Please refer to Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Biology Important Questions Biodiversity and Conservation
Statement Type Questions
Question. Mark the correct statement
(a) Amazonian rain forest has greatest biodiversity on earth.
(b) According to Robert May estimates, the global species diversity is 7 million.
(c) Biodiversity is greatest in tropics.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statement is correct for botanical garden?
(a) They provide a beautiful area for recreation.
(b) One can observe tropical plants there.
(c) They allow ex-situ conservation of germ plasm.
(d) They provide the natural habitat for wildlife.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following does not represent biodiversity of a geographical region?
(i) Genetic diversity present is in the dominant species of the region .
(ii) Species endemic to the region.
(iii) Endangered species found in the region.
(iv) The diversity in the organisms living in the region.
(a) (i) & (ii)
(b) (iii) & (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statement is true for genetic diversity?
(a) The total genetic information contained within all individuals of species.
(b) The total phenotypic information contained within all individuals of a species.
(c) The variety of life-forms on earth.
(d) The variety of biotic communities in a region along with abiotic components.
Answer
A
Question. Which one is the most important human activity leading to extinction of wildlife?
(a) Alteration and destruction of the natural habitats.
(b) Hunting for commercially valuable wildlife products.
(c) Pollution of air and water.
(d) Introduction of alien species.
Answer
A
Question. Modern ex-situ conservation includes
(i) cryopreservation techniques
(ii) in vitro-fertilization
(ii) propagation of plants by using tissue culture methods
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The major cause of loss of numbers of migratory birds is
(i) Bad weather
(ii) Urbanization
(iii) Pesticides
(iv) Fragmentation
(v) Loss of habitat
(a) (i) and (ii) only
(b) (iv) and (v) only
(c) (i), (ii), (v) only
(d) (ii), (iv), (v) only
Answer
B
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Species diversity decreases while ascending a mountain.
Reason : With increase in altitude and rise in temperature diversity of species becomes less.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Tropical rain forests are disappearing fast from developing countries such as India.
Reason : No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity.
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Nile Perch in Lake | I. Obvious reasons for Victoria biodiversity conservation |
| B. Narrowly utilitarian | II. Habitat destruction |
| C. Main cause for | III. High endemism biodiversity loss |
| D. Hotspots | IV. Alien species |
(a) A – II, B – I, C – IV, D – III
(b) A – IV, B – I, C – II, D – III
(c) A – I, B – III, C – II , D – IV
(d) A – II, B – I, C – III, D – IV
Answer
B
Question. Match the following and then choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Endemism | I. Khasi and Jaintia hills Meghalaya |
| B. Hotspot of India | II. Advanced ex-situ conservation |
| C. Sacred groove | III. Species found in a particular area only |
| D. Cryopreservation | IV. Zoological park and Botanical gardens |
| E. Ex-situ conservation | V. Western Ghats |
(a) A – III, B – V, C – I, D – II, E – IV
(b) A – I, B – II, C – III, D – IV, E– V
(c) A – II, B – III, C – IV, D – V, E – I
(d) A – V, B – I, C – IV, D – II, E – III
Answer
A
Question. Match the following and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Over-exploitation | I. Environmental damage by humans and threat to native species |
| B. Introduction of Nile | II. Decline in plant Perch in Lake Victoria population |
| C. Less solar energy | III. Extinction of more than 2000 species of native birds |
| D. Introduction of Water | IV. Extinction of Cichlid fish Hyacinth in India |
| E. Colonization of | V. Extinction of Passenger tropical pacific pigeon Islands |
(a) A – II, B – V, C – IV, D – III, E – I
(b) A – V, B – IV, C – II, D – I, E – III
(c) A – I, B – II, C – III, D – IV, E – V
(d) A – IV, B – I, C – II, D – V, E – III
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions
Question. Given below are pie diagrams A, B and C related to proportionate number of species of major taxa of invertebrates, vertebrates and plants respectively.
Critically study and fill in the blanks I, II, III and IV.
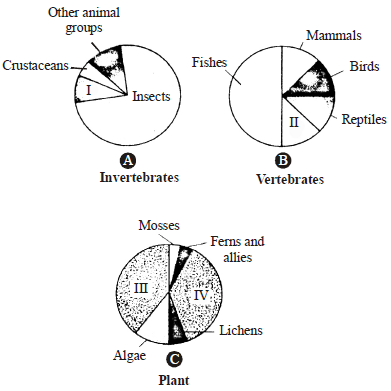
(a) I- Molluscs, II-Amphibians, III-Fungi,IV-Angiosperms
(b) I- Molluscs, II-Amphibians, III-Angiosperms,IV-Fungi
(c) I- Hexapoda, II-Amphibians, III-Fungi,IV-Angiosperms
(d) I- Turtles, II-Amphibians, III-Fungi, IV-Angiosperms
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following boxes show maximum, greater and minimum diversity ?

(a) A- Minimum diversity, B – Greater diversity, C -Maximum diversity
(b) A – Maximum diversity, B – Greater diversity,C – Minimum diversity
(c) A – Maximum diversity, B – Minimum diversity,C – Greater diversity
(d) A – Minimum diversity, B – Maximum diversity,C – Greater diversity.
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Questions
Question. India’s share in global species diversity is around
(a) 8%
(b) 14 %
(c) 17 %
(d) 2.4 %
Answer
A
Question. Which animal has become extinct from India?
(a) Snow Leopard
(b) Hippopotamus
(c) Wolf
(d) Cheetah
Answer
D
Question. In your opinion, which is the most effective way to conserve the plant diversity of an area?
(a) By developing seed bank
(b) By tissue culture method
(c) By creating botanical garden
(d) By creating biosphere reserve
Answer
D
Question. Management of biosphere for providing maximum benefit to the present generation and also maintaining its potential for future generations, is the theme of
(a) afforestation
(b) conservation
(c) deforestation
(d) population
Answer
B
Question. Species diversity increase as one proceeeds from
(a) high altitude to low altitude and high latitude to low latitude.
(b) low altitude to high altitude and high latitude to low latitude.
(c) low altitude to high altitude and low latitude to high latitude.
(d) high altitude to low altitude and low latitude to high latitude.
Answer
A
Question. The table below give the populations (in thousands) of ten species (A = J) in four areas (I – IV) consisting of the number of habitats given within brackets against each area. Study the table and answer the questions.
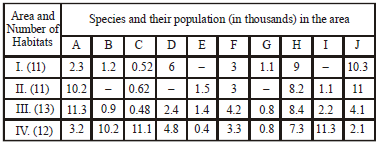
Which area out of I to IV shows maximum species diversity?
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer
C
Question. Why do migratory species present special preservation challenges?
(a) Because they are endemic, they are especially susceptible to habitat destruction.
(b) Their conservation may require international cooperation when they require habitats in different countries.
(c) They are often prone to population number decline during their long migratory journeys.
(d) They reside in biodiversity hotspots that are most susceptible to habitat degradation.
Answer
B
Question. Sacred groves are especially useful in
(a) preventing soil erosion.
(b) year-round flow of water in rivers.
(c) conserving rare and threatened species.
(d) generating environmental awareness.
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Name the type of biodiversity represented by the following:
(i) 50,000 different strains of rice in India
(ii) Estuaries and alpine meadows in India.
Ans. (i) Genetic diversity
(ii) Ecological diversity
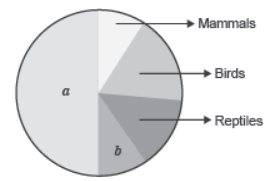
Question. Name the unlabelled areas ‘a’ and ‘b’ of the pie chart representing biodiversity of vertebrates showing the proportionate number of species of major taxa
Ans. a → Fishes;
b → Amphibians.
Question. Write the importance of cryopreservation in conservation of biodiversity.
Ans. By cryopreservation, the reproductive parts of rare species can be preserved.
Question. Can you think of a situation where we deliberately want to make a species extinct? How would you justify it?
Ans. Species which are harmful to human beings can be made extinct, e.g., HIV, polio virus, etc. Such micro-organisms are not part of any food chain and thus, their extinction would not affect the ecosystem.
Question. What are seed banks?
Ans. The collection of seeds of many different genetic strains of commercially important plants, that are kept viable for longer periods in place are called seed banks.
Question. What is the difference between endemic and exotic species?
Ans. Endemic species are native species restricted to a particular geographical region. Exotic species are species which are introduced from other geographical regions into an area.
Question. Name the alien fish species which is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes in our rivers.
Ans. Clarias gariepinus (African catfish)
Short Answer Questions
Question. What is IUCN red list? Give any two uses of this list.
Ans. IUCN red list is a catalogue of species and subspecies that are facing the risk of extinction.
The two uses of this list are:
(i) Provides information and develops awareness about the importance of threatened species.
(ii) Identification and documentation of endangered species and so measures can be taken for their protection.
Question. A particular species of wild cat is endangered. In order to save them from extinction, which is a desirable approach in situ or ex situ? Justify your answer and explain the difference between the two approaches.
Ans. Ex situ is a desirable approach to protect the wild cat. The organism is protected outside their natural habitat where special care is taken to protect them. By using cryopreservation techniques,gametes of threatened species can also be preserved under very low temperature.
For difference, QU Biodiversity can be conserved by protecting its whole ecosystem.
QU There are two basic approaches for conservation of biodiversity.
Question. Is it true that there is more solar energy available in the tropics? Explain briefly.
Ans. As one moves from the equator to the polar regions, the length of the day decreases and the length of the night increases. The length of day and night are same at the equator.
Therefore, it is true that there is more solar energy available in the tropics.
Question. State the use of biodiversity in modern agriculture.
Ans. Biodiversity is a source of hybrids, GM plants, biopesticides, organic farming, biofertiliser, improved varieties of plants, disease resistant plants. (Any two).
Question. List any four techniques where the principle of ex situ conservation of biodiversity has been employed.
Ans. Cryopreservation, in vitro fertilisation, micropropagation/tissue culture, sperm bank/seed bank/gene bank.
Question. In an experiment, the slope of regression (Z) is 0.2 and in another experiment the value obtained is 1.2. Explain the two situations in respect of species area relationships.
Ans. 0.2 is obtained in studies regardless of the taxonomic group and the region 1.2 is obtained if species area relationship is analysed among very large areas like the entire continents.
Question. Would the extinction of one insect pollinator affect the ecosystem? Explain.
Ans. It would affect the ecosystem because insect pollinators form a part of food web. It may lead to coextinction of species in the case of a co-evolved plant. It is a case of mutualism where extinction of one invariably leads to the extinction of the other.
Question. Among the ecosystem services are control of floods and soil erosion. How is this achieved by the biotic components of the ecosystem?
Ans. Control of soil erosion: Plant roots hold the soil particles tightly and do not allow the top soil to be drifted away by winds or moving water. Plants increase the porosity and fertility of the soil.
Control of floods: It is carried out by retaining water and preventing run off of rain water. Litter and humus of plants function as sponges thus retaining the water which percolates down and get stored as underground water. Hence, the flood is controlled.
Question. What is cryopreservation? Give its one use.
Ans. Cryopreservation is a preservation technique in which sperms, eggs, cells, tissues, etc., are stored at ultra-low temperature of −196ºC under nitrogen. Cells and gametes of threatened species can also be preserved by this method.
Long Answer Questions
Question. There are many animals that have become extinct in the wild but continue to be maintained in Zoological parks.
(i) What type of biodiversity conservation is observed in this case?
(ii) Explain any two other ways which help in this type of conservation.
Ans. (i) Ex-situ conservation
(ii) (a) In-vitro fertilisation: Gametes of threatened species can be fertilised for their propagation.
(b) Cryopreservation techniques: Gametes of threatened species can be preserved in viable and fertile condition for long periods.
Question. Compare narrowly utilitarian and broadly utilitarian approaches to conserve biodiversity, with the help of suitable examples.
Ans. (i) Narrowly utilitarian arguments
OU Human beings derive direct economic benefits from nature, like food, firewood, fibre, construction material, industrial products (resins, gums, dyes, tannins, etc.) and medicinally important products.
• More than 25 per cent of the drugs are derived from plants and about 25,000 species of plants are used by native people as traditional medicines.
(ii) Broadly utilitarian arguments
• Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining and sustaining supply of goods and services from various species as well as ecological systems.
• The different ecological services provided are:
(a) Amazon forest is estimated to contribute 20 per cent of the total oxygen in the atmosphere on earth by photosynthesis.
Question. Many plant and animal species are on the verge of their extinction because of loss of forest land by indiscriminate use by the humans. As a biology student what method would you suggest along with its advantages that can protect such threatened species from getting extinct?
Ans. Ex situ conservation method can be used. Refer to Basic Concepts Point 8 (ii).
Question. Name and describe any three causes of biodiversity losses.
Ans. (i) Habitat loss and fragmentation
• Destruction of habitat is the primary cause of extinction of species.
(ii) Over-exploitation
• When biological system is over-exploited by man for the natural resources, it results in degradation and extinction of the resources.
(iii) Alien (exotic) species invasions
• Some alien (exotic) species when introduced unintentionally or deliberately, become invasive and cause harmful impact, resulting in extinction of the indigenous species.
(iv) Co-extinctions
• When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory manner, also become extinct.
