Please refer to Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Objective Questions
Question. The total volume of air a person can expire after normal inspiration is called
(a) residual volume
(b) vital capacity
(c) expiratory capacity
(d) functional residual capacity
Answer
C
Question. The total lung capacity is represented by
(a) Tidal volume + Vital capacity
(b) Tidal volume + Residual volume
(c) Vital capacity + Residual volume
(d) Inspiratory + Expiratory reserve volumes
Answer
C
Question. The volume of air breathed in and out during normal breathing is called
(a) vital capacity
(b) inspiratory reserve volume
(c) expiratory reserve volume
(d) tidal volume
Answer
D
Question. Every 100 ml of oxygenated blood delivers following amount of O2 to the tissues under normal physiological contition.
(a) 5 ml
(b) 25 ml
(c) 50 ml
(d) More than 50 ml
Answer
A
Question. As blood becomes fully O2 saturated, haemoglobin combines with____ molecule(s) of oxygen.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Answer
C
Question. Partial pressure of oxygen in inspired and expired air is ____ and _____ mm of Hg.
(a) 100, 46
(b) 158, 40
(c) 158, 90
(d) 100, 95
Answer
B
Question. Most oxygen is carried by the blood __(i)__. Most carbon dioxide is carried by the blood __(ii)__.
(a) (i) attached to haemoglobin. (ii) in the form of bicarbonate ions.
(b) (i) dissolved in plasma . (ii) dissolved in plasma.
(c) (i) in the form of H+ ions . (ii) in the form of bicarbonate ions.
(d) (i) attached to haemoglobin. (ii) attached to haemoglobin.
Answer
A
Question. In mammals, carbon dioxide is transported from tissues to respiratory surface by
(a) plasma
(b) R.B.C.
(c) W.B.C.
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Carbonic anhydrase is found in high concentration in
(a) leucocytes
(b) blood plasma
(c) erythrocytes
(d) lymphocytes
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following structures is the actual gas exchange surface in the mammalian respiratory system ?
(a) Bronchus
(b) Alveolus
(c) Bronchiole
(d) Trachea
Answer
B
Question. Every 100 ml of deoxygenated blood delivers approximately _________________.
(a) 5ml of CO to the alveoli
(b) 6ml of CO2 to the plasma
(c) 4ml of CO2 to the alveoli
(d) 7ml of CO to the plasma
Answer
C
Question. Emphysema developes mainly because of
(a) allergy or hypersensitization.
(b) spasm of the smooth muscles of bronchioles.
(c) cigarette smoking.
(d) inflammation of the alveoli
Answer
C
Question. The respiratory centre, which regulates respiration, is located in
(a) cerebral peduncle
(b) vagus nerve
(c) pons varolii
(d) medulla oblongata
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following normally contains the highest concentration of oxygen ?
(a) Body cells
(b) Inhaled air
(c) Air in the pulmonary trunk
(d) Blood entering the lungs
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following organ receives electrical messages from the brain for breathing in and out?
(a) Diaphragm
(b) Bronchi
(c) Bronchioles
(d) Alveoli
Answer
A
Question. Thoracic chamber is formed (A) by the vertebral column, (B) by the sternum, (C) by the ribs and on the (D) side by the dome shaped diaphragm.
Identify A, B, C and D.
(a) A – dorsally, B – ventrally, C – laterally, D – lower
(b) A – ventrally, B – laterally, C – dorsally, D – upper
(c) A – laterally, B – ventrally, C – dorsally, D – lower
(d) A – dorsally, B – laterally, C – ventrally, D – upper
Answer
A
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Diffusion membrane is made up of 3-major layers.
(b) Solubility of CO2 is higher than O2 by 25 times.
(c) Breathing volumes are estimated by spirometer.
(d) High conc. of hydrogen ions favours oxyhaemoglobin formation.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement correctly defines Bohr effect?
(a) Rise in p50 with a decrease in CO2 conc.
(b) Rise in p50 with decrease in pH.
(c) Rise in p50 with increase in O2.
(d) Fall in p50 with decrease in pH.
Answer
B
Question. The correct statement in respect of protein haemoglobin is that it
(a) maintains blood sugar level.
(b) acts as an oxygen carrier in the blood.
(c) functions as a catalyst for biological reactions.
(d) forms antibodies and offers resistance to diseases.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is the correct statement for respiration in humans?
(a) Workers in grinding and stone-breaking industries may suffer from lung fibrosis.
(b) About 90% of carbon dioxide (CO2) is carried by haemoglobin as carbaminohaemoglobin.
(c) Cigarette smoking may lead to inflammation of bronchi.
(d) Neural signals from pneumotaxic centre in pons region of brain can increase the duration of inspiration.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Inspiration is a passive process whereas expiration is active.
(b) Inspiration is active process whereas expiration is passive.
(c) Inspiration and expiration are active process.
(d) Inspiration and expiration are passive process.
Answer
B
Question. What happens during breathing?
(i) Size of our chest increases.
(ii) Size of our chest decreases.
(iii) Carbon dioxide is removed out from body.
(iv) Air enters our lungs.
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are true/false?
(i) The blood transports CO2 comparatively easily because of its higher solubility.
(ii) Approximately 8 -.9% of CO2 is transported being dissolved in the plasma of blood.
(iii) The carbon dioxide produced by the tissues, diffuses passively into the blood stream and passes into red blood corpuscles and react with water to form H2CO3
(iv) The oxyhaemoglobin (HbO2) of the erythrocytes is basic.
(v) The chloride ions diffuse from plasma into the erythrocytes to maintain ionic balance.
(a) (i), (iii) and (v) are true; (ii) and (iv) are false.
(b) (i), (iii) and (v) are false; (ii) and (iv) are true.
(c) (i), (ii), and (iv) are true; (iii) and (v) are false.
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv) are false; (iii) and (v) are true.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the followings statements is not correct?
(a) Total volume of air a person can expire after a normal inspiration is called expiratory capacity.
(b) Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily related to partial pressure of CO2.
(c) Every 100 ml of deoxygenated blood delivers approximately 4 ml of CO2 to the alveoli.
(d) Every 100 ml of oxygenated blood can deliver around 5 ml of O2 to the tissues under normal physiological conditions.
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The given diagram represents the human respiratory system with few structures labelled as I, II, III and IV.
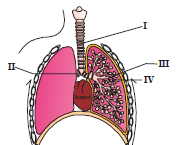
The exchange of gases takes place in which labelled structure?
(a) I →trachea
(b) II → Bronchi
(c) III → bronchioles
(d) IV → alvedi
Answer
D
Question. In the given diagarm of human respiratory system which marked label (I, II, III & IV) is the common passageway where the nasal and oral cavities meet?
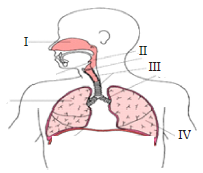
(a) I →nasal-cavity
(b) II → pharynx
(c) III→trachea
(d) IV→lungs
Answer
B
Question. In the given diagram of human respiratory system, few parts are marked as I, II, III, IV, V & VI. Choose the correct combination of labelling from the given options.
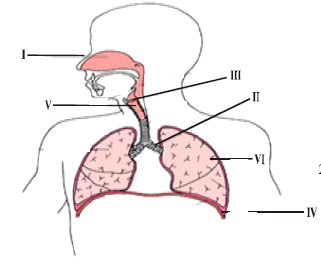
(a) I- Nose, II- Bronchus, III- Larynx, IV- Diaphragm, V- Trachea, VI- Lung
(b) I- Nose, II- Larynx, III- Bronchus, IV- Lung, V- Diaphragm, VI- Trachea
(c) I- Mouth, II- Trachea, III- Larynx, IV-Lung, V- Diaphragm, Vi- Bronchus.
(d) I- Mouth, II- Diaphragm, III- Trachea, IV- Bronchi, V-Larynx, VI- Lung
Answer
A
Question. Refer the given figure and answer the question.
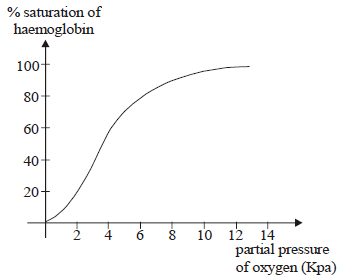
Which of the following statement is correct regarding the above figure?
(a) When percentage saturation of haemoglobin is plotted against the partial pressure of oxygen, a sigmoid curve is obtained.
(b) Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily related to partial pressure of carbon monoxide.
(c) The given graph illustrates the amount of HbO2 as similar to Hb at different pO2.
(d) None of the above.
Answer
A
Question. The figure given below shows the mechanism of breathing. Identify the stage (X) of breathing explained & A, B and C marked in the figure.
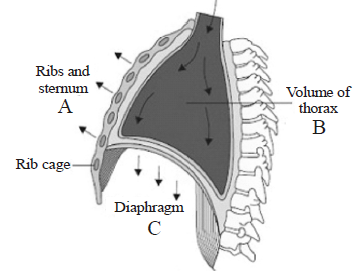
(a) X – Expiration, A– raised, B – decreased, C – relaxed
(b) X – Inspiration, A – raised, B – decreased, C – relaxed
(c) X – Expiration, A – raised, B – increased, C –contracted
(d) X – Inspiration, A– raised, B – increased, C –contracted
Answer
D
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Common feature in the alveoli of lungs and villi of intestine in mammals is that both
(a) provide a large surface area.
(b) have ciliated epithelium.
(c) are suited for diffusion of gases.
(d) have rich supply of blood vessels and lymph ducts.
Answer
A
Question. Maximum amount of oxygen is exchanged from the blood in the ________
(a) capillaries-surrounding tissue cells.
(b) arteries of the body.
(c) left auricle of the heart.
(d) capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
Answer
A
Question. A large proportion of oxygen is left unused in the human blood even after its uptake by the body tissues. This O2
(a) helps in releasing more O2 to the epithelium tissues.
(b) acts as a reserve during muscular exercise.
(c) raises the pCO2 of blood to 75 mm of Hg.
(d) is enough to keep oxyhaemoglobin saturation at 96%.
Answer
B
Question. The urge to inhale in humans results from
(a) rising pCO2
(b) rising pO2
(c) falling pCO2
(d) falling pO2
Answer
A
Question. In man and mammals, air passes from outside into the lungs through
(a) nasal cavity → pharynx →larynx → trachea → bronchioles → bronchi→ alveoli
(b) nasal cavity→ pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
(c) nasal cavity → larynx → pharynx→ trachea → bronchi→ alveoli
(d) nasal cavity →larynx → pharynx → trachea →bronchioles → alveoli
Answer
B
Question. External gills, tracheae, and lungs all share which of the following sets of characteristics ?
(a) Part of gas-exchange system, exchange both CO2 and O2; increase surface area for diffusion.
(b) Used by water breathers; based on countercurrent exchange; use negative pressure breathing.
(c) Exchange only O2; are associated with a circulatory system; found in vertebrates.
(d) Found in insects; employ positive-pressure pumping based on crosscurrent flow.
Answer
A


