Please refer to Diversity in Living Organisms Chapter 7 Class 9 Science Assignments below. We have provided important questions and answers for Diversity in Living Organisms which is an important chapter in Class 9 Science. Students should go through the notes and also learn the solved assignment with solved questions provided below. All examination and class tests questions are as per the latest syllabus and books issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have also provided Class 9 Science Assignments for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Science Assignments
Question. What are unicellular organisms? Give an example for unicellular organisms?
Answer
One celled or Single celled organisms are called unicellular organisms.
Example : Chlamydomonas, Amoeba, Euglena.
Question. Name the five kingdoms of living organisms?
Answer
(1) Kingdom — Monera,
(2) Kingdom — Protista,
(3) Kingdom — Fungi (mycota),
(4) Kingdom — Plantae (metaphyta),
(5) Kingdom — Animalia (metazoan).
Question. Which fungi act as a source of antibiotics?
Answer
Penicillium.
Question. Why should we keep fruits and vegetables in refrigerator?
Answer
To prevent food from getting bad due to bacterial or fungal infections.
Question. Who proposed five kingdom classification?
Answer
R.H. Whittaker (1969).
Question. Define species.
Answer
Species are organisms within genus with slight difference from other and capable of breeding and perpetuate.
Question. Give an example for kingdom Monera.
Answer
Bacteria, Nostoc, Mycoplasma.
Question. What are heterotrophic bacteria?
Answer
The bacteria which do not synthesize their own food but depend on other organisms or dead organic matter are called heterotrophic bacteria.
Question. What are cyano bacteria?
Answer
Bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis.
Question. Name the cell wall component of fungi.
Answer
Chitin and polysaccharides.
Question. What are chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria?
Answer
The bacteria which oxidize inorganic substances like nitrate, nitrities and ammonia to release energy in the form of ATP are called chemosynthetic bacteria.
Question. What are mycoplasmas?
Answer
The smallest living organisms without cell walls and survive without oxygen are called mycoplasmas.
Question. Which is the locomotory organ of paramecium or ciliated protozoans.
Answer
Cilia.
Question. Name the kingdom which includes single celled eukaryotes.
Answer
Kingdom Protista.
Question. Name the 2 methods of protistan’s reproduction.
Answer
(1) Asexual reproduction (cell fusion),
(2) Sexual reproduction (zygote formation).
Question. What are multicellular organisms? Give an example for multi cellular organisms.
Answer
Organisms whose body is made up of many numbers of cells are called multicellular organisms.
Example : Spirogyra, Mango, Man.
Question. What is diatomaceous earth?
Answer
Accumulation of cell wall deposition of dead diatoms.
Question. Which are chief producer of oceans?
Answer
Diatoms.
Question. What are euglenoids?
Answer
The fresh water organisms found in stagnant water with protein rich particle in their cell wall are called euglenoids.
Question. Give an example for euglenoids.
Answer
Euglena (photosynthetic protozoan).
Question. What are slime moulds?
Answer
Saprophytic protists are called slime moulds.
Question. What is biological classification?
Answer
Grouping of organisms based on similarities and dissimilarities is called biological classification.
Question. What is taxonomy?
Answer
The systematic study of identification, classification and naming of oraganisms is called taxonomy.
Question. What are plasmodium?
Answer
Aggregation of slime moulds under suitable conditions are called plasmodium, which may grow and spread over several feet. During unfavorable conditions they differentiate and follows fruiting bodies.
Question. Name parasitic protozoa.
Answer
Entamoeba, Plasmodium (Malarial parasite).
Question. Give an example for flagellated protozoans.
Answer
Trypanosoma, Euglena.
Question. Give one example for ciliated protozoans.
Answer
Paramecium.
Question. Give one example for sporozoan.
Answer
Plasmodium.
Question. Which one is called malarial parasite?
Answer
Plasmodium.
Question. Name the disease caused by plasmodium.
Answer
Malaria.
Question. Name the kingdom which includes Bacteria.
Answer
Kingdom Monera.
Question. Name the kingdom which includes eukaryotic heterotrophic organisms.
Answer
Kingdom Mycota (Fungi).
Question. Name unicellular fungi.
Answer
Yeast.
Question. What are saprophytic fungi?
Answer
The heterotrophic fungi which absorb soluble organic matter from dead substrates are called saprophytes.
Question. What are planktons?
Answer
The microscopic organisms which floats on water are called planktons.
Question. What are heterocysts?
Answer
The colourless specialized cells of nostoc filament meant for fixing atmospheric nitrogen are called heterocysts.
Question. Name the chemical component of cell wall of Diatoms.
Answer
Chitin.
Question. What are parasitic fungi?
Answer
The heterotrophic fungi which absorb food from living plants and animals are called parasitic fungi.
Question. What are autotrophic bacteria? Give an example for autotrophic bacteria.
Answer
The bacteria which synthesize their own food from inorganic substances are called autotrophic bacteria.
Example : Nostoc, Anabaena.
Question. Give the characteristic features of Echinodermata.
Answer.
(a) Spikes present on skin.
(b) Free living, marine animals.
(c) Triploblastic and have a coelomic cavity.
(d) Have a peculiar water driven tube system used for moving around.
(e) Have hard calcium carbonate structure that is used as a skeleton.
Examples : Starfish, sea-urchin.
Question. What are the conventions followed for writing the scientific names?
Answer.The conventions followed while writing the scientific names are :
1. The name of the genus begins with a capital letter.
2. The name of the species begins with a small letter.
3. When printed, the scientific name is given in italic.
4. When written by hand, the genus name and the species name have to be underlined separately.
Question. Name the phylum of the following organisms, whose
exclusive characteristics is given below :
(a) Hollow bones
(b) Jointed appendages
(c) Flatworm
(d) Round worms, parasitic
(e) Soft body, muscular marine animal
(f) Radially symmetrical, spiny skin.
Answer.
(a) Phylum chordata, subphylum—vertebrata,class—Aves
(b) Phylum—Arthropoda
(c) Phylum—Platyhelmithes
(d) Phylum—Aschelminthes
(e) Phylum—Mollusca
(f) Phylum—Echinodermata
Question. Give the characteristics of amphibians.
Answer. Amphibians are vertebrates that live on land and in water.
(a) They are cold-blooded.
(b) Heart is three-chambered.
(c) Fertilization is external.
(d) Respiration through lungs on land and through moist skin when in water. Examples : Frog, Toads.
Question. Give specific characteristics of Coelenterate.
Answer.
(a) Water living animals.
(b) Body is made of two layers of cells.
(c) Some of them live in colonies (corals), while others have solitary life-span (Hydra).
(d) Body cavity present.
(e) Radially symmetrical.
Question. Give the characteristics of Ayes.
Answer.
(a) Aves/birds can fly.
(b) Streamlined body.
(c) Hollow and light bones.
(d) Forelimbs are modified into wings.
(e) Warm-blooded animals, heart with four chambers.
(f) Egg laying animals.
(g) Beak present, teeth are absent.
Question. Mention the main criteria of R.H. Whittaker’s classification.
Answer.
(1) Cell structure;
(2) Thallus organization;
(3) Mode of nutrition;
(4) Reproduction;
(5) Phlogenetic relationships were considered by Whittaker.
Question. Why do most of the amphibians lay their eggs in water while reptiles lay their eggs on land?
Answer. Amphibians lay their eggs in water because the young ones have gills in initial stages of hatching out of egg by that they can breathe in water. But in case of reptiles the young ones’ need warmth in initial stages of hatching out of egg so the reptiles lay their eggs on land.
Question. Give the hierarchy of 5 kingdom classification of living world.
Answer.
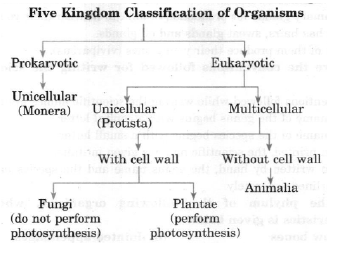
Question. Give the characteristics of mammals.
Answer.
(a) Mammals are warm-blooded animals.
(b) Four-chambered heart.
(c) Mammary glands for production of milk to nourish their younger one.
(d) Skin has hairs, sweat glands and oil glands.
(e) Most of them produce their young ones (viviparous).
Question. Identify the phylum for the following characteristics given :
(a) Organisms with joint appendages.
(b) Organisms are generally flatworms.
(c) Body is segmented.
(d) Skin of organisms is full of spikes.
Answer.
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Platyhelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d) Echinodermata
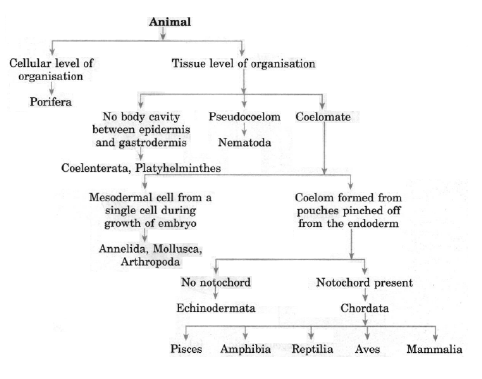
Question.Give general characteristics of fungi.
Answer.
Characteristics of Fungi :
1. Saprophytes
2. Membrane bound nucleus
3. Cell wall made up of Chitin
4. Food stored in the form of glycogen
5. Examples : Rhizopus, Yeast, Agaricus, Penicillium.

Question. Draw labelled diagram of three protozoa.
Answer.


Question.Give the characteristics of flatworms, roundworms and segmented worms. Give their phylum.
Answer.
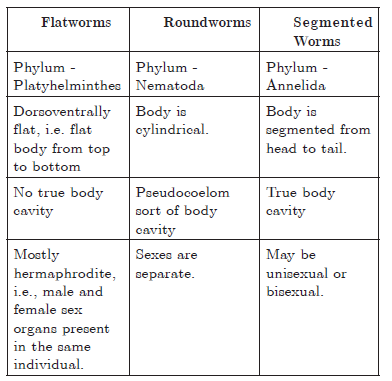
Question.Write the salient features of protozoans.
Answer.
(1) All protozoans are eukaryotic, microscopic,unicellular.
(2) They are heterotrophic, live as predators or parasites (plasmodium and Trypanosoma).
(3) They are believed to be primitive relatives of animals.
(4) Protozoans are grouped into four major groups, such as :
(p) Amoeboid protozoans
(q) Flagellated protozoans
(r) Ciliated protozoans
(s) Sporozoans
Question.Write the important characters of the kingdom – animalia.
Answer.
(1) Kingdom Animalia includes heterotrophic, multicellular, eukaryotic organisms.
(2) Cells are not containing cell walls.
(3) Animals directly or indirectly depend on plants for food.
(4) They digest their food in an internal cavity.
(5) Animals store food reserves as glycogen or fat.
(6) The mode of nutrition in animals is holozoic (by ingestion of food).
(7) Higher forms animals show elaborate sensory and neuromotor mechanism.
(8) Most of the animals are capable of locomotion.
(9) The sexual reproduction is by copulation of male and female, followed by embryological development.

