Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 12 Chemistry issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 14 Biomolecules in Class 12 Chemistry provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 14 Biomolecules MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 14 Biomolecules MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 14 Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following statements about enzymes are true?
I. Enzymes lack in nucleophilic groups.
II. Pepsin is proteolytic enzyme.
III. Enzymes catalyse chemical reactions enhances the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy.
IV. Enzymes are highly specific both in binding chiral substrates and in catalysing their reactions.
(a) Both I and II
(b) Both I and III
(c) Both I and IV
(d) II, III and IV
Answer
D
Question. Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
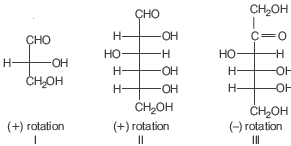
(a) I, II and III
(b) II and III
(c) I and II
(d) Only III
Answer
A
Question. A decapeptide (mol. wt. 796) on complete hydrolysis gives glycine (mol. wt. 75), alanine and phenylalanine. Glycine contributes 47% to the total weight of the hydrolysed products. The number of glycine units present in the decapeptide is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer
B
Question. D-glucose contains
(a) 50%each of α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose
(b) 64%of α-D-glucose and 36% of β-D-glucose
(c) 36%of α-D-glucose and 64% of β-D-glucose
(d) 33%of each α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose
Answer
C
Question. Following amino acid has been found in protein prothrombin, but remained undetected due to formation of another common acid (A).

Answer
A
Question. The reagent which forms crystalline osazone derivative when treated with glucose, is
(a) Fehling’s solution
(b) phenyl hydrazine
(c) Benedict’s solution
(d) hydroxylamine
Answer
B
Question. The reaction with sugars are carried out in neutral or acid medium and not in alkaline medium because in alkaline medium sugars undergoes
(a) decomposition
(b) racemisation
(c) inversion
(d) rearrangement
Answer
D
Question. Match the following enzymes with the reactions they catalyse.
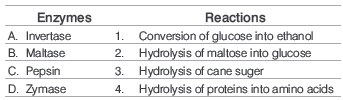
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 1 4 3
(b) 3 2 4 1
(c) 1 4 2 3
(d) 4 2 3 1
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following biomolecules contains a non-transition metal ion?
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Insulin
(d) Vitamin B12
Answer
B
Question. In the following structure, anomeric carbon is
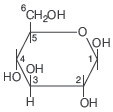
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following monosaccharides is a pentose?
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Arabinose
(d) Galactose
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following pairs give positive Tollen’s test?
(a) Glucose, sucrose
(b) Glucose, fructose
(c) Hexanal, acetophenone
(d) Fructose, sucrose
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds will behave as a reducing sugar in an aqueous KOH solution?
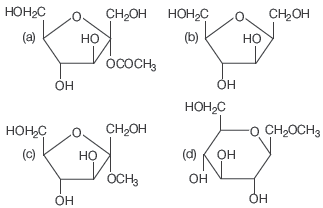
Answer
A
Question. The beta and alpha glucose have different specific rotations. When either is dissolved in water, their rotation changes until the same fixed value results. This is called
(a) epimerisation
(b) racemisation
(c) anomerisation
(d) mutarotation
Answer
D
Question. Glucose on prolonged heating with HI gives
(a) n-hexane
(b) 1-hexene
(c) hexanoic acid
(d) 6-iodohexanal
Answer
A
Question. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides, i.e. aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars. Which of the following disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar?
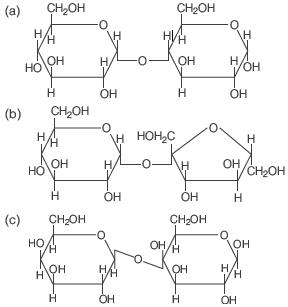
Answer
B
Question. The two form of D-glucopyranose obtained from the solution of D-glucose are called
(a) isomer
(b) anomer
(c) epimer
(d) enantiomer
Answer
B
Question. The chemical name of vitamin B1 is
(a) ascorbic acid
(b) riboflavin
(c) pyridoxine
(d) thiamine
Answer
D
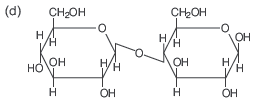
Question. D- (+) – glucose reacts with hydroxyl amine and yields an oxime. The structure of the oxime would be.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose
(b) On heating with HI it forms n -hexane
(c) It is present in furanose form
(d) It does not give 2, 4-DNP test
Answer
C
Question. The term invert sugar refers to an equimolar mixture of
(a) D-glucose and D-galactose
(b) D-glucose and D-fructose
(c) D-glucose and D-mannose
(d) D-glucose and D-ribose
Answer
B
Question. Dalda is prepared from oils by
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) hydrolysis
(d) distillation
Answer
B
Question. Mammals’ fats are hydrolysed to relase fatty acids by
(a) amylase
(b) lactase
(c) lipase
(d) insulin
Answer
C
Question. Waxes are esters of
(a) glycerol
(b) long chain alcohols
(c) glycerol and fatty acid
(d) long chain alcohols and long chain fatty acids
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is a non-steroidal hormone?
(a) Estradiol
(b) Prostaglandin
(c) Progesterone
(d) Estrone
(e) Testosterone
Answer
B
Question. Insulin regulates the metabolism of
(a) minerals
(b) amino acids
(c) glucose
(d) vitamins
Answer
C
Question. A distinctive and characteristic functional group of fats is
(a) a peptide group
(b) an ester group
(c) an alcoholic group
(d) a ketonic group
Answer
B
Question. The one which has least iodine value is
(a) sunflower oil
(b) ginger oil
(c) ghee
(d) groundnut oil
Answer
C
Question. The enzyme which hydrolysis triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol is called
(a) maltase
(b) lipase
(c) zymase
(d) pepsin
Answer
B
Question. Iodised salt prevents . . . . . . . . .
(a) TB
(b) anaemia
(c) goitre
(d) beri-beri
Answer
C
Question. Which lipid is not obtained by the hydrolysis of simple lipid and compound lipid from the following?
(a) Cholesterols
(b) Neutral fats
(c) Carotenoids
(d) Terpenes
Answer
B
Question. Iodine value related to
(a) fats and oils
(b) alcohols
(c) esters
(d) hydrocarbons
Answer
A
Question. Fats are ester of
(a) sugar
(b) glycerol
(c) tributyrine
(d) polypeptide
Answer
B
Question. The hormone that helps in the conversion of glucose to glycogen is
(a) cortisone
(c) adrenaline
(b) bile acids
(d) insulin
Answer
D
Question. Wax is
(a) alcohol
(b) ester
(c) ketone
(d) acid
Answer
B
Question. The process used in the conversion oftriolein to tristearin is
(a) hydrolysis
(b) hydration
(c) hydrogenation
(d) dehydrogenation
Answer
C
Question. A metal present in vitamin B12 is
(a) aluminium
(b) zinc
(c) iron
(d) cobalt
Answer
D
Question. Acrolein test is positive for
(a) polysaccharides
(b) proteins
(c) oils and fats
(d) reducing sugars
Answer
C
Question. Match the following Columns.

Codes
A B C D E
(a) 4 3 1 5 2
(b) 5 3 4 1 2
(c) 3 2 1 5 4
(d) 2 4 1 3 5
(e) 1 5 4 2 3
Answer
E
Question. Phospholipids are esters of glycerol with
(a) one carboxylic acid residue and two phosphate groups
(b) three phosphate groups
(c) three carboxylic acid residues
(d) two carboxylic acid residues and one phosphate groups
Answer
D
Question. Hardening of fat (lipid) is due to
(a) hydrogenation
(b) dehydrogenation
(c) halogenation
(d) dehydrohalogenation
Answer
A
Question. Insulin production and its action in human body are responsible for the level of diabetes. This compound belongs to which of the following categories ?
(a) a coenzyme
(b) a hormone
(c) an enzyme
(d) an antibiotic
Answer
B
Question. Enzyme trypsin converts
(a) proteins into a-amino acids
(b) starch into sugar
(c) glucose into glycogen
(d) α-amino acids into proteins
Answer
A
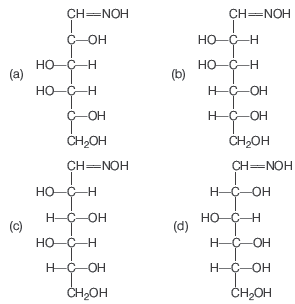
Question. Compound A, C5H10O5 gives a tetra acetate with Ac2O and oxidation of ‘A’ with Br2 / H2O gives an acid, C5H10O6. Reduction of ‘A’ with HI gives iso -pentane. What is the possible structure of A?
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following enzymes hydrolyses triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol?
(a) Amylase
(b) Maltase
(c) Lipase
(d) Pepsin
Answer
C
Question. Which of the vitamins given below is water soluble?
(a) Vitamin C
(b) Vitamin D
(c) Vitamin E
(d) Vitamin K
Answer
A
Question. The bond that determines the secondary structure of proteins is
(a) coordinate bond
(b) covalent bond
(c) hydrogen bond
(d) ionic bond
Answer
C
Question. The substituents R1 and R2 for nine peptides are listed in the table given below. How many of these peptides are positively charged at pH = 7.0?

(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. The secondary structure of a protein refers to
(a) α-helical backbone
(b) hydrophobic interaction
(c) sequence of a-amino acids
(d) fixed configuration of the polypeptide back bone
Answer
D
Question. On heating with conc. HNO3 proteins give yellow colour. This test is called
(a) oxidising test
(b) xanthoproteic test
(c) Hoppe’s test
(d) acid-base test
Answer
B
Question. Identify the vitamin whose deficiency in our blood decreases reproductive power?
(a) Vitamin E
(b) Vitamin D
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Vitamin C
Answer
A
Question. The base adenine occurs in
(a) Only DNA
(b) Only RNA
(c) Both DNA and RNA
(d) protein
Answer
C
Question. The presence or absence of hydroxy group on which carbon atom of sugar differentiates RNA and DNA?
(a) 1st
(b) 2nd
(c) 3rd
(d) 4th
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following bases is not present in DNA?
(a) Quinoline
(b) Adenine
(c) Cytosine
(d) Thymine
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds can be detected by Molisch’s test?
(a) Nitro compounds
(b) Sugars
(c) Amines
(d) Primary alcohols
Answer
B
Question. The vitamin which is water soluble and antioxidant is
(a) Vitamin E
(b) Vitamin D
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin B1
Answer
C
Question. How can you say that glucose is cyclic compound?
(a) Glucose undergoes Tollen’s reaction
(b) Glucose reacts with phenyl hydrazine
(c) Glucose fails to react with sodium hydrogen sulphate
(d) Glucose react with nitric acid
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reaction establishes difference between glucose and fructose?
(a) Tollen’s reagent reaction
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
(c) P/HI
(d) Conc.HNO3
Answer
D
Question. The type of bond that is most important in maintaining secondary structure of a protein in
(a) disulphide bridges
(b) hydrogen bonding within the backbone
(c) hydrogen bonding between R groups
(d) salt bridges
Answer
B
Question. When a monosaccharide forms a cyclic hemiacetal, the carbon atom that contained the carbonyl group is identified at the anomeric carbon atom because
(a) the carbonyl group is drawn to the right
(b) the carbonyl group is drawn to the left
(c) its substituents can assume α or β-position
(d) it forms bond to an —OR and an —OR′
Answer
C
Question. A sugar is classified as a D-isomer if the hydroxyl group
(a) on the chiral carbon nearest to the carbonyl point in the left
(b) on the chiral carbon nearest to the carbonyl point on the right
(c) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl point to the left
(d) on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl point to the right
Answer
D
Question. Consider the following reagents.
I. Br2 water
II. Tollen’s reagent
III. Fehling’s solution
Which can be used to make distinction between an aldose and a ketose?
(a) I, II and III
(b) Both II and III
(c) Only I
(d) Only II
Answer
C
Question. The backbone of a nucleic acid molecule consists of
(a) alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphate ester bonds
(b) alternating sugar and nitrogen base groups linked by amide bonds
(c) alternating nitrogen bases and phosphate groups linked by amide bonds and strengthened by hydrogen bonds
(d) sugar molecules bonded from the C-3 of one molecule to the C-5 of the other by glycosidic linkages
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a fat soluble vitamin?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Riboflavin
(c) Pyridoxine
(d) Thiamine
Answer
A
Question. Adenosine is an example of
(a) nucleotide
(b) nucleoside
(c) purine base
(d) pyrimidine base
Answer
B
Question. Biuret test is not given by
(a) carbohydrates
(b) polypeptides
(c) urea
(d) proteins
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) All amino acids except lysine are optically active
(b) All amino acids are optically active
(c) All amino acids except glycine are optically active
(d) All amino acids except glutamic acids are optically active
Answer
C

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.

