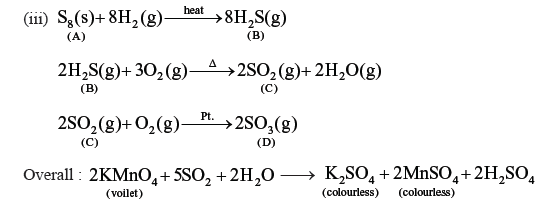Please refer to The p – Block Elements HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. The correct statement(s) about O3 is(are)
(i) O—O bond lengths are equal
(ii) Thermal decomposition of O3 is endothermic
(iii) O3 is diamagnetic in nature
(iv) O3 has a bent structure
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Consider the following statements regarding interhalogen compounds
(i) For all types of interhalogen compounds (XX1 , XX13,XX15 and XX17) X is the halogen of lesser electronegativity in comparison to X1.
(ii) At 298 K all interhalogen compounds are either volatile solids or liquids.
(iii) ClF undergoes hydrolysis as below, ClF + H2O → HF + HOCl
(iv) Fluorine containing interhalogen compounds are very useful as fluorinating agents.
(a) TTFF
(b) TFTT
(c) FTFT
(d) TFFT
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) All the three N—O bond lengths in HNO3 are equal.
(ii) All P—Cl bond lengths in PCl5 molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(iii) P4 molecule in white phohsphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(iv) PCl5 is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) only
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Arsenic and antimony are metalloids.
(ii) Phosphorus, arsenic and antimony are found mainly as sulphide minerals.
(iii) Covalent redii increases equally from N to Bi.
(iv) Elements of group 15 have extra stability and higher ionisation energy due to exactly half filled ns2np3 electronic configuration.
(v) In group 15 elements only nitrogen is gas whereas all others are solids.
(a) (i), (iv) and (v)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (v)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the correct code for statements below ?
(i) Due to small size oxygen has less negative electron gain enthalpy than sulphur.
(ii) Oxygen shows only –2 oxidation state whereas S, Se and Te shows +4 O.S in their compounds with oxygen and +6 with fluorine.
(iii) All hydrides of oxygen family possess reducing property which increases from H2S to H2Te.
(iv) Among hexahalides of group 16 hexafluorides are the onlys table halides.
(v) Dimeric monohalides of group 16 undergo disproportionation.
(a) TFFTT
(b) FTTFF
(c) FTFTF
(d) TFTFT
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Natural abundance of noble gases is ~ 1% by volume of which Ar is the major constituent.
(ii) Noble gases have high positive values of electron gain enthalpy.
(iii) Preparation of XeF2 requires F2 in excess amount.
(iv) Complete hydrolysis of all three XeF2, XeF4 and XeF6 gives Xe as one of product.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
C
Question. Consider the following statements
(i) Reaction 2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42- + 4H+ shows reducing character of sulphur dioxide
(ii) H2S2O8 contains four S = O, two S – OH and one O– O bond
(iii) NH3 gas can be dried effectively by using conc. H2SO4.
(iv) One of the major use of H2SO4 is in the manufacture of fertilizers.
Which of the following is the correct code for the statements above?
(a) TTFF
(b) TTFT
(c) FTFT
(d) TFFT
Answer
B
Question. Read the following statements regarding chemical reactivity of group 15 elements.
(i) Only compound of Bi with +5 oxidation state is BiF5.
(ii) Intermediate oxidation states for both nitrogen and phosphorus disproportionate in both acid and alkali.
(iii) Nitrogen due to absence of d-orbitals in its valence shell cannot form dπ-pπ bond as the heavier elements thus R3P = O exists but R3N = O does not exists.
(iv) BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent amongst the hydrides of nitrogen family.
(v) P2O3 is more acidic than P2O5.
Which of the following is the correct code for the statements above?
(a) FTFFT
(b) FFTTF
(c) TFTTF
(d) TFTFT
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(ii) Leaving F—F bond, all halogens have weaker X—X bond than X—X bond in interhalogens.
(iii) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms are present in iodine fluoride.
(iv) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements regarding properties of halogens are correct?
(i) Due to small size electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine.
(ii) Iodine has same physical state but different colour as compare to other members of the group.
(iii) Fluorine shows no positive oxidation state.
(iv) In X2(g) + H2O(l) → HX(aq) + HOX(aq)
(where X2 = Cl or Br)
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column – I Column – II
(A) Metal that shows no (p) Platinum
reaction with dioxygen
(B) Metal forms strong (q) Nitrogen
acidic oxide with oxygen
(C) A non-metal discharge (r) Manganese
of whose oxide might
be slowly depleting the
concentration of the
ozone layer
(D) Metal which forms (s) Aluminium
amphoteric oxide
(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
(c) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(d) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(Oxyacid) (Materials for preparation)
(A) H3PO2 (p) Red P + alkali
(B) H3PO3 (q) P4O10 + H2O
(C) H3PO4 (r) P2O3 + H2O
(D) H4P2O6 (s) White P + alkali
(a) (A) – (s), (B) – (r), (C) – (q), (D) – (p)
(b) (A) – (p), (B) – (r), (C) – (q), (D) – (s)
(c) (A) – (s), (B) – (r), (C) – (p), (D) – (q)
(d) (A) – (q), (B) – (r), (C) – (p), (D) – (s)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(A) Pb3O4 (p) Neutral oxide
(B) N2O (q) Acidic oxide
(C) Mn2O7 (r) Basic oxide
(D) Bi2O3 (s) Mixed oxide
(a) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(b) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
(c) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p)
(d) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(A) XeF6 (p) sp3d3– distorted octahedral
(B) XeO3 (q) sp3d2 – square planar
(C) XeOF4 (r) sp3 – pyramidal
(D) XeF4 (s) sp3d2 – square pyramidal
(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (s), D – (r)
(c) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column – I Column – II
(Oxides of halogens) (Uses)
(A) O2F2 (p) in water treatment
(B) ClO2 (q) in estimation of CO
(C) I2O5 (r) for removing plutonium
from spent nuclear fuel.
(a) A – (q) , B – (p), C – (r)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q)
(c) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q)
(d) A – (r), B – (q), C – (p)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(A) Partial hydrolysis of the (p) He
compound does not change
oxidation state of central atom
(B) It is used in modern diving (q) XeF6
apparatus
(C) It is used to provide inert (r) XeF4
atmosphere for filling electrical
bulbs
(D) Its central atom is in sp3d2 (s) Ar
hybridisation
(a) A – (p), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(c) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(d) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns
Column – I Column – II
(A) HClO2 (p) Contains all different bonds
(B) HClO3 (q) Contains maximum Cl = O bond
(C) HClO (r) Contains Cl with lowest O.S.
(D) HClO4 (s) Contains three types of bonds
(a) A – (s), B – (p, s), C – (p, r), D – (q, s)
(b) A – (p, s), B – (s), C – (p, r), D – (q, s)
(c) A – (s), B – (p, r), C – (p, s), D – (q, s)
(d) A – (p, s), B – (s), C – (q, s), D – (p, r)
Answer
B
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : White phosphorus is more reactive than red phosphorus.
Reason : Red phosphorus consists of P4 tetrahedral units linked to one another to form linear chains.
Answer
B
Question.Assertion : Dinitrogen is inert at room temperature.
Reason : Dinitrogen directly combines with lithium to form ionic nitrides.
Answer
C
Question.Assertion : SF6 cannot be hydrolysed but SF4 can be.
Reason : Six F atoms in SF6 prevent the attack of H2O on sulphur atom of SF6.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : When a metal is treated with conc. HNO3 it generally yields a nitrate, NO2 and H2O.
Reason : Conc. HNO3 reacts with metal and first produces a metal nitrate and nascent hydrogen. The nascent hydrogen then further reduces HNO3 to NO2.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur exist as S8 but oxygen exists as O2.
Reason : Oxfygen forms pπ – pπ multiple bond due to small size and small bond length but pπ – pπ bonding is not possible in sulphur.
Answer
A
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Bond dissociation enthalpy of E—H (E = element) bonds is given below. Which of the compounds will act as strongest reducing agent?
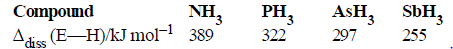
(a) NH3
(b) PH3
(c) AsH3
(d) SbH3
Answer
D
Question. Blue solid which is obtained on reacting equimolar amounts of two gases at 245K is?
(a) N2O
(b) N2O3
(c) N2O4
(d) N2O5
Answer
B
Question. End-product of the hydrolysis of XeF6 is
(a) XeF4O
(b) XeF2O2
(c) XeO3
(d) XeO3–
Answer
B
Question. Concentrated nitric acid, upon long standing, turns yellow brown due to the formation of
(a) NO
(b) NO2
(c) N2O
(d) N2O4
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following order is/are incorrect regarding the property indicated against it?
(i) HF > HI > HBr > HCl : Thermal stability
(ii) Cl2O7 > Cl2O6 > ClO2 > Cl2O : Acidic character
(iii) SbCl3 > SbCl5 : Covalent character
(iv) MCl > MBr : Ionic character
(a) (iii) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Ammonia on catalytic oxidation gives an oxide from which nitric acid is obtained. The oxide is :
(a) N2O3
(b) NO
(c) NO2
(d) N2O5
Answer
C
Question. What is the change observed when AgCl reacts with NH3?
(a) White ppt is formed
(b) Solution become colourless
(c) Yellow ppt is formed
(d) No change is observed
Answer
B
Question. In nitrogen family, the H-M-H bond angle in the hydrides gradually becomes closer to 90º on going from N to Sb. This shows that gradually
(a) The basic strength of the hydrides increases
(b) Almost pure p-orbitals are used for M-H bonding
(c) The bond energies of M-H bonds increase
(d) The bond pairs of electrons become nearer to the central atom
Answer
B
Question. In which of the following equations the product formed has similar oxidation state for nitrogen?
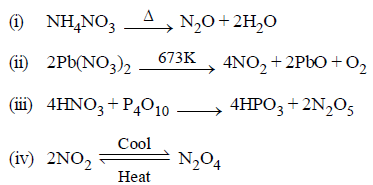
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (v)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. What are the products formed in the reaction of xenon hexafluoride with silicon dioxide ?
(a) XeSiO4 + HF
(b) XeF2 + SiF4
(c) XeOF4 + SiF4
(d) XeO3 + SiF2
Answer
C
Question. XeO4 molecule is tetrahedral having :
(a) Two pπ – dπ bonds
(b) One pπ – dπ bonds
(c) Four pπ – dπ bonds
(d) Three pπ– dπ bonds
Answer
C
Question. It is possible to obtain oxygen from air by fractional distillation because
(a) oxygen is in a different group of the periodic table from nitrogen
(b) oxygen is more reactive than nitrogen
(c) oxygen has higher b.p. than nitrogen
(d) oxygen has a lower density than nitrogen.
Answer
C
Question. What is X and Y in the given reactions ?
2X2 (g) + 2H2O (l) → 4H+ (aq) + 4X– (aq) + O2 (g)
Y2 (g) + H2O (l) → HY(aq) + HOY(aq)
(a) X = Cl , Y = F
(b) X = Cl , Y = Br
(c) X = F , Y = Cl
(d) X = I , Y = F
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following structures is the most preferred and hence of lowest energy for SO3 ?
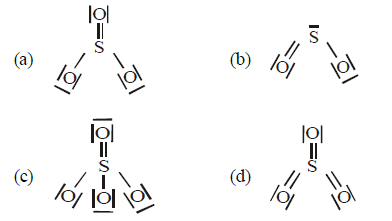
Answer
D
Question. The correct order of the thermal stability of hydrogen halides (H–X) is
(a) HI > HCl < HF > HBr
(b) HCl< HF > HBr < HI
(c) HF > HCl > HBr > HI
(d) HI < HBr > HCl < HF
Answer
C
Question. In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order:
(a) MF > MCl > MBr > MI
(b) MF > MCl > MI > MBr
(c) MI > MBr > MCl > MF
(d) MCl > MI > MBr > MF
Answer
C
Question. The deep blue colour produced on adding excess of ammonia to copper sulphate is due to presence of
(a) Cu2+
(b) Cu(NH3 )42+
(c) Cu(NH3 )62+
(d) Cu(NH3)22+
Answer
B
Question. Which pair gives Cl2 at room temperature :
(a) NaCl + Conc. H2SO4
(b) Conc. HCl + KMnO4
(c) NaCl + Conc. HNO3
(d) NaCl + MnO2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is correct about the reaction?
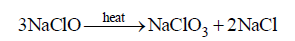
(a) It is disproportionation reaction
(b) Oxidation number of Cl decreases as well as increases in this reaction
(c) This reaction is used for the manufacture of halates
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. In the reaction
4HNO3 + P4O10 → 4HPO3 + X , the product X is
(a) N2O5
(b) N2O3
(c) NO2
(d) H2O
Answer
A
Question. The elements which occupy the peaks of ionisation energy curve are
(a) Na, K, Rb, Cs
(b) Na, Mg, Cl, I
(c) Cl, Br, I, F
(d) He, Ne, Ar, Kr
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it ?
(i) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidizing power
(ii) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electron gain enthalpy
(iii) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
(iv) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity.
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Electronegativity of oxygen is more than sulphur yet H2S is acidic while water is neutral. This is because
(a) water is highly associated compound
(b) molecular mass of H2S is more than H2O
(c) H2S is gas while H2O is a liquid
(d) H–S bond is weaker than H–O bond
Answer
D
Question. The formation of O2+[PtF6]– is the basis for the formation of xenon fluorides. This is because
(a) O2 and Xe have comparable sizes
(b) both O2 and Xe are gases
(c) O2 and Xe have comparable ionisation energies
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. What is Z in following reaction
CuSO4 + Z→ Cu3P2 +H2SO4
HgCl2 + Z → Hg3P2 +HCl
(a) White phosphorus
(b) Red phosphorus
(c) Phosphine
(d) Orthophosphoric acid
Answer
C
GROUP 18 ELEMENTS
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Why do some noble gases form compounds with fluorine and oxygen only ?
Answer. Due to high electronegativity of F and oxygen.
Question. Write the chemical equation involved in the preparation of XeF4.
Answer. Xe (g) + 2F2 (g) → XeF4 (s)
Ratio 1 : 5
Question. Predict the shape and the bond angle (90º or more or less) in the following case :
XeF2 and the angle
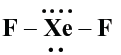
Answer. Linear, 180º
Question. Structure of Xenon fluoride cannot be explained by valence bond approach. Why ?
Answer. Due to fully filled octet of Xe.
Question. XeF2 has a straight linear structure and not a bent angular structure. Why ?
Answer. In XeF2, 2 bond pairs and 3 lone pairs are present hence linear structure.
Question. What inspired N. Barlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6 ?
Answer. Almost same ionization enthalpy of oxygen and Xe.
Question. Why do noble gases have very low boiling point ?
Answer. Because noble gases are stabilized by weak van der Waal’s forces.
SHORT ANSWER-I TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Write chemical equations when :
(i) XeF2 is hydrolysed.
(ii) PtF6 and Xenon are mixed together.
Answer. (i) 2XeF2 (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2Xe (g) + 4HF (aq) + O2 (g)
(ii) Xe + PtF6 → Xe+[PtF6]−
Question. (i) Hydrolysis of XeF6 is not regarded as a redox reaction. Why ?
(ii) Write a chemical equation to represent the oxidizing nature of XeF4.
Answer. (i) Because oxidation number of Xe do not change during hydrolysis of XeF6.
(ii) XeF4 + 2H2 → Xe + 4HF
Question. Suggest reason why only known binary compounds of noble gases are fluorides and oxides of Xenon and to a lesse extent of Kryton.
Answer. F and O are most electronegative elements Kr and Xe both have low ionization enthalpies as compared to He and Ne.
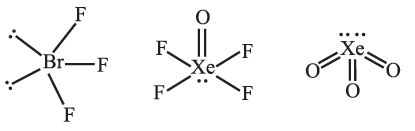
Question. Draw the structure of BrF3, XeOF4, XeO3 using VSEPR theory.
Answer.
SHORT ANSWER-II TYPE QUESTIONS
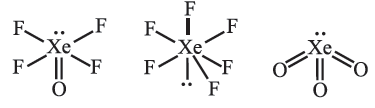
Question. Draw the structure of :
(i) XeOF4 (ii) XeF6 (iii) XeO3
Answer.
Question. Assign reason to the following :
(i) Noble gases have large positive values of electron gain enthalpy.
(ii) Helium is used by scuba divers.
(iii) No chemical compound of helium is known.
Answer. (i) Due to their electron configuration.
(ii) Due to its less solubility in blood.
(iii) Due to its high ionization enthalpy.
Question. (i) How is XeO3 prepared from XeF6 ? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
(ii) Draw the structure of XeF4.
Answer. (i) XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
Or
6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
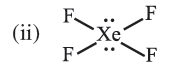
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
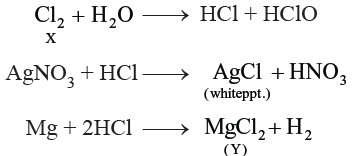
Question. A greenish yellow gas ‘X’ is passed through water to form a saturated solution.
The aqueous solution on treatment with silver nitrate solution gives a white precipitate. The saturated aqueous solution also dissolves magnesium ribbon with the evolution of a colourless gas ‘Y’. Identify gases ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
Answer.
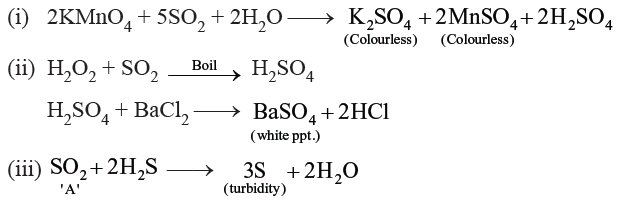
Question. An aqueous solution of gas ‘A’ gave the following data (reactions):
(a) It decolourised an acidified KMnO4 solution.
(b) On boiling with H2O2 followed by cooling and then adding an aqueous solution of BaCl2, a white precipitate insoluble in dilute HCl was obtained.
(c) On passing H2S through the solution of the gas, white turbidity was obtained. Identify the gas and give equations for gas steps (i), (ii), and (iii).
Answer.
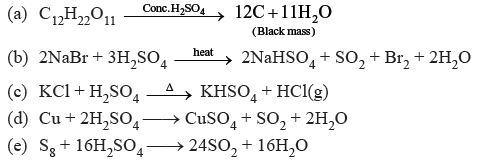
Question. Concentrated sulphuric acid is added followed by heating in each of the following test types labelled (i) to (v)

Identify in which of the above test tubes, the following changes will be observed. Support your answer with the help of a chemical equation.
(a) formation of black substance
(b) evolution of brown gas
(c) evolution of colourless gas
(d) formation of brown substance which on dilution becomes blue.
(e) disappearance of yellow powder along with the evolution of a colourless gas.
Answer.
Question. (a) How is XeF6 prepared from the XeF4 ? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
(b) Deduce the structure of XeF6 using VSEPR theory.
(c) How does XeF2 reacts with PF5 ?
(d) Give one use each of helium and neon.
(e) Write the chemical equation for the hydrolysis of XeF4.
Answer. (a) XeF4 + O2F2 → XeF6 + O2
(b) Distorted octahedral (6BP + 1LP)
(c) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+[PF6]−
(d) He is used in filling balloons/used by scuba divers.
Ne is used in discharge tubes, advertisement display purposes.
(e) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
Question. An element ‘A’ exist as a yellow solid in standard stae. It forms a voilet hydride ‘B’ which is a foul smelling gas and is extensively used in qualitative analysis of salts. When reated with oxygen. ‘B’ forms an oxide ‘C’ which is a colourless and pungent smelling gas. The gas when passed through acidified kMnO4 solution, decolourises it, ‘C’ gets oxidised to another oxide ‘D’ in the presence of heterogenous catalyst. Identifier A, B, C, D and also give the chemical equation of reaction ‘C’ with acidified KmnO4 solution and for conversion of ‘C’ into ‘D’.
Answer.