Please refer to The d – and f – Block Elements HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
The d – and f – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. Which of the following d-block element has half-filled penultimate as well as valence subshell?
(a) Cu
(b) Au
(c) Ag
(d) Cr
Answer
D
Question. The correct order of EM2+/M values with negative sign for the four successive elements Cr, Mn, Fe and Co is
(a) Fe > Mn > Cr > Co
(b) Cr > Mn > Fe > Co
(c) Mn > Cr > Fe > Co
(d) Cr > Fe > Mn > Co
Answer
C
Question. Fe3+ ion is more stable than Fe2+ ion because
(a) more the charge on the atom, more is its stability
(b) configuration of Fe2+ is 3d6 while Fe3+ is 3d5
(c) Fe2+ has a larger size than Fe3+
(d) Fe3+ ions are coloured hence more stable.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is a ‘d-block element’?
(a) Gd
(b) Hs
(c) Es
(d) Cs
Answer
B
Question. Find the incorrect analogy for lanthanoids.
(a) Good oxidising agent : Ce4+
(b) Paramagnetic lanthanide ion : Yb2+
(c) Ions that can exist in aqueous solution : Eu2+, Yb2+
(d) Colourless ions : Ce3+, Yb3+
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following transition metal ions has highest magnetic moment?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Co2+
(d) Fe2+
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not correctly matched with the example given?
(a) An element of first transition series which has highest second ionisation enthalpy – Cu
(b) An element of first transition series with highest third ionisation enthalpy – Zn
(c) An element of first transition series with lowest enthalpy of atomisation – Zn
(d) Last element of third transition series – Cd
Answer
D
Question. The correct order of number of unpaired electrons is
(a) Cu2+ > Ni2+ > Cr3+ > Fe3+
(b) Ni2+ > Cu2+ > Fe3+ > Cr3+
(c) Fe3+ > Cr3+ > Ni2+ > Cu2+
(d) Cr3+ > Fe3+ > Ni2+ > Cu2+
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following lanthanide is commonly used?
(a) Lanthanum
(b) Nobelium
(c) Thorium
(d) Cerium
Answer
D
Question. Consider the following statements with respect to lanthanides :
1. The basic strength of hydroxides of lanthanides increases from La(OH)3 to Lu(OH)3.
2. The lanthanide ions Lu3+, Yb2+ and Ce4+ are diamagnetic.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
B
Question. Although zirconium belongs to 4d and hafnium to 5d-transition series even they show similar physical and chemical properties because both
(a) belong to d-block
(b) have same number of electrons
(c) have similar atomic radius
(d) belongs to the same group of the periodic table.
Answer
C
Question. Reactivity of transition elements decreases almost regularly from Sc to Cu because of
(a) lanthanoid contraction
(b) regular increase in ionisation enthalpy
(c) regular decrease in ionisation enthalpy
(d) increase in number of oxidation states.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is correct about stability of the complexes of lanthanoids?
(a) Stability of complexes increases as the size of lanthanoid decreases.
(b) Stability of complexes decreases as the size of lanthanoid decreases.
(c) Lanthanoids do not form complexes.
(d) All the complexes of lanthanoids have same stability.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following has no unpaired electrons but is coloured?
(a) K2Cr2O7
(b) K2MnO4
(c) CuSO4⋅5H2O
(d) MnCl2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following are basic oxides?
Mn2O7, V2O3, V2O5, CrO, Cr2O3
(a) Mn2O7 and V2O3
(b) V2O3 and CrO
(c) CrO and Cr2O3
(d) V2O5 and V2O3
Answer
B
Question. The second and third row elements of transition metals resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row because of
(a) lanthanoid contraction which results in almost same radii of second and third row metals
(b) diagonal relationship between second and third row elements
(c) similar ionisation enthalpy of second and third row elements
(d) similar oxidation states of second and third row metals.
Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following in increasing value of magnetic moments.
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(ii) [Fe(CN)6]3–
(iii) [Cr(NH3)6]3+
(iv) [Ni(H2O)4]2+
(a) (i) < (ii) < (iii) < (iv)
(b) (i) < (ii) < (iv) < (iii)
(c) (ii) < (iii) < (i) < (iv)
(d) (iii) < (i) < (ii) < (iv)
Answer
B
Question. The salts of Cu in +1 oxidation state are unstable because
(a) Cu+ has 3d10 configuration
(b) Cu+ disproportionates easily to Cu(0) and Cu2+
(c) Cu+ disproportionates easily to Cu2+ and Cu3+
(d) Cu+ is easily reduced to Cu2+.
Answer
B
Question. General electronic configuration of transition metals is
(a) (n – 1)d1-10ns0-2
(b) nd10ns2
(c) (n – 1)d10ns2
(d) (n – 1)d1-5ns2
Answer
A
Question. Colour of transition metal ions are due to absorption of some wavelength. This results in
(a) d-s transition
(b) s-s transition
(c) s-d transition
(d) d-d transition.
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following pairs of ions, the lower oxidation state in aqueous solution is more stable than the other?
(a) Tl+, Tl3+
(b) Cu+, Cu2+
(c) Cr2+, Cr3+
(d) V2+, VO2+ (V4+)
Answer
A
Question. The observed values and calculated values of E° of various 3d-series elements are shown in the figure.

Which of the following facts cannot be explained on the basis of the given graph?
(a) Inability of Cu to liberate H2 from acids
(b) Extra stability of d5(Mn2+) and d10(Zn2+) configuration
(c) Extra stability of Ni2+ due to d10 configuration
(d) All of these.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are amphoteric oxides?
(i) Mn2O7 (ii) CrO3
(iii) Cr2O3 (iv) CrO
(v) V2O5 (vi) V2O4
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (v)
(d) (ii) and (vi)
Answer
C
Question. W, X, Y and Z are four consecutive members of 3d-series.
Trend in their melting point are shown in the given figure.
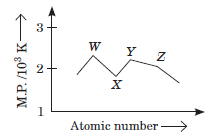
Correct statement about W, X, Y and Z is
(a) magnetic moment of X in its +2 oxidation state is 2.83 B.M.
(b) W 3+ ion is green in colour.
(c) Y3+ catalyses reaction between iodide and persulphate ions.
(d) stable oxidation states of Z are +1, +2 and+6.
Answer
C
Question. Magnetic moment of Ce3+ ion on the basis of ‘spin-only’ formula will be _____ B.M.
(a) 1.232
(b) 1.332
(c) 1.532
(d) 1.732
Answer
D
Question. Fe3+ compounds are more stable than Fe2+ compounds because
(a) Fe3+ has smaller size than Fe2+
(b) Fe3+ has 3d5 configuration (half-filled)
(c) Fe3+ has higher oxidation state
(d) Fe3+ is paramagnetic in nature.
Answer
B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : Cu+ is paramagnetic.
Reason : Cu+ is less stable than Cu2+.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Reduction potential of Mn (+3 to +2) is more positive than Fe (+3 to +2).
Reason : Ionisation potential of Mn is more than that of Fe.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is a coloured ion.
Reason : Ti shows +2, +3, +4 oxidation states.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : The maximum oxidation state of chromium in its compounds is +6.
Reason : Chromium has only six electrons in ns and (n – 1)d orbitals.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Chromium is hard but mercury is soft.
Reason : Chromium is a 3d transition element.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Co (IV) is known but Ni (IV) is not.
Reason : Ni (IV) has d6 electronic configuration.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Transition metals are poor reducing agents.
Reason : Transition metals form numerous alloys with other metals.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Transition metals are good catalysts.
Reason : V2O5 or Pt is used in the preparation of H2SO4 by Contact process.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : In transition elements, ns orbital is filled up first and (n – 1)d afterwards, during ionization ns electrons are lost prior to (n – 1)d electrons.
Reason : The effective nuclear charge felt by (n – 1)d electrons is higher as compared to that by ns electrons.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Mn2+ is more stable than Mn3+.
Reason : Mn2+ has half-filled configuration.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : When Zn is placed in a magnetic field, it is feebly magnetised in a direction opposite to that of the magnetising field.
Reason : Zn has completely filled atomic orbitals.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Transition metals form substitutional alloys.
Reason : Alloys are made to develop some useful properties which are absent in the constituent elements.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : The correct order of oxidising power is : VO2+ < VO < VO2+.
Reason : The oxidation state of Mn in MnO4 is +7.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Transition metals form a large number of interstitial compounds.
Reason : They have high melting point and boiling point.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Europium (II) is more stable than cerium (II).
Reason : Cerium salts are used as a catalyst in petroleum cracking.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Members of 4d and 5d series of transition elements have nearly same atomic radii.
Reason : Atomic and ionic radii for transition elements are smaller than their corresponding s-block elements.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Promethium is a man-made element.
Reason : It is radioactive and has been prepared by artificial means.
Answer
A