brief the process of hydrogenation mentioning the conditions of the reaction and also state any one physical property of substances changes due to hydrogenation.
Answer.
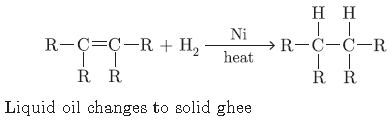
Question. A compound X on heating with excess of cone. H2SO4 at 443 K gives an unsaturated compound Y. X also reacts with sodium metal to evolve a colourless gas Z. Identify X, Y and Z. Write the equations of the chemical reaction of formation of Y and also write the role of conc. sulphuric acid in the reaction.
Answer.
Question. a. Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity?
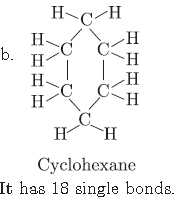
b. Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound.
Answer.
a. It is because covalent compounds do not form ions, therefore, do not conduct electricity
Question. Draw the structural formula of all the possible isomers of the compound with the molecular formula C3H6O and also give electron dot structures.
Answer.
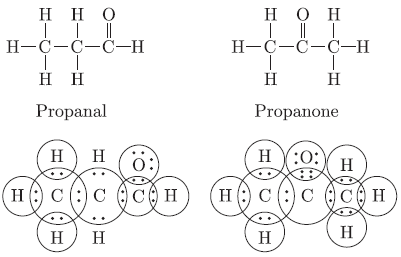
Question. An aldehyde as well as ketone can be represented by the same molecular formula say C3H6O. Write their structures and name them. State the relationship between two in language of science.
Answer.

These are functional isomers
Question. The carbon compounds X and Y have the molecular formula C4H3 and C5H12 respectively. Which one of these is most likely to show addition reaction? Justify your answer. Also give chemical equations to explain the process of addition reaction in this case.
Answer.
C4H3 will undergo addition reaction. It is because it has double bond while C5H12 is a saturated hydrocarbon which cannot undergo addition reaction.

Question. Complete the following equations:
a. CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH →
b. CH3COOH + NaOH →
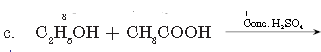
Answer.
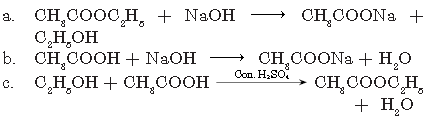
Question. Complete the following reactions:
a. CH3COOH + N2CO3 →
b. CH4 + O2 →
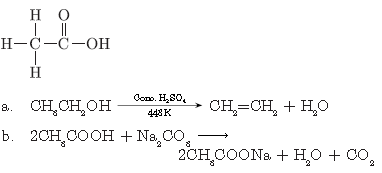
c. C2H5OH + Na →
Answer.
a. 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
b. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
c. 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question. What happens when:
(Write chemical equation in each case)
a. Ethanol is burnt in air?
b. Ethanol is heated with excess cone. H2SO4 at 443 K?
c. A piece of sodium is dropped in ethanol.
Answer.
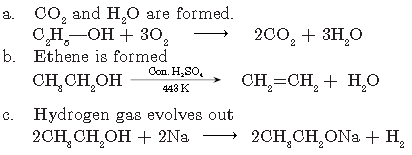
Question. Explain esterification reaction with the help of a chemical equation. Describe an activity to show esterification.
Answer.
Esterification is the process in which carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in presence of conc. H2SO4 to form pleasant fruity smelling compound ester.
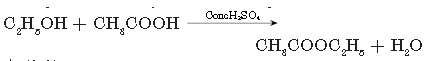
Activity:
To carry out esterification reaction.
• Take 2 mL of ethanol (100% alcohol) in a test tube.
• Add 2 mL of glacial acetic acid.
• Add few drops of conc. H2SO4.
• Set the apparatus as shown in diagram.
• Heat the mixture in test tube in water bath for 5 to 10 minutes observe what happens.
• Observation: Pleasant fruity smell is observed.
• Conclusion: Ester is formed.
Question. Name two oxidising agents that are used to convert alcohols to acids. Distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid on the basis of (a) litmus test (b) reaction with NaHCO3.
Answer.
These two oxidising agents will convert alcohols to acids (i) Alkaline KMnO4 (ii) Acidified K2Cr2O7
a. Litmus test: Acetic acid turns blue litmus red but ethanol does not.
b. NaHCO3 test: Acetic acid will give brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2 whereas ethanol will not react
Question. Explain giving reasons, why carbon can neither form C4+ cation nor C4- anion but forms covalent compounds which are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting and boiling points.
Answer.
Carbon cannot lose four electrons because high energy is needed to remove four electrons. It cannot gain 4 electrons because 6 protons cannot hold 10 electrons. It can share 4 electrons to form covalent bonds. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because these do not form ions. They have low melting and boiling points due to weak force of attraction between molecules.
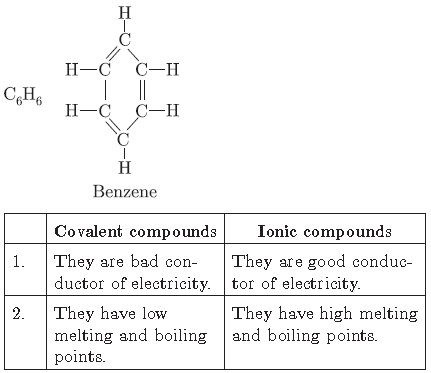
Question. Write the molecular formula of benzene and draw its structure. List in tabular form how covalent compounds differ from ionic compounds.
Answer.
Question. What are hydrocarbons? Write the general formula of (a) saturated hydrocarbons (b) unsaturated hydrocarbons and draw the structure of one hydrocarbon of each type.
Answer.
Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen only
a. CnH2n+2 is general formula of saturated hydrocarbon. For example, CH4

b. CnH2n(alkenes) and CnH2n-2 (alkynes) are general formulae of unsaturated hydrocarbons. For example,
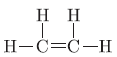
Question. What is an oxidising agent? What happens when oxidising agent is added to propanol? Explain with the help of a chemical equation.
Answer.
Oxidising agent is a substance which adds oxygen or remove hydrogen. Propanol will get oxidised to propanoic acid.

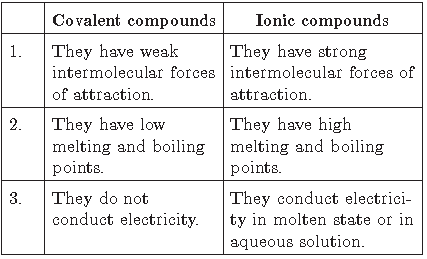
Question. What are covalent compounds? Why are they different from ionic compounds? List three characteristic properties.
Answer.
Those compounds in which bonds are formed by sharing of electrons are covalent compounds. While ionic compounds are formed by complete transfer of electrons.
Question. When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in presence of cone. H2SO4, a substance with fruity smell is produced.
Answer the following questions:
a. State the class of compounds to which fruity smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation and write the chemical name of the
product formed.
b. State the role of cone. H2SO4 in this reaction.
Answer.
a. The fruity smelling compounds are esters

Question. Name the compound formed when ethanol is heated with excess of cone. H2SO4 at 443 K. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction stating the role of cone. H2SO4 in it. What would happen if hydrogen is added to the product in presence of catalyst such as Pd or Ni?
Answer.
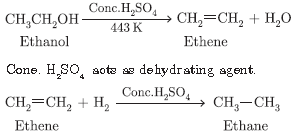
Question. a. Give chemical tests to detect the presence of (a) ethanol (b) ethanoic acid.
b. Why ethanoic acid is called glacial acetic acid?
Answer.
(i) (a) Ethanol reacts with Na to liberate H2 gas
2CH3CH2OH + 2Na → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
(b) Ethanoic acid gives brisk effervescence of CO2 with NaHCO3
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
(ii) It is because pure acetic acid (anhydrous) solidifies into solid crystals just below the room temperature at 16.7°C and look like glacier of snow.
Question. a. Chemical properties of ethanol is different from methyl ethanoate. Justify the statement with proper reason.
b. Methyl ethanoate is used in making perfume. Justify.
c. Ethanol is converted into ethene when excess of cone. H2SO4 is added. Justify with the help of reaction.
Answer.
a. Chemical properties of a compound depends on its functional group. Ethanol and methyl ethanoate have different functional group thus behave differently. CH3CH2OH has functional group — OH. It has specific smell, reacts with Na metal to liberate H2. CH2COOCH3 has ester (RCOOR’) as functional group. It has pleasant fruity smell, undergoes saponification reaction with NaOH.
b. It is due to pleasant fruity smell.
c. Conc H2SO4 dehydrates ethanol to ethene.
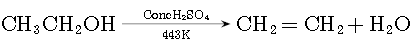
Question. The structural formula of an ester is
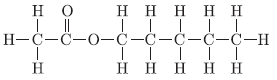
Write the structural formula of the acid and the alcohol from which it might be prepared. Name the process of formation of an ester.
Answer.
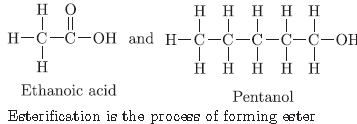
Question. Write any three physical properties and three uses of ethanol.
Answer.
Properties
a. Ethanol has specific smell.
b. It is soluble in water.
c. It has burning taste.
Uses
a. It is used as solvent.
b. It is used as an antiseptic.
c. It is used in wine, beer, whisky, etc.
d. It is used for preparation of ethanoic acid, ethyl ethanoate (esters).
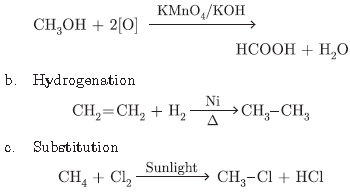
Question. Explain the following reactions with chemical equations:
a. Oxidation
b. Hydrogenation
c. Substitution
Answer.
a. Oxidation
Question. C3H6, C4H8 and C5H10 belong to same 1 homologous series.
a. Define homologous series.
b. Why the melting and boiling point of C5H10 is higher than C4H3?
c. Arrange these hydrocarbons in order of increasing boiling points.
Answer.
a. The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
b. C5H10 has higher molecular mass, more surface area, more van der Waal’s forces of attraction, hence higher boiling point than C4H8.
c. C3H6 < C4H8 < C5H10
Question. The general formula of three compounds A, B and C is Cn (H2n . ‘B’ has highest boiling point and ‘C’ has lowest boiling point.
a. Mention the type of compounds A, B, C.
b. Which of these have minimum number of carbon atoms?
c. Name the homologous series to which A, B and C belong.
Answer.
a. A, B, C are unsaturated compounds.
b. C has minimum number of carbon atoms..
c. They belong to alkene homologous series.
Question. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is burnt for welding. In your opinion, why cannot we use a mixture of ethyne and air for this purpose?
Answer.
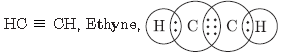
Ethyne and oxygen will produce lot of heat on combustion needed for welding whereas ethyne and air will not produce enough heat needed for welding purposes.
Question. Classify the following carbon compounds into two homologous series and name them.
C3H4, C3H6, C4H6, C4H8, C5H8, C5H10
Answer.
The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
Alkene: C3H6, C4H8, C5H10
Alkyne: C3H4, C4H6, C5H3
Question. Write the name and general formula of a chain of hydrocarbons in which an addition reaction with hydrogen is possible. State the essential conditions for an addition reaction. Stating this condition, write a chemical equation giving the name of the reactant and the product of the reaction.
Answer.
Alkenes CnH2n Alkynes CnH2n-2 In above two series of hydrocarbons, addition of H2 is possible.
Hydrogen is added in presence of nickel as catalyst and heating is needed.
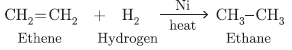
Question. Why should we prefer vegetable oils over animal fats for cooking food? Give a balanced chemical equation for reaction of hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Name the catalyst in the reaction.
Answer.
Vegetable oils are unsaturated and do not lead to formation of cholesterol. Animals fats are saturated lead to formation of cholesterol which can be deposited in arteries.
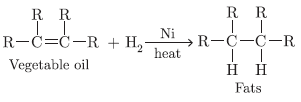
Question. Convert CH4 into CC14 by substituting hydrogen atom with chlorine atom in successive reactions. Why this reaction is referred to as substitution reaction.
Answer.
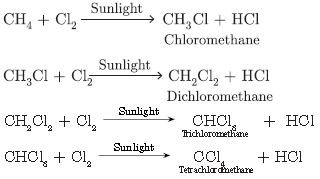
This reaction is called substitution reaction because hydrogen atom is being substituted by ‘Cl’ in each step.
Question. What is difference between the molecule of soaps and detergents, chemically? Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer.
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids. They contain —COONa group. Detergents are sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acids. They contains —SO3Na or —SO4Na group. Soap has ionic end which is hydrophilic, interacts with water while carbon chain is hydrophobic interacts with oil, grease. The soap molecules orient themselves in a cluster in which hydrophobic tails are inside the cluster and ionic ends face outside. These cluster are called micelles. These attract oil which is washed away by water.
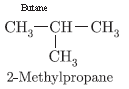
Question. What is meant by isomers? Draw the structures of two isomers of butane, C4H10. Explain why we cannot have isomers of first three members of alkane series.
Answer.
Isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
CH3– CH2– CH2– CH3
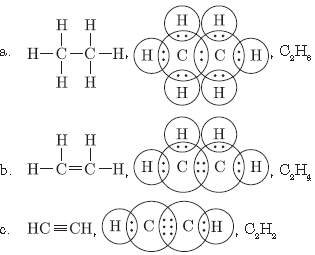
Question. Write the molecular formula of the following compounds and draw their electron dot structures:
(a) Ethane (b) Ethene (c) Ethyne
Answer.
Question. Why is homologous series of carbon compounds so called? Write the chemical formula of two consecutive members of any two homologous series and state the part of these compounds that determines their (a) physical and (b) chemical properties.
Answer.
Homologous means members of same family that is why series of carbon compounds having same functional group and similar properties is called homologous series.
Homologous series of alcohol.
CH3OH Methanol
C2H5OH Ethanol
CH3— and C2H5— groups determine physical properties and —OH group determines chemical properties. Homologous series of aldehyde.
CH3OH Ethanol
C2H5OH Propanal
Here, CH3—and C2H5— groups determine physical properties while —CHO group determines chemical properties.
Question. What are esters? How are they prepared? List two uses of esters.
Answer.
Esters are pleasant fruity smelling compounds with general formula R—COOR’. They are prepared by reaction of carboxylic acid and alcohol in presence of cone. H2SO4
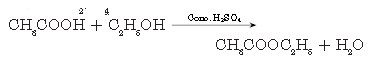
Uses
i. They are used in cold drinks and ice creams as synthetic flavours.
ii. They are used in perfumes.
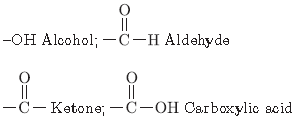
Question. State the meaning of functional group in an organic compound. Write the formula of the functional group present in alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids.
Answer.
Functional group is an atom or group of atoms which determine chemical properties of organic compounds
(a) Aldehyde, (b) Carboxylic acid.
Question. A carboxylic acid (molecular formula C2H4O2) reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a compound X. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 following by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid C2H4O2. Write the name and structure of (i) carboxylic acid, (ii) alcohol and (iii) the compound ‘X’.
Answer.
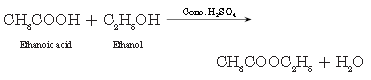
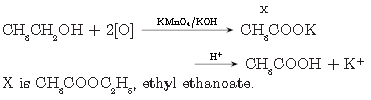
Question. What is meant by homologous series of carbon compounds? Write the general formula of (i) alkenes, and (ii) alkynes. Draw the structures of the first member of each series to show the bonding between the two carbon atoms.
Answer.
The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
i. Alkenes CnH2n
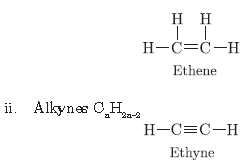
Question. Write the chemical equations to show what happens when
a. an ester reacts with a base?
b. methane is treated with chlorine in the presence of sunlight?
c. ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of sulphuric acid?
Answer.
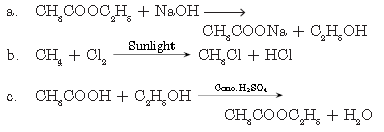
Question. Write the respective chemical equations to show what happens when
a. methane is burned in presence of oxygen?
b. ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K?
c. ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in the presence of an acid acting as a catalyst?
Answer.
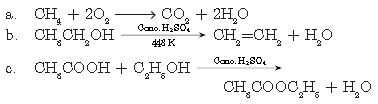
Question. Write chemical equations to describe two different oxidations of ethanol. List two uses of ethanol.
Answer.
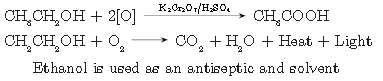
Question. A carbon compound X turns blue litmus to red and has a molecular formula C2H4O2. Identify X and draw its structure. Write chemical equation for the reaction and name of the product formed in each case when X reacts with
a. ethanol in the presence of concentrate H2SO4.
b. sodium carbonate.
Answer.
X is CH3COOH
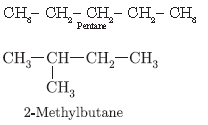
Question. What is meant by isomers? “We cannot have isomers of first three members of alkane series.” Give reason to justify this statement. Draw the structures of two isomers of pentane, C5H12.
Answer.
Isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Question. An ester has the molecular formula C4H8O2. Write its structural formula. What happens when this ester is heated in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution? Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the products. What is a saponification reaction.
Answer.
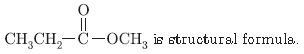
When ester is heated with NaOH, sodium salt of acid and alcohol are formed. It is called saponification reaction.
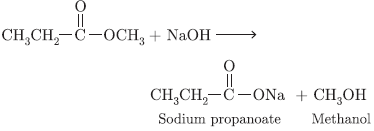
Question. a. What is meant by a functional group in an organic compound? Name the functional group present in
(1) CH3CH2OH
(2) CH3COOH
b. State one point of difference between soap and synthetic detergent.
Answer.
a. Functional group is an atom or group of atoms which determine chemical properties of organic compounds. (1) Alcohol, (2) Carboxylic acid.
a. Soaps do not work well with hard water as form insoluble scum whereas detergents work well with hard water.
Question. Give reasons for the following observations:
a. The element carbon forms a very large number of compounds.
b. Air holes of a gas burner have to be adjusted when the heated vessels get blackened by the flame.
c. Use of synthetic detergents causes pollution of water.
Answer.
a. It is due to tetravalency of carbon and property of catenation shown by carbon to maximum extent.
b. Air holes must be kept open fully so that complete combustion of fuel takes place producing blue flame.
c. Some of detergents are not bio¬degradable, they create water pollution.
Question. a. Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
b. Name the following compound:
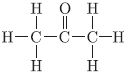
c. Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid is added to sodium carbonate. How will you test the presence of this gas.
Answer.
a. It is because they do not form ions in their aqueous solution.
b. Propanone
c. Carbon dioxide gas will be liberated. Test: Pass the gas through lime water. If lime water turns milky it shows the presence of CO2 gas.
Long Answer Type Questions
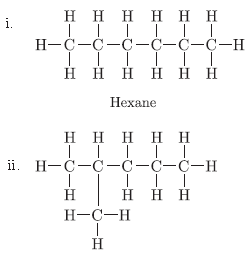
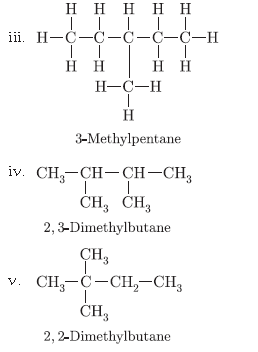
Question. You are given balls and stick model of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms and sufficient number of sticks. In how many ways one can join the models of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms to form different molecules of C6H14.
Answer.
There are five ways in which six carbons can be joined with 14 hydrogen atoms.
Question. Soaps and detergents are both types of salts. State the difference between the two. Write the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps. Why do soaps not form lather (foam) with hard water? Mention any two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Answer.
a. Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids e.g. —COONa. Detergents are sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acids e.g. —SO3Na or —SO4Na
b. Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids. They contain —COONa group. Detergents are sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acids. They contains —SO3Na or —SO4Na group. Soap has ionic end which is hydrophilic, interacts with water while carbon chain is hydrophobic interacts with oil, grease. The soap molecules orient themselves in a cluster in which hydrophobic tails are inside the cluster and ionic ends face outside. These cluster are called micelles. These attract oil which is washed away by water.
c. Soaps react with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in hard water to form calcium or magnesium salts of fatty acids which are insoluble in water and thus interfere in action of soap,
d. (i) Detergents are more expensive than soaps.
(ii) Some detergents are not biodegradable i.e. will create pollution.
Question. Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction which converts alkene into alkane. Also write the chemical equation to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
Answer.
Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
Alkane CnH2n+2
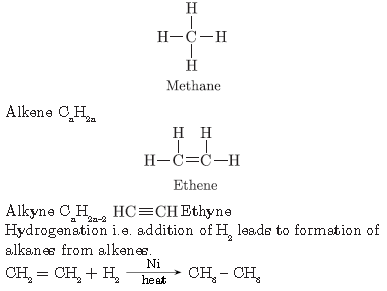
Question. Complete the following chemical equations and write the chemical name of the products formed.
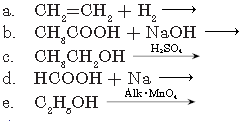
Answer.
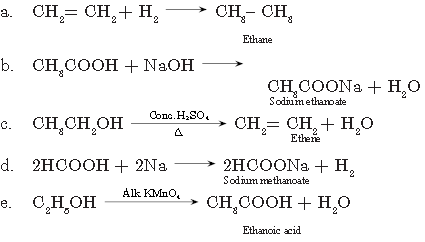
Question. a. Differentiate between soap and detergent.
b. Explain why, soaps form scum with water whereas detergent do not.
Answer.
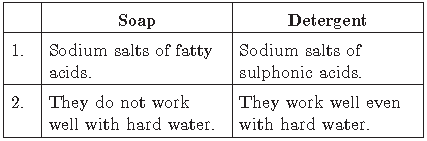
b. Sodium salts of fatty acids (soaps) react with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in hard water to form insoluble salts called scum. Detergents form soluble salts with Ca2+ and Mg2+.
Question. a. How is vinegar made?
b. What is glacial acetic acid? What is its melting point?
c. Why are carboxylic acids called weak acids?
d. Write the name and formula of compounds formed when the ester CH3COOC2H5 undergoes saponification.
Answer.
a. Vinegar is 5-8% solution of acetic acid (Ethanoic acid) in water. It can be made by fermentation of ethanol in presence of oxygen.
b. Glacial acetic is pure (100%) acetic acid. Its melting point is 290 K.
c. They do not ionise completely in aqueous solution.
d. CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH →
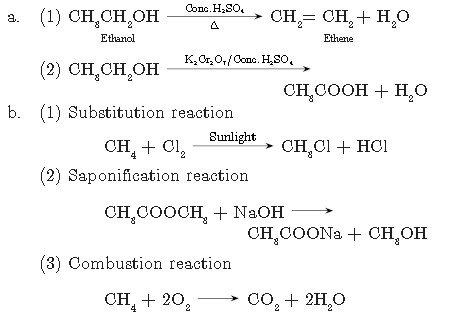
Question. a. How will you bring out following reactions? Write the concerned chemical reaction.
(1) Ethanol to ethene
(2) Ethanol to ethanoic acid
b. Give one example with chemical equation for the following reactions:
(1) Substitution reaction
(2) Saponification reaction
(3) Combustion reaction
Answer.
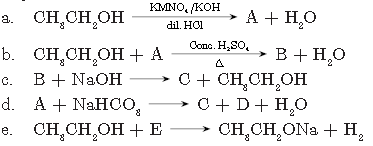
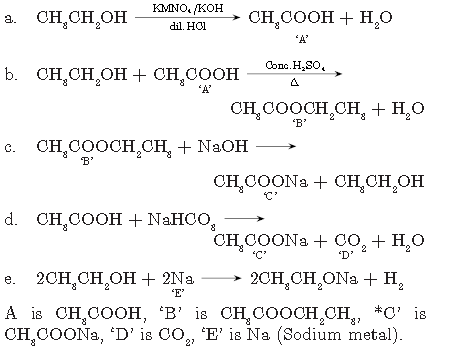
Question. Identify the compounds ‘A’ to ‘E’ in the following sequence:
Answer.
Question. a. In a tabular form, differentiate between ethanol and ethanoic acid under the following heads:
(i) Physical state
(ii) Taste
(iii) NaHCO3 test
(iv) Ester test
b. Write a chemical reaction to show dehydration of ethanol.
Answer.
(i)
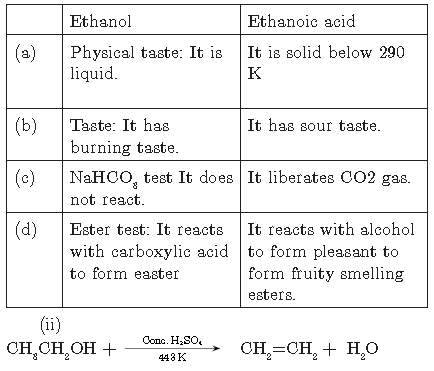
Question. Give reasons for the following:
a. Element carbon forms compound mainly by covalent bonding.
b. Diamond has high melting point.
c. Graphite is good conductor of electricity.
d. Acetylene bums with sooty flame.
e. Kerosene does not decolourise bromine water whereas cooking oil does.
Answer.
a. It is because carbon can neither lose 4 electrons nor gain 4 electrons. It can share four electrons to form covalent bonds.
b. Diamond has strong C—C bonds and compact 3-D structure in which one carbon atom is covalently bonded to other four carbon atoms therefore, has high melting point.
c. In graphite, one carbon atom is bonded to other three carbon atoms. Remaining one electron on each carbon is free to move due to which graphite conducts electricity.
d. Acetylene has high carbon content, therefore partial oxidation causes it to bum with sooty or smoky flame.
e. Kerosene is a saturated compound, therefore, does not decolourise bromine water